Spiral - Vikipedi

Spiral matematikte, bir merkez noktadan doğan, bu nokta etrafında dönerek kademeli olarak uzaklaşan bir eğridir.

İki boyutlu spiraller[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]
İki boyutlu spiraller, r yarıçapı θ açısının tekdüze bir sürekli fonksiyonu iken; kutupsal koordinat sistemi ile açıklanabilir.
Bir daire, bu fonksiyonun monoton (tekdüze) değil sabit olduğu özel bir durumudur.
İki boyutlu spirallerin önemli türlerinden bazıları şunlardır:
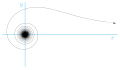
- Arşimet spirali: (ayrıca bakınız:İnvolüt)
- Euler spirali, Cornu spirali ya da clothoid
- Fermat spirali:
- The hiperbolik spiral:
- Lituus:
- logaritmik spiral: ; bunun yaklaşık değerleri doğada bulunur.
- Fibonacci spirali ve altın spiral: Logaritmik spiralin özel bir durumudur (ayrıca bakınız: altın oran)
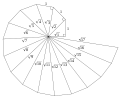
- Theodorus’un Spirali: bitişik sağ üçgenlerden meydana gelen bir Arşimet spirali yakınsamasıdır.
- Bir dairenin involütü, hemen hemen her modern dişlinin her dişinde iki defa kullanılır.
- Arşimet spirali
- Cornu ya da Euler spirali
- Fermat spirali
- Hiperbolik spiral
- Lituus
- Logaritmik spiral
- Theodorus’un Spirali
- Dairenin involütü (siyah) Arşimet spirali (kırmızı) ile özdeş değildir.
Üç boyutlu spiraller[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]
Bir küre yüzeyi üzerinde iki farklı çeşit spiral
Basit 3-d spiraller için, üçüncü değişken, h (yükseklik) de θ açısının tekdüze bir sürekli fonksiyonudur. Örneğin, bir konik sarmal bir konik yüzey üzerinde, apexe mesafesi θnın üstel bir fonksiyonu olan bir spiral olarak tanımlanabilir.
Sarmal ve girdap üç boyutlu spirallerin bir çeşidi olarak görülebilir.
Ayrıca bakınız[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]
İlişkili yayınlar[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]
- Cook, T., 1903. Spirals in nature and art. Nature 68 (1761), 296.
- Cook, T., 1979. The curves of life. Dover, New York.
- Habib, Z., Sakai, M., 2005. Spiral transition curves and their applications. Scientiae Mathematicae Japonicae 61 (2), 195 – 206.
- Dimulyo, S., Habib, Z., Sakai, M., 2009. Fair cubic transition between two circles with one circle inside or tangent to the other. Numerical Algorithms 51, 461–476 [1] 27 Kasım 2018 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Harary, G., Tal, A., 2011. The natural 3D spiral. Computer Graphics Forum 30 (2), 237 – 246 [2] 22 Kasım 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Xu, L., Mould, D., 2009. Magnetic curves: curvature-controlled aesthetic curves using magnetic fields. In: Deussen, O., Hall, P. (Eds.), Computational Aesthetics in Graphics, Visualization, and Imaging. The Eurographics Association [3] 3 Mart 2016 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Wang, Y., Zhao, B., Zhang, L., Xu, J., Wang, K., Wang, S., 2004. Designing fair curves using monotone curvature pieces. Computer Aided Geometric Design 21 (5), 515–527 [4] 24 Eylül 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- A. Kurnosenko. Applying inversion to construct planar, rational spirals that satisfy two-point G2 Hermite data. Computer Aided Geometric Design, 27(3), 262–280, 2010 [5] 24 Eylül 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- A. Kurnosenko. Two-point G2 Hermite interpolation with spirals by inversion of hyperbola. Computer Aided Geometric Design, 27(6), 474–481, 2010.
- Miura, K.T., 2006. A general equation of aesthetic curves and its self-affinity. Computer-Aided Design and Applications 3 (1–4), 457–464 [6].
- Miura, K., Sone, J., Yamashita, A., Kaneko, T., 2005. Derivation of a general formula of aesthetic curves. In: 8th International Conference on Humans and Computers (HC2005). Aizu-Wakamutsu, Japan, pp. 166 – 171 [7].
- Meek, D., Walton, D., 1989. The use of Cornu spirals in drawing planar curves of controlled curvature. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 25 (1), 69–78 [8] 24 Eylül 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Farin, G., 2006. Class A Bézier curves. Computer Aided Geometric Design 23 (7), 573–581 [9] 24 Eylül 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Farouki, R.T., 1997. Pythagorean-hodograph quintic transition curves of monotone curvature. Computer-Aided Design 29 (9), 601–606.
- Yoshida, N., Saito, T., 2006. Interactive aesthetic curve segments. The Visual Computer 22 (9), 896–905 [10] 4 Mart 2016 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Yoshida, N., Saito, T., 2007. Quasi-aesthetic curves in rational cubic Bézier forms. Computer-Aided Design and Applications 4 (9–10), 477–486 [11] 3 Mart 2016 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Ziatdinov, R., Yoshida, N., Kim, T., 2012. Analytic parametric equations of log-aesthetic curves in terms of incomplete gamma functions. Computer Aided Geometric Design 29 (2), 129 – 140 [12] 24 Eylül 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Ziatdinov, R., Yoshida, N., Kim, T., 2012. Fitting G2 multispiral transition curve joining two straight lines, Computer-Aided Design 44(6), 591–596 [13] 24 Eylül 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Ziatdinov, R., 2012. Family of superspirals with completely monotonic curvature given in terms of Gauss hypergeometric function. Computer Aided Geometric Design 29(7): 510–518 [14] 24 Eylül 2015 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..
- Ziatdinov, R., Miura K.T., 2012. On the Variety of Planar Spirals and Their Applications in Computer Aided Design. European Researcher 27(8–2), 1227-–1232 [15]23 Temmuz 2020 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi..


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch