Southern Europe - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Southern Europe is a region of the European continent. The official definition of Southern Europe includes the Iberian Peninsula, Italian Peninsula and Balkan Peninsula. Spain, Portugal, Italy and Greece and all northern Mediterranean countries of the European continent are considered part of Southern Europe. Most importantly, in a European Union context, Portugal, Spain, France, Italy, Malta, Greece, Cyprus, Croatia and Slovenia officially belong to the Group of the South.
Geographical definition[change | change source]
Geographically, Southern Europe would be the south half of the landmass of Europe. This definition is relative, with no clear limits. The Alps mountains are a physical barrier between Italy and the rest of Europe.
Geopolitical definition of the United Nations[change | change source]
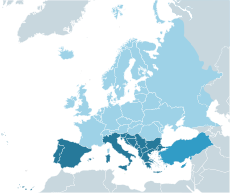
For its official works and publications, the United Nations Organization has its own special definition of regions. Corsica for example is part of France, thus not part of Southern Europe, but Italian South Tyrol belongs to Southern Europe as it is part of Italy.
Climatical definition[change | change source]
The climatic definition of southern Europe would be similar to the areas of Mediterranean climate. The Mediterranean climate is often thought to be a typical characteristic of Southern Europe.
Linguistic and cultural definition[change | change source]
Countries of Latin Europe are often associated with the concept of Southern Europe, especially Italy, Spain and Portugal. Greece, Malta and Cyprus are also associated with the concept of Southern Europe, even though Cyprus is geographically in Asia.
List of countries[change | change source]
Although there is no precise definition, the following territories are commonly thought to be parts of Southern Europe:
- Iberian Peninsula
- Italian Peninsula and Western Mediterranean islands
- Balkans and Aegean islands


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch