Stoat
| Stoat | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mustelidae |
| Genus: | Mustela |
| Species: | M. erminea |
| Binomial name | |
| Mustela erminea | |
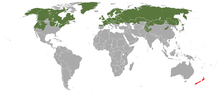 | |
| Stoat range (includes M. richardsonii and M. haidarum) native introduced | |
The stoat (Mustela erminea), also known as the Eurasian ermine, Beringian ermine and ermine, is a mustelid native to Eurasia and the northern regions of North America. Because of its wide circumpolar distribution, it is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.[1] It was introduced into New Zealand in the late 19th century to control rabbits, but had a devastating effect on native bird populations and was nominated as one of the world's top 100 "worst invaders".[2]
The name ermine (/ˈɜːrmɪn/) is used for species in the genus Mustela, especially the stoat, in its pure white winter coat, or the fur thereof.[3] Ermine fur was used in the 15th century by Catholic monarchs, who sometimes used it as the mozzetta cape. It has long been used on the ceremonial robes of members of the United Kingdom House of Lords. It was also used in capes on images such as the Infant Jesus of Prague.
Etymology[edit]

The root word for "stoat" is likely either the Dutch word stout ("bold")[4] or the Gothic word 𐍃𐍄𐌰𐌿𐍄𐌰𐌽 (stautan, "to push").[5] According to John Guillim, in his Display of Heraldrie, the word "ermine" is likely derived from Armenia, the nation where it was thought the species originated,[4] though other authors have linked it to the Norman French from the Teutonic harmin (Anglo-Saxon hearma). This seems to come from the Lithuanian word šarmu.[5] In Ireland (where the least weasel does not occur), the stoat is referred to as a weasel, while in North America it is called a short-tailed weasel. A male stoat is called a dog, hob, or jack, while a female is called a jill. The collective noun for stoats is either gang or pack.[6]
Taxonomy[edit]
Formerly considered a single species with a very wide circumpolar range, a 2021 study split M. erminea into three species: M. erminea sensu stricto (Eurasia and northern North America), M. richardsonii (most of North America), and M. haidarum (several islands off the Pacific Northwest coast).[7][8][9]
Subspecies[edit]
As of 2021[update], 21 subspecies are recognized.[7]
| Subspecies | Trinomial authority | Description | Range | Synonyms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern stoat M. e. erminea | Linnaeus, 1758 | A small-to-medium-sized subspecies with a relatively short and broad facial region[10] | The Kola Peninsula, Scandinavia | hyberna (Kerr, 1792) maculata (Billberg, 1827) |
| Middle Russian stoat M. e. aestiva | Kerr, 1792 | A moderately sized subspecies with dark, tawny or chestnut summer fur[10] | European Russia (except for the Kola Peninsula), Central and Western Europe | algiricus (Thomas, 1895) alpestris (Burg, 1920) |
| Tundra stoat M. e. arctica | Merriam, 1826 | A large subspecies, with a dark yellowish-brown summer coat, a deep yellow underbelly and a massive skull; it resembles the Eurasian stoat subspecies more closely than any other American stoat subspecies[11] | Alaska, northwestern Canada, and the Arctic Archipelago (except for Baffin Island) | audax (Barrett-Hamilton, 1904) kadiacensis (Merriam, 1896) |
| M. e. augustidens | Brown, 1908 | |||
| Fergana stoat M. e. ferghanae | Thomas, 1895 | A small subspecies; it has a very light, straw-brownish or greyish coat, which is short and soft. Light spots, sometimes forming a collar, are present on the neck. It does not turn white in winter.[12][13] | Tien Shan and Pamir-Alay mountains, Afghanistan, India, western Tibet and the adjacent parts of the Tien Shan in China | shnitnikovi (Ognev, 1935) whiteheadi (Wroughton, 1908) |
| Irish stoat M. e. hibernica | Thomas and Barrett-Hamilton, 1895 | Larger than aestiva, but smaller than stabilis. It is distinguished by the irregular pattern on the dividing line between the dark and pale fur on the flanks, though 13.5% of Irish stoats exhibit the more typical straight dividing line.[14] | Ireland and the Isle of Man | |
| Kodiak stoat M. e. kadiacensis | Merriam, 1896 | Kodiak Island | ||
| East Siberian stoat (known locally as Ezo stoat in Japan) M. e. kaneii | Baird, 1857 | A moderately sized subspecies. It is smaller than M. e. tobolica, with close similarities to M. e. arctica. The colour of the summer coat is relatively light, with varying intensities of browning-yellow tinges.[15] | Eastern Siberia and the Russian Far East including Kamchatka, except the Amur Oblast and Ussuriland, Transbaikalia and the Sayan Mountains. Also in Hokkaidō. | baturini (Ognev, 1929) digna (Hall, 1944) |
| Karaginsky stoat M. e. karaginensis | Jurgenson, 1936 | A very small subspecies with a light chestnut-coloured summer coat[16] | Karaginsky Island, along the eastern coast of Kamchatka | |
| Altai stoat Mustela e. lymani | Hollister, 1912 | A moderately sized subspecies with less dense fur than M. e. tobolica. The colour of its summer coat consists of weakly developed reddish-brown tones. The skull is similar to that of M. e. aestiva.[15] | The mountains of southern Siberia eastwards to Baikal and the contiguous parts of Mongolia | |
| M. e. martinoi | Ellerman and Morrison-Scott, 1951 | birulai (Martino and Martino, 1930) | ||
| Swiss stoat M. e. minima | Cavazza, 1912 | Switzerland | ||
| Gobi stoat M. e. mongolica | Ognev, 1928 | The Govi-Altai Province | ||
| Japanese stoat M. e. nippon | Cabrera, 1913 | northern Honshū | ||
| M. e. ognevi | Jurgenson, 1932 | |||
| Polar stoat M. e. polaris | Barrett-Hamilton, 1904 | Greenland | ||
| Hebrides stoat M. e. ricinae | Miller, 1907 | The Hebrides | ||
| M. e. salva | Hall, 1944 | |||
| British stoat M. e. stabilis | Barrett-Hamilton, 1904 | Larger than mainland European stoats[14] | Great Britain; introduced to New Zealand | |
| Caucasian stoat M. e. teberdina | Korneev, 1941 | A small subspecies with a coffee to reddish-tawny summer coat[10] | The northern slope of the middle part of the main Caucasus range | balkarica (Basiev, 1962) |
| Tobolsk stoat M. e. tobolica | Ognev, 1923 | A large subspecies; it is somewhat larger than aestiva, with long and dense fur.[17] | Western Siberia, eastwards to the Yenisei and Altai Mountains and in Kazakhstan |
Evolution[edit]
The stoat's direct ancestor was Mustela palerminea, a common carnivore in central and eastern Europe during the Middle Pleistocene,[18] that spread to North America during the late Blancan or early Irvingtonian.[19] The stoat is the product of a process that began 5–7 million years ago, when northern forests were replaced by open grassland, thus prompting an explosive evolution of small, burrowing rodents. The stoat's ancestors were larger than the current form, and underwent a reduction in size as they exploited the new food source. The stoat first arose in Eurasia, shortly after the long-tailed weasel, which is in a different genus (Neogale), arose as its mirror image in North America 2 million years ago. The stoat thrived during the Ice Age, as its small size and long body allowed it to easily operate beneath snow, as well as hunt in burrows. The stoat and the long-tailed weasel remained separated until 500,000 years ago, when falling sea levels exposed the Bering land bridge.[20]
Fossilised stoat remains have been recovered from Denisova Cave.[21] Combined phylogenetic analyses indicate the stoat's closest living relatives are the American ermine (M. richardsonii) and Haida ermine (M. haidarum), the latter of which partially descends from M. erminea.[7] It is basal to most other members of Mustela, with only the yellow-bellied (M. kathia), Malayan (M. katiah), and back-striped (M. strigidorsa) weasels being more basal.[22] The mountain weasel (Mustela altaica) was formerly considered its closest relative although more recent analyses have found it to be significantly more derived. It was also previously thought to be allied with members of the genus Neogale such as the long-tailed weasel, but as those species have since been separated into a new genus, this is likely not the case.[23]
Description[edit]
Build[edit]

The stoat is similar to the least weasel in general proportions, manner of posture, and movement, though the tail is relatively longer, always exceeding a third of the body length,[clarification needed][24] though it is shorter than that of the long-tailed weasel. The stoat has an elongated neck, the head being set exceptionally far in front of the shoulders. The trunk is nearly cylindrical, and does not bulge at the abdomen. The greatest circumference of body is little more than half its length.[25] The skull, although very similar to that of the least weasel, is relatively longer, with a narrower braincase. The projections of the skull and teeth are weakly developed, but stronger than those of the least weasel.[26] The eyes are round, black and protrude slightly. The whiskers are brown or white in colour, and very long. The ears are short, rounded and lie almost flattened against the skull. The claws are not retractable, and are large in proportion to the digits. Each foot has five toes. The male stoat has a curved baculum with a proximal knob that increases in weight as it ages.[27] Fat is deposited primarily along the spine and kidneys, then on gut mesenteries, under the limbs and around the shoulders. The stoat has four pairs of nipples, though they are visible only in females.[27]

The dimensions of the stoat are variable, but not as significantly as the least weasel's.[28] Unusual among the Carnivora, the size of stoats tends to decrease proportionally with latitude, in contradiction to Bergmann's rule.[18] Sexual dimorphism in size is pronounced, with males being roughly 25% larger than females and 1.5-2.0 times their weight.[14] On average, males measure 187–325 mm (7.4–12.8 in) in body length, while females measure 170–270 mm (6.7–10.6 in). The tail measures 75–120 mm (3.0–4.7 in) in males and 65–106 mm (2.6–4.2 in) in females. In males, the hind foot measures 40.0–48.2 mm (1.57–1.90 in), while in females it is 37.0–47.6 mm (1.46–1.87 in). The height of the ear measures 18.0–23.2 mm (0.71–0.91 in) in males and 14.0–23.3 mm (0.55–0.92 in). The skulls of males measure 39.3–52.2 mm (1.55–2.06 in) in length, while those of females measure 35.7–45.8 mm (1.41–1.80 in). Males average 258 g (9.1 oz) in weight, while females weigh less than 180 g (6.3 oz).[28]
The stoat has large anal scent glands measuring 8.5 mm × 5 mm (0.33 in × 0.20 in) in males and smaller in females. Scent glands are also present on the cheeks, belly and flanks.[27] Epidermal secretions, which are deposited during body rubbing, are chemically distinct from the products of the anal scent glands, which contain a higher proportion of volatile chemicals. When attacked or being aggressive, the stoat secretes the contents of its anal glands, giving rise to a strong, musky odour produced by several sulphuric compounds. The odour is distinct from that of least weasels.[29]
Fur[edit]

The winter fur is very dense and silky, but quite closely lying and short, while the summer fur is rougher, shorter and sparse.[24] In summer, the fur is sandy-brown on the back and head and a white below. The division between the dark back and the light belly is usually straight, though this trait is only present in 13.5% of Irish stoats. The stoat moults twice a year. In spring, the moult is slow, starting from the forehead, across the back, toward the belly. In autumn, the moult is quicker, progressing in the reverse direction. The moult, initiated by photoperiod, starts earlier in autumn and later in spring at higher latitudes. In the stoat's northern range, it adopts a completely white coat (save for the black tail-tip) during the winter period.[27] Differences in the winter and summer coats are less apparent in southern forms of the species.[30] In the species' southern range, the coat remains brown, but is denser and sometimes paler than in summer.[27]
Distribution and habitat[edit]
The stoat has a circumboreal range throughout North America, Europe, and Asia. The stoat in Europe is found as far south as 41ºN in Portugal, and inhabits most islands with the exception of Iceland, Svalbard, the Mediterranean islands and some small North Atlantic islands. In Japan, it is present in central mountains (northern and central Japan Alps) to northern part of Honshu (primarily above 1,200 m) and Hokkaido. Its vertical range is from sea level to 3,000 m (9,800 ft).[1] In North America, it is found throughout Alaska and western Yukon to most of Arctic Canada east to Greenland. Throughout the rest of North America, as well as parts of Nunavut, including Baffin Island and some islands in southeast Alaska, it is replaced by M. richardsonii.[7]
Introduction to New Zealand[edit]
Stoats were introduced into New Zealand during the late 19th century to control rabbits and hares, but are now a major threat to native bird populations. The introduction of stoats was opposed by scientists in New Zealand and Britain, including the New Zealand ornithologist Walter Buller. The warnings were ignored and stoats began to be introduced from Britain in the 1880s, resulting in a noticeable decline in bird populations within six years.[31] Stoats are a serious threat to ground- and hole-nesting birds, since the latter have very few means of escaping predation. The highest rates of stoat predation occur after seasonal gluts in southern beechmast (beechnuts), which enable the reproduction of rodents on which stoats also feed, enabling stoats to increase their own numbers.[32] For instance, the endangered South Island takahē's wild population dropped by a third between 2006 and 2007, after a stoat plague triggered by the 2005–06 mast wiped out more than half the takahē in untrapped areas.[33]
Behaviour and ecology[edit]
Reproduction and development[edit]

In the Northern Hemisphere, mating occurs in the April–July period. In spring, the male's testes are enlarged, a process accompanied by an increase of testosterone concentration in the plasma. Spermatogenesis occurs in December, and the males are fertile from May to August, after which the testes regress.[34] Female stoats are usually only in heat for a brief period, which is triggered by changes in day length.[35] Copulation can last as long as 1 hour.[36] Stoats are not monogamous, with litters often being of mixed paternity. Stoats undergo embryonic diapause, meaning that the embryo does not immediately implant in the uterus after fertilization, but rather lies dormant for a period of nine to ten months.[37] The gestation period is therefore variable but typically around 300 days, and after mating in the summer, the offspring will not be born until the following spring – adult female stoats spend almost all their lives either pregnant or in heat.[35] Females can reabsorb embryos and in the event of a severe winter they may reabsorb their entire litter.[38] Males play no part in rearing the young, which are born blind, deaf, toothless and covered in fine white or pinkish down. The milk teeth erupt after three weeks, and solid food is eaten after four weeks. The eyes open after five to six weeks, with the black tail-tip appearing a week later. Lactation ends after 12 weeks. Prior to the age of five to seven weeks, kits have poor thermoregulation, so they huddle for warmth when the mother is absent. Males become sexually mature at 10–11 months, while females are sexually mature at the age of 2–3 weeks whilst still blind, deaf and hairless, and are usually mated with adult males before being weaned.[39]
Territorial and sheltering behaviour[edit]

Stoat territoriality has a generally mustelid spacing pattern, with male territories encompassing smaller female territories, which they defend from other males. The size of the territory and the ranging behaviour of its occupants varies seasonally, depending on the abundance of food and mates. During the breeding season, the ranges of females remain unchanged, while males either become roamers, strayers or transients. Dominant older males have territories 50 times larger than those of younger, socially inferior males. Both sexes mark their territories with urine, faeces and two types of scent marks; anal drags are meant to convey territorial occupancy, and body rubbing is associated with agonistic encounters.[29]
The stoat does not dig its own burrows, instead using the burrows and nest chambers of the rodents it kills. The skins and underfur of rodent prey are used to line the nest chamber. The nest chamber is sometimes located in seemingly unsuitable places, such as among logs piled against the walls of houses. The stoat also inhabits old and rotting stumps, under tree roots, in heaps of brushwood, haystacks, in bog hummocks, in the cracks of vacant mud buildings, in rock piles, rock clefts, and even in magpie nests. Males and females typically live apart, but close to each other.[40] Each stoat has several dens dispersed within its range. A single den has several galleries, mainly within 30 cm (12 in) of the surface.[41]
Diet[edit]
As with the least weasel, mouse-like rodents predominate in the stoat's diet. It regularly preys on larger rodent and lagomorph species, and takes individuals far larger than itself. In Russia, its prey includes rodents and lagomorphs such as European water voles, common hamsters, pikas and others, which it overpowers in their burrows. Prey species of secondary importance include small birds, fish, and shrews and, more rarely, amphibians, lizards, and insects.[42] It also preys on lemmings.[43] In Great Britain, European rabbits are an important food source, with the frequency in which stoats prey on them having increased between the 1960s and mid 1990s since the end of the myxomatosis epidemic. Typically, male stoats prey on rabbits more frequently than females do, which depend to a greater extent on smaller rodent species. British stoats rarely kill shrews, rats, squirrels and water voles, though rats may be an important food source locally. In Ireland, shrews and rats are frequently eaten. In mainland Europe, water voles make up a large portion of the stoat's diet. Hares are sometimes taken, but are usually young specimens.[44] In New Zealand, the stoat feeds principally on birds, including the rare kiwi, kaka, mohua, yellow-crowned parakeet, and New Zealand dotterel.[44] Cases are known of stoats preying on young muskrats. The stoat typically eats about 50 g (1.8 oz) of food a day, which is equivalent to 25% of the animal's live weight.[45]

The stoat is an opportunistic predator that moves rapidly and checks every available burrow or crevice for food. Because of their larger size, male stoats are less successful than females in pursuing rodents far into tunnels. Stoats regularly climb trees to gain access to birds' nests, and are common raiders of nest boxes, particularly those of large species. The stoat reputedly mesmerises prey such as rabbits by a "dance" (sometimes called the weasel war dance), though this behaviour could be linked to Skrjabingylus infections.[44] The stoat seeks to immobilize large prey such as rabbits with a bite to the spine at the back of the neck. The stoat may surplus kill when the opportunity arises, though excess prey is usually cached and eaten later to avoid obesity, as overweight stoats tend to be at a disadvantage when pursuing prey into their burrows.[46] Small prey typically die instantly from a bite to the back of the neck, while larger prey, such as rabbits, typically die of shock, as the stoat's canine teeth are too short to reach the spinal column or major arteries.[44]
Communication[edit]
The stoat is a usually silent animal, but can produce a range of sounds similar to those of the least weasel. Kits produce a fine chirping noise. Adults trill excitedly before mating, and indicate submission through quiet trilling, whining and squealing. When nervous, the stoat hisses, and will intersperse this with sharp barks or shrieks and prolonged screeching when aggressive.[29]
Aggressive behavior in stoats is categorized in these forms:[29]
- Noncontact approach, which is sometimes accompanied by a threat display and vocalization from the approached animal
- Forward thrust, accompanied by a sharp shriek, which is usually done by stoats defending a nest or retreat site
- Nest occupation, when a stoat appropriates the nesting site of a weaker individual
- Kleptoparasitism, in which a dominant stoat appropriates the killing of a weaker one, usually after a fight.
Submissive stoats express their status by avoiding higher-ranking animals, fleeing from them or making whining or squealing sounds.[29]
Predators[edit]
Larger mammalian predators such as red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and sables (Martes zibellina) are known to prey on stoats.[47] Additionally, a wide range of birds of prey can take stoats, from small northern hawk-owls (Surnia ulula) and short-eared owls (Asio flammeus) to various buzzards, kites, goshawks, and even Eurasian eagle-owls (Bubo bubo) and golden eagles (Aquila chrysaetos).[48] Although not classified as birds of prey, grey herons (Ardea cinerea) are known to prey on stoats.[49]
Diseases and parasites[edit]
Tuberculosis has been recorded in stoats inhabiting the former Soviet Union and New Zealand. They are largely resistant to tularemia, but are reputed to suffer from canine distemper in captivity. Symptoms of mange have also been recorded.[50]
Stoats are vulnerable to ectoparasites associated with their prey and the nests of other animals on which they do not prey. The louse Trichodectes erminea is recorded in stoats living in Canada, Ireland and New Zealand. In continental Europe, 26 flea species are recorded to infest stoats, including Rhadinospylla pentacantha, Megabothris rectangulatus, Orchopeas howardi, Spilopsyllus ciniculus, Ctenophthalamus nobilis, Dasypsyllus gallinulae, Nosopsyllus fasciatus, Leptospylla segnis, Ceratophyllus gallinae, Parapsyllus n. nestoris, Amphipsylla kuznetzovi and Ctenopsyllus bidentatus. Tick species known to infest stoats are Ixodes canisuga, I. hexagonus, and I. ricinus and Haemaphysalis longicornis. Louse species known to infest stoats include Mysidea picae and Polyplax spinulosa. Mite species known to infest stoats include Neotrombicula autumnalis, Demodex erminae, Eulaelaps stabulans, Gymnolaelaps annectans, Hypoaspis nidicorva, and Listrophorus mustelae.[50]
The nematode Skrjabingylus nasicola is particularly threatening to stoats, as it erodes the bones of the nasal sinuses and decreases fertility. Other nematode species known to infect stoats include Capillaria putorii, Molineus patens and Strongyloides martes. Cestode species known to infect stoats include Taenia tenuicollis, Mesocestoides lineatus and rarely Acanthocephala.[50]
In culture[edit]

National Museum, Kraków, Poland.
Folklore and mythology[edit]
In Irish mythology, stoats were viewed anthropomorphically as animals with families, which held rituals for their dead. They were also viewed as noxious animals prone to thieving, and their saliva was said to be able to poison a grown man. To encounter a stoat when setting out for a journey was considered bad luck, but one could avert this by greeting the stoat as a neighbour.[51] Stoats were also supposed to hold the souls of infants who died before baptism.[52]
In the folklore of the Komi people of the Urals, stoats are symbolic of beautiful and coveted young women.[53] In the Zoroastrian religion, the stoat is considered a sacred animal, as its white winter coat represented purity. Similarly, Mary Magdalene was depicted as wearing a white stoat pelt as a sign of her reformed character.
One popular European legend had it that a white stoat would die before allowing its pure white coat to be besmirched. When it was being chased by hunters, it would supposedly turn around and give itself up to the hunters rather than risk soiling itself.[54]
The former nation (now region) of Brittany in France uses a stylized ermine-fur pattern in forming the coat of arms and flag of Brittany. Gilles Servat's song La Blanche Hermine ("The White Ermine") became an anthem for Bretons (and is popular among French people in general).
In the 16th century Chinese novel Investiture of the Gods, Erlang Shen transforms into an ermine to demonstrate his shapeshifting abilities.[citation needed]
Fur use[edit]
Stoat skins are prized by the fur trade, especially in winter coat, and used to trim coats and stoles. The fur from the winter coat is referred to as ermine and is the traditional ancient symbol of the Duchy of Brittany, forming its earliest flag. There is also a design called ermine inspired by the winter coat of the stoat and painted onto other furs, such as rabbit.[55] In Europe these furs are a symbol of royalty and high status. The ceremonial robes of members of the United Kingdom House of Lords and the academic hoods of the universities of Oxford and Cambridge are traditionally trimmed with ermine.[55] In practice, rabbit or fake fur is now often used due to expense or animal rights concerns. Prelates of the Catholic Church still wear ecclesiastical garments featuring ermine (a sign of their status equal to that of the nobility). Cecilia Gallerani is depicted holding an ermine in her portrait, Lady with an Ermine, by Leonardo da Vinci. Henry Peacham's Emblem 75, which depicts an ermine being pursued by a hunter and two hounds, is entitled "Cui candor morte redemptus" ("Purity Bought with His Own Death"). Peacham goes on to preach that men and women should follow the example of the ermine and keep their minds and consciences as pure as the legendary ermine keeps its fur.[56]
Ermine (both M. erminea and M. richardsonii, both of which inhabited the Tlingit's territory) were also valued by the Tlingit and other indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast. They could be attached to traditional regalia and cedar bark hats as status symbols, or they were also made into shirts.[57]
The stoat was a fundamental item in the fur trade of the Soviet Union, with no less than half the global catch coming from within its borders. The Soviet Union also contained the highest grades of stoat pelts, with the best grade North American pelts being comparable only to the 9th grade in the quality criteria of former Soviet stoat standards. Stoat harvesting never became a specialty in any Soviet republic, with most stoats being captured incidentally in traps or near villages. Stoats in the Soviet Union were captured either with dogs or with box-traps or jaw-traps. Guns were rarely used, as they could damage the pelt.[58]
- American actress Alice Maison shown wearing ermine fur in a Mack Sennett comedy film
- Thea Sternheim, wife of playwright Carl Sternheim, wearing an ermine hat
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ a b c Reid, F.; Helgen, K.; Kranz, A. (2016). "Mustela erminea". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29674A45203335. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T29674A45203335.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "100 of the World's Worst Invasive Species". Invasive Species Specialist Group. Archived from the original on 2011-01-03. Retrieved 2011-03-17.
- ^ Shorter Oxford English dictionary. UK: Oxford University Press. 2007. p. 3804. ISBN 978-0199206872.
- ^ a b Coues 1877, pp. 124–125
- ^ a b Johnston 1903, p. 160
- ^ Harris & Yalden 2008, p. 456
- ^ a b c d Colella, Jocelyn P.; Frederick, Lindsey M.; Talbot, Sandra L.; Cook, Joseph A. (2021). "Extrinsically reinforced hybrid speciation within Holarctic ermine (Mustela spp.) produces an insular endemic". Diversity and Distributions. 27 (4): 747–762. doi:10.1111/ddi.13234. S2CID 234059194.
- ^ Fleming, Melissa A.; Cook, Joseph A. (2002). "Phylogeography of endemic ermine (Mustela erminea) in southeast Alaska". Molecular Ecology. 11 (4): 795–807. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01472.x. PMID 11972765. S2CID 18874091.
- ^ "Explore the Database". www.mammaldiversity.org. Archived from the original on 2020-10-28. Retrieved 2021-07-12.
- ^ a b c Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1010
- ^ Merriam 1896, p. 15
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1014
- ^ Kotia, A.; Angmo, K.; Bharti, R. R.; Adhikari, B. S.; Rawat, G. S. (2011). "A record of the little-known Stoat Mustela erminea ferghanae from Ladakh, India". Small Carnivore Conservation. 44: 42–43. Archived from the original on 2023-01-19. Retrieved 2023-01-19.
- ^ a b c Harris & Yalden 2008, p. 459
- ^ a b Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1012
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1013
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1011
- ^ a b Kurtén 1968, pp. 101–102
- ^ Kurtén 1980, p. 150
- ^ Macdonald 1992, p. 205
- ^ Puzachenko, A.Yu.; Titov, V.V.; Kosintsev, P.A. (20 December 2021). "Evolution of the European regional large mammals assemblages in the end of the Middle Pleistocene – The first half of the Late Pleistocene (MIS 6–MIS 4)". Quaternary International. 605–606: 155–191. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2020.08.038. Archived from the original on 11 January 2024. Retrieved 13 January 2024 – via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ^ Law, C. J.; Slater, G. J.; Mehta, R. S. (2018-01-01). "Lineage Diversity and Size Disparity in Musteloidea: Testing Patterns of Adaptive Radiation Using Molecular and Fossil-Based Methods". Systematic Biology. 67 (1): 127–144. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syx047. PMID 28472434.
- ^ Harris & Yalden 2008, p. 458
- ^ a b Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 997
- ^ Coues 1877, pp. 117–121
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 999
- ^ a b c d e Harris & Yalden 2008, p. 457
- ^ a b Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1002
- ^ a b c d e Harris & Yalden 2008, pp. 460–461
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 998
- ^ King, Carolyn (1984). Immigrant Killers. Auckland, NZ: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-558121-0.
- ^ Purdey, D. C.; King, C. M.; Lawrence, B. (2004). "Age structure, dispersion and diet of a population of stoats (Mustela erminea) in southern Fiordland during the decline phase of the beechmast cycle" (PDF). New Zealand Journal of Zoology. 31 (3). The Royal Society of New Zealand: 205–225. doi:10.1080/03014223.2004.9518373. S2CID 55061896. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2009-11-30.
- ^ "Stoats decimating takahe in Fiordland". stuff.co.nz. 4 March 2008. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- ^ Gulamhusein, A. P., and W. H. Tam. "Reproduction in the male stoat, Mustela erminea Archived 2022-08-06 at the Wayback Machine." Reproduction 41.2 (1974): 303-312.
- ^ a b King & Powell 2007, pp. 215
- ^ Amstislavsky, Sergei, and Yulia Ternovskaya. "Reproduction in mustelids." Animal Reproduction Science 60 (2000): 571-581.
- ^ King & Powell 2007, pp. 209–210
- ^ King & Powell 2007, pp. 255
- ^ Harris & Yalden 2008, pp. 464–465
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, pp. 1021–1022
- ^ Harris & Yalden 2008, p. 461
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1018
- ^ American Association For The Advancement Of Science (2003). "It's Feast Or Famine: Predators May Drive Lemming Cycles, Science Researchers Say". ScienceDaily. Archived from the original on 2016-09-05. Retrieved 2023-11-28.
- ^ a b c d Harris & Yalden 2008, p. 463
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1020
- ^ Verts & Carraway 1998, p. 417
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, p. 1025
- ^ Korpimäki, Erkki, and Kai Norrdahl. "Avian predation on mustelids in Europe 1: occurrence and effects on body size variation and life traits." Oikos (1989): 205-215.
- ^ SAWARA, Yuji, Muneki SAKUYAMA, and Gen DEMACHI. "Diets and foraging site utilization of the Grey Heron, Ardea cinerea, in the breeding season." Japanese Journal of Ornithology 43.2 (1994): 61-71.
- ^ a b c Harris & Yalden 2008, p. 466
- ^ Monaghan, Patricia (2004) The encyclopedia of Celtic mythology and folklore: Facts on File library of religion and mythology, page 426, Infobase Publishing, ISBN 0-8160-4524-0
- ^ Daniels, Cora Linn & Stevans, C. M. Encyclopedia of Superstitions, Folklore, and the Occult Sciences of the World, Volume 2 (2003), The Minerva Group, Inc., ISBN 1-4102-0915-6
- ^ Laakso, Johanna (2005) Our otherness: Finno-Ugrian approaches to women's studies, or vice versa, Volume 2 of Finno-Ugrian studies in Austria, LIT Verlag Münster, ISBN 3-8258-8626-3
- ^ Sax, Boria (2001) The mythical zoo: an encyclopedia of animals in world myth, legend, and literature, ABC-CLIO, ISBN 1-57607-612-1
- ^ a b "A house of traditions". BBC News. January 19, 1999. Archived from the original on February 12, 2022. Retrieved July 27, 2009.
- ^ The Minerva Britanna Project Archived 2003-04-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Tlingit Ermine-Skin Shirt (Daa dugu k'oodas')". Archived from the original on 2013-05-13. Retrieved 2012-09-20.
- ^ Heptner & Sludskii 2002, pp. 1029–1030
Bibliography[edit]
- Ahern, Albert (1922). Fur Facts. St. Louis: C. P. Curran printing company.
- Coues, Elliott (1877). Fur-bearing Animals: A Monograph of North American Mustelidae. Government Printing Office.
- Harris, Stephen; Yalden, Derek (2008). Mammals of the British Isles (4th Revised ed.). Mammal Society. ISBN 978-0-906282-65-6.
- Johnston, Harry Hamilton (1903). British mammals; an attempt to describe and illustrate the mammalian fauna of the British islands from the commencement of the Pleistocene period down to the present day. London, Hutchinson.
- King, Carolyn M.; Powell, Roger A. (2007). The Natural History of Weasels and Stoats: Ecology, Behavior, and Management. Illustrations by Consie Powell (2nd ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-530056-7. OCLC 228781387. Archived from the original on 2024-03-05. Retrieved 2018-07-31.
- Kurtén, Björn (1968). Pleistocene mammals of Europe. Weidenfeld and Nicolson.
- Kurtén, Björn (1980). Pleistocene mammals of North America. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-03733-3.
- Heptner, V. G.; Sludskii, A. A. (2002). Mammals of the Soviet Union. Vol. II, part 1b, Carnivores (Mustelidae and Procyonidae). Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Libraries and National Science Foundation. ISBN 90-04-08876-8.
- Macdonald, David (1992). The Velvet Claw: A Natural History of the Carnivores. New York: Parkwest. ISBN 0-563-20844-9.
- Merriam, Clinton Hart (1896). Synopsis of the weasels of North America. Washington, D.C.: Govt. Print. Off.
- Verts, B. J.; Carraway, Leslie N. (1998). Land Mammals of Oregon. University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-21199-5. Archived from the original on 2024-03-05. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
External links[edit]
- Erminea (Mustela erminea) at ARKive
- Mustela erminea taxonomy
- Stoat control information
- Stoat 'playing'(?) in snow
- Fiordland Islands NZ stoat eradication
- BBC Wildlife finder including video footage and sound files
- Stoat images Archived 2012-07-31 at the Wayback Machine
- Smithsonian Institution—North American Mammals: Mustela erminea
- Smithsonian Wild: Mustela erminea


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch






