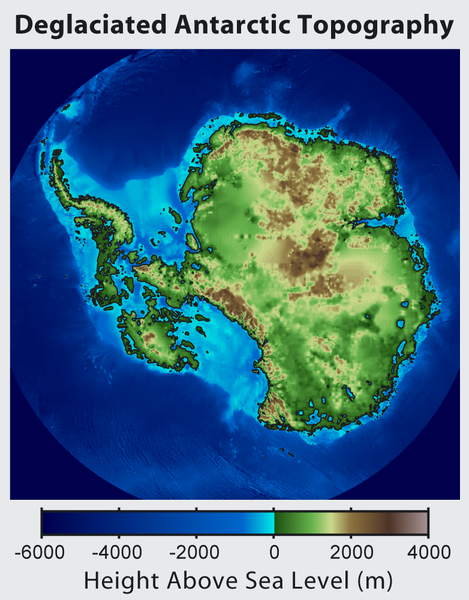
Файл:Antarctica Without Ice Sheet.png — Вікіпедія
Розмір при попередньому перегляді: 469 × 600 пікселів. Інші роздільності: 188 × 240 пікселів | 375 × 480 пікселів | 782 × 1000 пікселів.
Повна роздільність (782 × 1000 пікселів, розмір файлу: 675 КБ, MIME-тип: image/png)
Історія файлу
Клацніть на дату/час, щоб переглянути, як тоді виглядав файл.
| Дата/час | Мініатюра | Розмір об'єкта | Користувач | Коментар | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| поточний | 16:56, 16 червня 2015 |  | 782 × 1000 (675 КБ) | Szczureq | larger image |
| 05:57, 10 жовтня 2012 |  | 469 × 600 (316 КБ) | Strannik27 | User created page with UploadWizard |
Використання файлу
Такі сторінки використовують цей файл:
Глобальне використання файлу
Цей файл використовують такі інші вікі:
- Використання в ar.wikipedia.org
- Використання в ast.wikipedia.org
- Використання в ban.wikipedia.org
- Використання в ba.wikipedia.org
- Використання в be-tarask.wikipedia.org
- Використання в be.wikipedia.org
- Використання в br.wikipedia.org
- Використання в bxr.wikipedia.org
- Використання в ca.wikipedia.org
- Використання в cs.wikipedia.org
- Використання в de.wikipedia.org
- Використання в en.wikipedia.org
- Використання в es.wikipedia.org
- Використання в es.wikibooks.org
- Використання в fr.wikipedia.org
- Використання в id.wikipedia.org
- Використання в it.wikipedia.org
- Використання в ja.wikipedia.org
- Використання в ka.wikipedia.org
- Використання в kn.wikipedia.org
- Використання в la.wikipedia.org
- Використання в mn.wikipedia.org
- Використання в nl.wikipedia.org
- Використання в no.wikipedia.org
- Використання в pl.wikipedia.org
- Використання в ru.wikipedia.org
- Використання в tg.wikipedia.org
- Використання в tr.wikipedia.org
- Використання в zh.wikipedia.org
- Використання в zu.wikipedia.org


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch