Laurasiatheria
| Laurasiatheria Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| From top to right: European hedgehog, Lyle's flying fox, Siberian tiger, Indian pangolin, red deer and white rhino. Representing the living orders: Eulipotyphla, Chiroptera, Carnivora, Pholidota, Artiodactyla and Perissodactyla, comprising Laurasiatheria. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Magnorder: | Boreoeutheria |
| Superorder: | Laurasiatheria Waddell et al., 1999[1] |
| Subgroups | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
Laurasiatheria (/lɔːrˌeɪʒəˈθɪəriə, -θɛriə/; "laurasian beasts") is a superorder of placental mammals that groups together true insectivores (eulipotyphlans), bats (chiropterans), carnivorans, pangolins (pholidotes), even-toed ungulates (artiodactyls), odd-toed ungulates (perissodactyls), and all their extinct relatives. From systematics and phylogenetic perspectives, it is subdivided into order Eulipotyphla and clade Scrotifera.[1][4][5] It is a sister group to Euarchontoglires with which it forms the magnorder Boreoeutheria. Laurasiatheria was discovered on the basis of the similar gene sequences shared by the mammals belonging to it; no anatomical features have yet been found that unite the group, although a few have been suggested such as a small coracoid process, a simplified hindgut (reversed in artiodactyls), high intelligence, lack of grasping hands (though mimicry of grasping is observed in felines) and allantoic vessels that are large to moderate in size.[6] The Laurasiatheria clade is based on DNA sequence analyses and retrotransposon presence/absence data. The superorder originated on the northern supercontinent of Laurasia, after it split from Gondwana when Pangaea broke up.[1] Its last common ancestor is supposed to have lived between ca. 76 to 90 million years ago.[7][8]
Etymology
[edit]The name of this superorder derives from the theory that this group of mammals originated on the supercontinent of Laurasia.[1] In contrast, extinct primitive mammals called Gondwanatheria existed in the supercontinent of Gondwana.
Classification and phylogeny
[edit]History of phylogeny
[edit]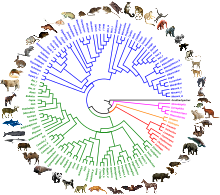
Uncertainty still exists regarding the phylogenetic tree for extant laurasiatherians, primarily due to disagreement about the placement of orders Chiroptera and Perissodactyla. Based on morphological grounds, bats (order Chiroptera) had long been classified in the superorder Archonta (e.g. along with primates, treeshrews and the gliding colugos) until genetic research instead showed their kinship with the other laurasiatheres.[10] The studies conflicted in terms of the exact placement of Chiroptera, however, with it being linked most closely to groups such as order Eulipotyphla in the clade Insectiphillia. Two 2013 studies retrieve that bats, carnivorans and euungulates form a clade Scrotifera, indicating that Eulipotyphla might be the sister group to all other Laurasiatheria taxa.[11][12]
Laurasiatheria is also posited to include several extinct orders and superorders. At least some of these are considered wastebasket taxa, historically lumping together several lineages based on superficial attributes and assumed relations to modern mammals. In some cases, these orders have turned out to either be paraphyletic assemblages, or to be composed of mammals now understood not to be laurasiatheres at all.
- Condylarthra (paraphyletic in relation to true ungulates, possibly polyphyletic since some forms may be afrotheres or even non-placental eutherians)
- Creodonta (order closely related to Carnivora, now polyphyletic and split in two orders: Hyaenodonta and Oxyaenodonta)
- Dinocerata (natural order suggested to be closely related to ungulates)[13]
- Meridiungulata (Collagen sequences found in Macrauchenia and Toxodon indicate this to be the sister taxon to perissodactyls, though in recent studies this clade was found to be polyphyletic)[14]
- Mesonychia (natural clade, though several members, such as genus Andrewsarchus, are now thought to belong in other groups)
Taxonomy
[edit]- Superorder: Laurasiatheria (Waddell, 1999)
- Clade: Scrotifera (Waddell, 1999)
- Order: Eulipotyphla (Waddell, 1999) (true insectivores)
See also
[edit]- Mammal classification
- Boreoeutheria
- Gondwanatheria – a clade of mammaliaformes named after supercontinent of Gondwana
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Waddell, Peter J.; Okada, Norihiro; Hasegawa, Masami (1999). "Towards Resolving the Interordinal Relationships of Placental Mammals". Systematic Biology. 48 (1): 1–5. doi:10.1093/sysbio/48.1.1. PMID 12078634.
- ^ Matsui, K.; Pyenson, N. D. (2023). "New evidence for the antiquity of Desmostylus (Desmostylia) from the Skooner Gulch Formation of California". Royal Society Open Science. 10 (6). 221648. Bibcode:2023RSOS...1021648M. doi:10.1098/rsos.221648. PMC 10264998.
- ^ Arnason U., Adegoke J. A., Gullberg A., Harley E. H., Janke A., Kullberg M. (2008.) "Mitogenomic relationships of placental mammals and molecular estimates of their divergences." Gene.; 421(1–2):37–51
- ^ Nikaido, M.; Rooney, A. P. & Okada, N. (1999). "Phylogenetic relationships among cetartiodactyls based on insertions of short and long interpersed elements: Hippopotamuses are the closest extant relatives of whales". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 96 (18): 10261–10266. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9610261N. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.18.10261. PMC 17876. PMID 10468596.
- ^ Groves, Colin; Grubb, Peter (1 November 2011). Ungulate Taxonomy. JHU Press. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-4214-0093-8. OCLC 708357723.
- ^ O'Leary, Maureen A.; Bloch, Jonathan I.; Flynn, John J.; Gaudin, Timothy J.; Giallombardo, Andres; Giannini, Norberto P.; Goldberg, Suzann L.; Kraatz, Brian P.; Luo, Zhe-Xi; Meng, Jin; Ni, Xijun; Novacek, Michael J.; Perini, Fernando A.; Randall, Zachary S.; Rougier, Guillermo W.; Sargis, Eric J.; Silcox, Mary T.; Simmons, Nancy B.; Spaulding, Michelle; Velazco, Paúl M.; Weksler, Marcelo; Wible, John R.; Cirranello, Andrea L. (2013). "The Placental Mammal Ancestor and the Post–K-Pg Radiation of Placentals". Science. 339 (6120): 662–667. Bibcode:2013Sci...339..662O. doi:10.1126/science.1229237. hdl:11336/7302. PMID 23393258. S2CID 206544776.
- ^ dos Reis, Mario; Inoue, Jun; Hasegawa, Masami; Asher, Robert J.; Donoghue, Philip C. J.; Yang, Ziheng (7 September 2012). "Phylogenomic datasets provide both precision and accuracy in estimating the timescale of placental mammal phylogeny". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 279 (1742): 3491–3500. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.0683. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 3396900. PMID 22628470.
- ^ Zhou, Xuming; Xu, Shixia; Xu, Junxiao; Chen, Bingyao; Zhou, Kaiya; Yang, Guang (1 January 2012). "Phylogenomic Analysis Resolves the Interordinal Relationships and Rapid Diversification of the Laurasiatherian Mammals". Systematic Biology. 61 (1): 150–64. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syr089. ISSN 1063-5157. PMC 3243735. PMID 21900649.
- ^ Pumo, Dorothy E.; Finamore, Peter S.; Franek, William R.; Phillips, Carleton J.; Tarzami, Sima; Balzarano, Darlene (1998). "Complete Mitochondrial Genome of a Neotropical Fruit Bat, Artibeus jamaicensis, and a New Hypothesis of the Relationships of Bats to Other Eutherian Mammals". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 47 (6): 709–717. Bibcode:1998JMolE..47..709P. doi:10.1007/PL00006430. PMID 9847413. S2CID 22900642.
- ^ Tsagkogeorga, G; Parker, J; Stupka, E.; Cotton, J. A.; Rossiter, S. J. (2013). "Phylogenomic analyses elucidate the evolutionary relationships of bats". Current Biology. 23 (22): 2262–2267. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2013.09.014. PMID 24184098.
- ^ Morgan, C. C.; Foster, P. G.; Webb, A. E.; Pisani, D.; McInerney, J. O.; O'Connell, M. J. (2013). "Heterogeneous models place the root of the placental mammal phylogeny". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 30 (9): 2145–2256. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst117. PMC 3748356. PMID 23813979.
- ^ Burger, Benjamin J., (2015.) "The systematic position of the saber-toothed and horned giants of the Eocene: the Uintatheres (order Dinocerata)", Utah State University Uintah Basin Campus, Vernal, Utah
- ^ Avilla, Leonardo S.; Mothé, Dimila (2021). "Out of Africa: A New Afrotheria Lineage Rises From Extinct South American Mammals". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 9. doi:10.3389/fevo.2021.654302. ISSN 2296-701X.
Further reading
[edit]- Murphy, William J.; Eizirik, Eduardo; O'Brien, Stephen J.; Madsen, Ole; Scally, Mark; Douady, Christophe J.; Teeling, Emma; Ryder, Oliver A.; Stanhope, Michael J.; de Jong, Wilfried W.; Springer, Mark S. (2001). "Resolution of the Early Placental Mammal Radiation Using Bayesian Phylogenetics". Science. 294 (5550): 2348–2351. Bibcode:2001Sci...294.2348M. doi:10.1126/science.1067179. PMID 11743200. S2CID 34367609.
- Springer, Mark S.; Murphy, William J.; Eizirik, Eduardo; O'Brien, Stephen J. (2003). "Placental mammal diversification and the Cretaceous–Tertiary boundary". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 100 (3): 1056–1061. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.1056S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0334222100. PMC 298725. PMID 12552136.
- Wildman, Derek E.; Chen, Caoyi; Erez, Offer; Grossman, Lawrence I.; Goodman, Morris; Romero, Roberto (2006). "Evolution of the mammalian placenta revealed by phylogenetic analysis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 103 (9): 3203–3208. Bibcode:2006PNAS..103.3203W. doi:10.1073/pnas.0511344103. PMC 1413940. PMID 16492730.
- Kriegs, Jan Ole; Churakov, Gennady; Kiefmann, Martin; Jordan, Ursula; Brosius, Jürgen; Schmitz, Jürgen (2006). "Retroposed Elements as Archives for the Evolutionary History of Placental Mammals". PLOS Biology. 4 (4): e91. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040091. PMC 1395351. PMID 16515367.

- Nikolaev, Sergey; Montoya-Burgos, Juan I.; Margulies, Elliott H.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Rougemont, Jacques; Nyffeler, Bruno; Antonarakis, Stylianos E. (2007). "Early History of Mammals is Elucidated with the ENCODE Multiple Species Sequencing Data". PLOS Genetics. 3 (1): e2. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030002. PMC 1761045. PMID 17206863.

- Kitazoe, Yasuhiro; Kishino, Hirohisa; Waddell, Peter J.; Nakajima, Noriaki; Okabayashi, Takahisa; Watabe, Teruaki; Okuhara, Yoshiyasu (2007). Hahn, Matthew (ed.). "Robust Time Estimation Reconciles Views of the Antiquity of Placental Mammals". PLOS ONE. 2 (4): e384. Bibcode:2007PLoSO...2..384K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000384. PMC 1849890. PMID 17440620.

- Goloboff, Pablo A.; Catalano, Santiago A.; Mirande, J. Marcos; Szumik, Claudia A.; Arias, J. Salvador; Källersjö, Mari; Farris, James S. (2009). "Phylogenetic analysis of 73 060 taxa corroborates major eukaryotic groups". Cladistics. 25 (3): 211–230. doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2009.00255.x. hdl:11336/78055. PMID 34879616. S2CID 84401375.
- Churakov, G.; Kriegs, J. O.; Baertsch, R.; Zemann, A.; Brosius, J. R.; Schmitz, J. R. (2009). "Mosaic retroposon insertion patterns in placental mammals". Genome Research. 19 (5): 868–875. doi:10.1101/gr.090647.108. PMC 2675975. PMID 19261842.
External links
[edit] Data related to Laurasiatheria at Wikispecies
Data related to Laurasiatheria at Wikispecies


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch