Albanian language - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article has a list of references or other websites, but its sources are not clear because it does not have inline citations. (March 2024) |
| Albanian | |
|---|---|
| shqip, gjuha shqipe, 𐔀𐔐𐔁𐔀𐔓𐔍𐔀𐔔 | |
| Pronunciation | [ʃcip] |
| Native to | Albania, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia and Bulgaria, Albanian diaspora |
Native speakers | 7.6 million (2011)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
| Dialects | |
| Latin (Albanian alphabet) Albanian Braille | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Officially by the Social Sciences and Albanological Section of the Academy of Sciences of Albania |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | sq |
| ISO 639-2 | alb (B) sqi (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | sqi – inclusive codeIndividual codes: aae – Arbëreshaat – Arvanitikaaln – Ghegals – Tosk |
| Glottolog | alba1267 |
| Linguasphere | 55-AAA-aaa to 55-AAA-ahe (25 varieties) |
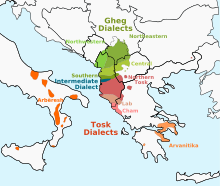 The dialects of the Albanian language. (The map does not indicate where the language is majority or minority.) | |
The Albanian language (Shqip) is an Indo-European language. It is spoken mostly in Albania (3,500,000), Kosovo and (500,000) Republic of North Macedonia.
Dialects[change | change source]
Ghegs, Tosks, Arbëresh, Arvanites, Arbanasi
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Albanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Arbëresh at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Arvanitika at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Gheg at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Tosk at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) - ↑ "Language and alphabet Article 13". Constitution of Montenegro. WIPO. 19 October 2007. Archived from the original on 31 December 2016. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
Serbian, Bosnian, Albanian and Croatian shall also be in the official use.
Other websites[change | change source]
Albanian edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- An overview of the Albanian language and culture Archived 2005-12-17 at the Wayback Machine
- Albanian language family tree
- List of free online resources for learners Archived 2004-02-09 at the Wayback Machine


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch