Aspirin - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | acetylsalicylic acid /əˌsiːtəlˌsælɪˈsɪlɪk/ |
| Trade names | Bayer Aspirin, many others |
| Synonyms | 2-acetoxybenzoic acid acetylsalicylate acetylsalicylic acid O-acetylsalicylic acid, Aspirin (BAN UK), Aspirin (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682878 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | by mouth, rectal, lysine acetylsalicylate may be given intravenously or intramuscularly |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80–100%[2] |
| Protein binding | 80–90%[1] |
| Metabolism | Liver, (CYP2C19 and possibly CYP3A), some is also hydrolysed to salicylate in the gut wall.[1] |
| Elimination half-life | Dose-dependent; 2 h to 3 h for low doses (100 mg or less), 15 h to 30 h for large doses.[1] |
| Excretion | Urine (80–100%), sweat, saliva, feces[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.059 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
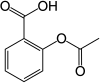
| Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molar mass | 180.158 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.40 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 136 °C (277 °F) |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F) (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | 3 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is a drug. It is most commonly used as a pain killer, or to reduce fever or inflammation. It also has an anti-platelet effect - it reduces the number of platelets in the blood which reduces blood clotting- in that function it is used to prevent heart attacks. Aspirin is one of the most-used medical drugs in the world.
There are some possible side-effects to this drug. For example, large amounts can damage the kidneys. Children taking aspirin can develop Reye's syndrome which causes the liver to become fatty and not work properly and also the brain to become enlarged. Reyes syndrome can be fatal, but most children survive it with treatment.
People with lung, kidney disease, gout, hyperuricemia (high amounts of uric acid in the blood), hemophilia (a blood clotting disorder), diabetes or high blood pressure should not take aspirin except on the advice of a qualified medical professional. Nor should people who are allergic to it, to ibuprofen or to naproxen. People with asthma where attacks are brought about by aspirin should avoid using any anti-inflammatory drugs based on it.
Aspirin was invented in Germany in 1897. Bayer has a trademark on the brand name "aspirin" in 80 countries. But in other countries, "aspirin" is the common name for the drug.
References[change | change source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Brayfield, A, ed. (14 January 2014). "Aspirin". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 3 April 2014.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Zorprin, Bayer Buffered Aspirin (aspirin) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 3 April 2014.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch