Treaty of Shimoda
| Treaty of Commerce and Navigation between Japan and Russia | |
|---|---|
 Japanese copy of the Treaty of Shimoda, February 7, 1855 | |
| Signed | February 7, 1855 |
| Location | Shimoda, Shizuoka, Japan |
| Effective | August 7, 1856 |
| Signatories | |
| Depositary | Diplomatic Record Office of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Japan) |
| Languages |
|
The Treaty of Shimoda (下田条約, Shimoda Jouyaku) (formally Treaty of Commerce and Navigation between Japan and Russia 日露和親条約, Nichi-Ro Washin Jouyaku) of February 7, 1855, was the first treaty between the Russian Empire, and the Empire of Japan, then under the administration of the Tokugawa shogunate. Following shortly after the Convention of Kanagawa signed between Japan and the United States, it effectively meant the end of Japan's 220-year-old policy of national seclusion (sakoku), by opening the ports of Nagasaki, Shimoda and Hakodate to Russian vessels and established the position of Russian consuls in Japan and defined the borders between Japan and Russia.
The isolation of Japan[edit]
Since the beginning of the seventeenth century, the Tokugawa shogunate pursued a policy of isolating the country from outside influences. Foreign trade was maintained only with the Dutch and the Chinese and was conducted exclusively at Nagasaki under a strict government monopoly. This policy had two main objectives. One was the fear that trade with western powers and the spread of Christianity would serve as a pretext for the invasion of Japan by imperialist forces, as had been the case with most of the nations of Asia. The second objective was fear that foreign trade and the wealth developed would lead to the rise of a daimyō powerful enough to overthrow the ruling Tokugawa clan.[1] The first contacts between Japan and Russia were made with the Matsumae clan in Hokkaido by the merchant Pavel Lebedev-Lastochkin in 1778 and by official envoy Adam Laxman in 1792. The Russian expedition around the world led by Adam Johann von Krusenstern stayed six months in the port of Nagasaki in 1804–1805, failing to establish diplomatic and trade relations with Japan.
By the early nineteenth century, this policy of isolation was increasingly under challenge. In 1844, King William II of the Netherlands sent a letter urging Japan to end the isolation policy on its own before change would be forced from the outside. In 1846, an official American expedition led by Commodore James Biddle arrived in Japan asking for ports to be opened for trade, but was sent away.[2]
The Putiatin mission[edit]

A few years later, Russia learned that the United States was preparing an expedition to be led by Commodore Matthew Perry, to open Japan by gunboat diplomacy if necessary. If successful, it was feared that this would provide more American influence in the Pacific region and Asia, and to give America the most advantage position in Japan. Russia immediately recommenced plans to send a mission to the Far East. Russian minister of Foreign Affairs Karl Nesselrode assigned Vice-Admiral Euphimy Vasil'evich Putiatin to head the Russian mission. The expedition included several notable Sinologists and a number of scientists and engineers, as well as the noted author Ivan Goncharov, and the Pallada under the command of Ivan Unkovsky was selected as the flagship. Goncharov would use the experience in his Fregat Pallada (1858), in which he described the details of the voyage and the negotiations. It is a valuable description of how the Japanese received and processed foreign trade vessels and the perception of the experience of the Russians.
Pallada departed Kronstadt on October 7, 1852, under orders to return only with a treaty at least as good as the one the Americans had obtained. Also on the Russian agenda was a delimitation of the borders between Japan and Russia in Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands.
However it became clear during the long voyage that the vessel was unsuited for the expedition, and the newer 52-gun frigate Diana was subsequently dispatched, but Perry and his fleet of Black Ships reached Japan while Putiatin was still between Hong Kong and the Bonin Islands. Despite years of debate on the isolation policy, Perry's visit created great controversy within the highest levels of the Tokugawa shogunate.

Eventually, Putiatin arrived in Japan with his four vessels on August 21, 1853, but at Nagasaki rather than attempting to force his way into Edo Bay as Perry had done. Putiatin and Perry had a somewhat differing approach to negotiating with the Japanese. Perry stressed the firepower of his warships and the possible consequences for Japan. Putiatin chose a more diplomatic and strategic approach in the hopes of undermining the American efforts, advising that he had chosen Nagasaki despite his orders to go to Edo out of respect for Japanese laws and the ardent desire of the Russian Emperor for good relations. Officials sent word to Edo, and while waiting for a response, Putiatin sailed to Shanghai for supplies and for news from home. On his return to Nagasaki, there was still no reply, so he renewed his threat to go directly to Edo. The alarmed Nagasaki bugyō urged Edo to accept Putiatin's terms, as the Russians seemed more accommodating that the Americans, and their huge empire might be used to offset threat posed by Perry. Again, there was no response, partly because the Shōgun himself, Tokugawa Ieyoshi died days after Perry's departure, and was succeeded by his sickly young son, Tokugawa Iesada, leaving effective administration in the hands of the Council of Elders (rōjū) led by Hotta Masayoshi, which was paralyzed with indecision. Putiatin grew increasingly impatient and renewed his threat to sail to Edo, when a response came in the form of the officials Kawaji Toshiakira and Tsutsui Masanori, asking for a delay of three to five years for a counter-proposal. Disappointed, Putiatin left Japan in November 1853 promising to return in the spring. Putiatin was not able to return until November 7, 1854. In the meantime, he had surveyed the coast of Korea and the Russian Maritime Province and had learned of the outbreak of the Crimean War, and that the British Royal Navy was hunting for his squadron in the Sea of Okhotsk and the seas around Japan, including Nagasaki. Problems with Pallada caused him to change his flag to the Diana. By the time Putiatin returned, the Americans had already succeeded in opening Japan with the Treaty of Kanagawa in early 1854. To prevent a Russian treaty and limit Russian influence, the British approached Japan to ask for Japanese neutrality in the war. Because of a bad translation, the British obtained an unintended Anglo-Japanese Friendship Treaty in 1854. Instead of Nagasaki, Putiatin chose Osaka Bay, which caused immediate consternation among the Japanese for its proximity to Kyoto. After remaining in Osaka Bay for two weeks, Putiatin set sail for Shimoda.

Putiatin was met in Shimoda by Kawaji and Tsutsui, and negotiations began on December 22, 1854, with Putiatin offering to cede the island of Etorofu to Japan in exchange for trade rights, whereas the Japanese countered that since Kamchatka belonged to Japan, it followed that all of the Kuril Islands were also Japanese as well.
On December 23, 1854, the Ansei Tokai earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 8.4 on the Richter magnitude scale, shook Japan and surroundings. A 7-meter-high tsunami destroyed most of Shimoda including Putiatin's ships, with the exception of Diana, which was badly damaged and which soon sank as she attempted to sail to Heda for repairs.
The Russian delegation now found itself stranded in Japan, and while the diplomats renegotiated, Russian sailors and technicians worked with Japanese carpenters to build a new vessel at Heda to enable the delegation to return to Russia.
On February 7, 1855, the long-awaited Russo-Japanese treaty of friendship was signed at the Chōraku-ji Temple in Shimoda by Putiatin as Russian Imperial Ambassador and Japanese representative Controller Moriyama Einosuke signing the Dutch-language version (the official version), Iosif Antonovich and Koga Kin'ichirō signing the Chinese-language version, and Toshiakira Kawaji and Tsutsui Masanori signing the Japanese-language version.
Patterned after Perry's Kanagawa Treaty and the Anglo-Japanese Friendship Treaty, the Shimoda Treaty contained many of the same provisions; however, perhaps out of sympathy or out of a favorable impression of Putiatin, the terms agreed upon by Japan were slightly more generous than that granted to the Americans and the British.
The Japanese found Putiatin to be a civilized and righteous man. Putiatin remarked to his Japanese colleague Tsutsui:
- "If we would compare our age, you have the wise age of my father for I only have the age of your son. I offer my hand so I can serve my father and this way will not lose the way of trust."
The schooner Heda was launched on April 14 and Putiatin was able to sail back to Russia, on May 8, 1855. The Japanese government ordered later six more ships to be built on the model of the Heda, thereby contributing to the development of western-style shipbuilding in Japan.[3]
[edit]
The "Shimoda Treaty" has nine articles:
| Article | Summary |
|---|---|
| I | Mutual peace between the Empire of Russia and the Empire of Japan, including safety of persons and property of both nations |
| II | Establishing the border between Japan and Russia to be the line between Etorofu and Urup, with the status of Sakhalin left undetermined. |
| III | Shimoda, Hakodate and Nagasaki to be opened to Russian vessels |
| IV | Shipwrecked sailors to be rendered assistance |
| V | Barter trade permitted at Shimoda and Hakodate |
| VI | Russian consul to be established in either Shimoda or Hakodate |
| VII | Any questions or issues regarding Japan are to be determined by the government of Japan |
| VIII | Mutual extraterritoriality for citizens of Russia and of Japan in each other's country |
| IX | Most favored nation status for Russia |
| XII | Treaty to be ratified within 18 months of signing |
The treaty opened Nagasaki, Shimoda and Hakodate to Russian ships for supplies and repairs, for a consul to be stationed at one of these ports, and for most favored nation status. The official border between Japan and Russia was set as in between Etorofu and Urup, with the status of Sakhalin left undetermined. An unequal treaty, it also provided for the extraterritoriality of Russians in Japan.
Consequences of the treaty[edit]
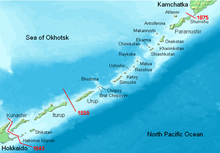
Although Putiatin was lionized after his return to St Petersburg, and was elevated to the title of Count, he was also criticized for the lack of a commercial agreement with Japan, and was forced to return in 1857 and again in 1858 to negotiate new treaties, which expanded on Russian commercial rights and extraterritoriality. One of the most important features of the 1855 Treaty of Shimoda was the agreement that the Kuril Islands were to be divided between Russia and Japan at a line running in between Etorofu and Urup, and the treaty is still frequently cited to this date by the Japanese government as one of its justifications in the current Kuril Islands dispute.[4]
Monument to the treaty[edit]
A memorial sign in honor of the 150th anniversary of the establishment of the Russian-Japanese relations was opened in Kronstadt in 2005. The monument is a black stone where on the Russian and Japanese languages described a brief history of the Putiatin mission. The monument was opened by the Consul General of Japan in St. Petersburg and St. Petersburg Governor.
See also[edit]
- Relations between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire
- History of Japan
- History of Russia
- Convention of Kanagawa
- Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875)
- List of Westerners who visited Japan before 1868
References[edit]
- Edgar Franz: Philipp Franz Von Siebold and Russian Policy and Action on Opening Japan to the West in the Middle of the Nineteenth Century. Deutsches Institut für Japanstudien. Judicium Verlag, München, 2005, ISBN 3-89129-871-4
- ^ W. G. Beasley, The Meiji Restoration, p.74–77
- ^ W. G. Beasley, The Meiji Restoration, p.78
- ^ Sutebusuton: a Japanese village on the British Columbia coast by Mitsuo Yesaki p.6
- ^ Japan's Northern Territories (Pamphlet). Japan Ministry of Foreign Affairs website.
External links[edit]
- Sources are found in the discussion.
- Internetlinks:
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology interactive site on the history of Japan starting from Commodore Perry
- Portraits of modern Japanese historic figures on a site of the National Diet Library, Japan
- Article concerning Northern Territories Day in the Koizumi Cabinet E-Mail Magazine
- MOFA (Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs) site dealing with the Northern Territories issue
- MOFA (Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs) site dealing with the Northern Territories issue
- Subject dealing with the Southern Kuril Islands- Northern Territories Dispute by Andrew Andersen, Department of Political Science, University of Victoria
- Timeline of Sakhalin
- Russian article about Putiatin
- Lieutenant James D. Johnston in chapter 16 of his book "China and Japan" on ""Golownin's Captivity in Japan and Release (1811-1813)"
- "Relations with Russia", Asahi Shimbun newsarticle
- German blogg on the Kuril Islands
- Open syllabus "Moderne geschiedenis van Japan" property of the Japanese Studies section, University of Louvain (KULeuven)
- History of the Northern Territories on the website of the prefectural government of Hokkaidō aimed at argumenting the Japanese right in the Northern Territories


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch