List of plastid genomes whose DNA sequence is known
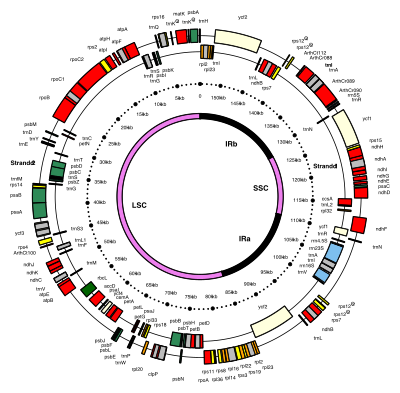
The 156 kb plastome gene map of Nicotiana tabacum The 154 kb plastid genome map of a model flowering plant (Arabidopsis thaliana The highly reduced, 27 kb plastome map of the parasitic Hydnora visseri A plastome genome of a plastid , a type of organelle found in plants and in a variety of protoctists . The number of known plastid genome sequences grew rapidly in the first decade of the twenty-first century. For example, 25 chloroplast genomes were sequenced for one molecular phylogenetic study.[1]
The flowering plants are especially well represented in complete chloroplast genomes. As of January, 2017, all of their orders are represented except Commelinales , Picramniales , Huerteales , Escalloniales , Bruniales , and Paracryphiales .
A compilation of all available complete plastid genomes is maintained by the NCBI in a public repository.[2]
Bryophytes s.l. [ edit ] Ferns and Lycophytes [ edit ] Gymnosperms [ edit ] Sequenced Plastomes Species Variety Size (bp ) Genes Reference Family Notes Cryptomeria japonica 131,810 114 [18] Cupressaceae Cycas micronesica [19] Cycadaceae Cycas taitungensis 163,403 133 [20] Cycadaceae Ephedra equisetina Ephedraceae Ginkgo biloba 156,945 134 [21] Ginkgoaceae Gnetum parvifolium Gnetaceae Picea engelmannii Se404-851 123,542 114 [22] Pinaceae Picea glauca PG29 123,266 114 [23] Pinaceae Picea glauca WS77111 123,421 114 [24] Pinaceae Picea sitchensis Q903 124,049 114 [25] Pinaceae Pinus koraiensis 116,866 Pinaceae Pinus thunbergii 119,707 [26] Pinaceae Podocarpus macrophyllus Podocarpaceae Welwitschia mirabilis 119,726 101 [27] Welwitschiaceae
Flowering plants [ edit ] This sortable table is expected to compile complete plastid genomes representing the largest range of sizes, number of genes, and angiosperm families.
Sequenced plastomes with complete genome size, number of unique genes, reference and publication year. Species Size (bp ) Genes Reference Year Family Notes Acorus americanus 153,819 [19] 2007 Acoraceae Agrostis stolonifera 135,584 110 [28] 2010 Poaceae Alniphyllum eberhardtii 155,384 113 [29] 2017 Styracaceae Alstroemeria aurea155,510 112 [30] 2013 Alstroemeriaceae Amborella trichopoda 162,686 [31] 2003 Amborellaceae Anethum graveolens 153,356 [19] 2007 Apiaceae Arabidopsis thaliana 154,478 [32] 1999 Brassicaceae Atropa belladonna 156,687 [33] 2002 Solanaceae Brachypodium distachyon 135,199 110 [28] 2010 Poaceae Buxus microphylla 159,010 113 [34] 2007 Buxaceae Calycanthus floridus glaucus 153,337 115 [35] 2003 Calycanthaceae Carpinus tientaiensis160,104 114 [36] 2017 Betulaceae Chloranthus spicatus 157,772 113 [34] 2007 Chloranthaceae Citrus sinensis 155,189 [37] 2006 Rutaceae Cocos nucifera 154,731 130 [38] 2013 Arecaceae Coffea arabica 155,189 [39] 2007 Rubiaceae Coix lacryma-jobi 140,745 [40] 2009 Poaceae Conopholis americana 45,673 42 [41] 2013 Orobanchaceae Non-photosynthetic parasite Cucumis sativus 155,293 [42] 2007 Cucurbitaceae Cuscuta exaltata125,373 [43] 2007 Convolvulaceae Cuscuta gronovii86,744 86 [44] 2007 Convolvulaceae Cuscuta reflexa 121,521 98 [44] 2007 Convolvulaceae Cypripedium formosanum 178,131 [45] 2015 Orchidaceae Cytinus hypocistis 19,400 23 [46] 2016 Cytinaceae Holoparasitic Daucus carota 155,911 [47] 2006 Apiaceae Dioscorea elephantipes 152,609 112 [34] 2007 Dioscoreaceae Drimys granadensis 160,604 113 [48] 2006 Winteraceae Epifagus virginiana 70,028 42 [49] 1992 Orobanchaceae Epipogium aphyllum 30,650 27 [50] 2015 Orchidaceae Mycoheterotrophic Epipogium roseum19,047 29 [50] 2015 Orchidaceae Mycoheterotrophic Erodium carvifolium116,935 107 [51] 2016 Geraniaceae Erodium chrysanthum168,946 96 [51] 2016 Geraniaceae Erodium texanum 130,812 106 [52] 2011 Geraniaceae Eucalyptus globulus globulus 160,286 [53] 2005 Myrtaceae Fagopyrum esculentum ancestrale 159,599 [54] 2008 Polygonaceae Geranium palmatum155,794 105 [52] 2011 Geraniaceae Glycine max 152,218 [55] 2005 Fabaceae Gossypium barbadense 160,317 114 [56] 2006 Malvaceae Gossypium hirsutum 160,301 [57] 2006 Malvaceae Helianthus annuus 151,104 [58] 2007 Asteraceae Hordeum vulgare vulgare 136,482 110 [28] 2010 Poaceae Hydnora visseri 27,233 24 [59] 2016 Aristolochiaceae Non-photosynthetic holoparasite Illicium oligandrum148,552 113 [34] 2007 Schisandraceae (sensu APG III ) Ipomoea purpurea 162,046 [43] 2007 Convolvulaceae Jasminum nudiflorum 165,121 [60] 2007 Oleaceae Juglans regia 160,367 129 [61] 2017 Juglandaceae Lactuca sativa 152,765 [58] 2007 Asteraceae Lemna minor 165,955 [62] 2008 Araliaceae Licania alba162,467 112 [63] 2014 Chrysobalanaceae Lilium longiflorum 152,793 114 [30] 2013 Liliaceae Liriodendron tulipifera 159,866 [48] [64] 2006 Magnoliaceae Lolium perenne 135,282 110 [28] 2010 Poaceae Lonicera japonica 155,078 [1] 2010 Caprifoliaceae Lotus japonicus 150,519 [65] 2000 Fabaceae Manihot esculenta 161,453 [66] 2008 Euphorbiaceae Monotropa hypopitys 35,336 45 [67] 2016 Ericaceae Mycoheterotrophic Monsonia speciosa 128,787 106 [52] 2011 Geraniaceae Morus indica156,599 [68] 2006 Moraceae Musa balbisiana 169,503 113 [69] 2016 Musaceae Nandina domestica 156,599 [70] 2006 Berberidaceae Neottia nidus-avis 92,060 56 [71] 2011 Orchidaceae Mycoheterotrophic Nelumbo nucifera 163,330 [1] 2010 Nelumbonaceae Nicotiana tabacum 155,943 113 [72] 1986 Solanaceae Nuphar advena 160,866 117 [73] 2007 Nymphaeaceae Nymphaea alba 159,930 [74] 2004 Nymphaeaceae Oenothera argillicola165,055 113 [75] 2008 Onagraceae Oenothera biennis 164,807 113 [75] 2008 Onagraceae Oenothera elata hookeri strain johansen Standard 165,728 113 [75] 2008 Onagraceae Oenothera glazioviana r /r -lamarckiana Sweden 165,225 113 [75] 2008 Onagraceae Oenothera parviflora163,365 113 [75] 2008 Onagraceae Oryza sativa indica 93-11 134,496 [76] 2005 Poaceae Oryza sativa japonica Nipponbare 134,551 110 [77] [28] 1989 Poaceae Oryza sativa japonica PA64S 134,551 [76] 2005 Poaceae Osyris alba 147,253 101 [78] 2015 Santalaceae Hemiparasitic Panax ginseng 156,318 [79] 2004 Araliaceae Pelargonium × hortorum 217,942 [80] 2006 Geraniaceae Petrosavia stellaris103,835 58 [81] 2014 Petrosaviaceae Mycoheterotrophic Phalaenopsis aphrodite formosana 148,964 [82] 2006 Orchidaceae Phaseolus vulgaris 150,285 [83] 2007 Fabaceae Pilostyles aethiopica11,348 5 [84] 2016 Apodanthaceae Endo-holoparasite Pilostyles hamiltonii15,167 5 [84] 2016 Apodanthaceae Endo-holoparasite Piper cenocladum 160,624 113 [48] 2006 Piperaceae Platanus occidentalis 161,791 [70] 2006 Platanaceae Populus alba 156,505 [85] 2006 Salicaceae Ranunculus macranthus155,158 117 [73] 2007 Ranunculaceae Rhizanthella gardneri 59,190 33 [86] 2011 Orchidaceae Subterranean mycoheterotroph Saccharum officinarum 141,182 110 [28] 2010 Poaceae Sciaphila densiflora21,485 28 [87] 2015 Triuridaceae Mycoheterotrophic Solanum tuberosum 155,298 [88] 2006 Solanaceae Sorghum bicolor 140,754 110 [28] 2010 Poaceae Spinacia oleracea 150,725 [89] 2001 Amaranthaceae Trachelium caeruleum 162,321 [90] 2008 Campanulaceae Trifolium subterraneum 144,763 111 [91] 2008 Fabaceae Triticum aestivum 134,545 110 [92] [93] [28] 2000 Poaceae Typha latifolia 165,572 113 [28] 2010 Typhaceae Vaccinium macrocarpon 176,045 147 [94] 2013 Ericaceae Viscum album 128,921 96 [78] 2015 Viscaceae Hemiparasitic Viscum minimum131,016 99 [78] 2015 Viscaceae Hemiparasitic Vitis vinifera 160,928 [95] 2006 Vitaceae Yucca schidigera 156,158 [21] 2005 Asparagaceae (sensu APG III ) Zea mays 140,384 110 [96] [28] 2010 Poaceae
Sequenced plastomes without information about size, number of genes and / or references. Species Size (bp ) Genes Reference Year Family Notes Acorus calamus 153,821 Acoraceae Aethionema cordifolium Brassicaceae Aethionema grandiflorum Brassicaceae Antirrhinum majus [1] 2010 Plantaginaceae Arabis hirsuta Brassicaceae Aucuba japonica [1] 2010 Garryaceae Bambusa oldhamii 139,350 Poaceae Barbarea verna Brassicaceae Berberidopsis corallina [1] 2010 Berberidopsidaceae Brassica rapa Brassicaceae Bulnesia arborea [1] 2010 Zygophyllaceae Capsella bursa-pastoris Brassicaceae Carica papaya Caricaceae Ceratophyllum demersum [97] 2007 Ceratophyllaceae Cornus florida [1] 2010 Cornaceae Crucihimalya wallichii Brassicaceae Cuscuta obtusiflora Convolvulaceae Cuscuta reflexa Convolvulaceae Dendrocalamus latiflorus 139,365 Poaceae Dillenia indica [1] 2010 Dilleniaceae Draba nemorosa Brassicaceae Ehretia acuminata [1] 2010 Boraginaceae Elaeis oleifera [19] 2007 Arecaceae Euonymus americanus [1] 2010 Celastraceae Festuca arundinacea Poaceae Ficus [1] 2010 Moraceae Guizotia abyssinica Asteraceae Gunnera manicata [1] 2010 Gunneraceae Hedyosmum unpublished Chloranthaceae Heuchera sanguinea [1] 2010 Saxifragaceae Ilex cornuta [1] 2010 Aquifoliaceae Lepidium virginicum Brassicaceae Liquidambar styraciflua Altingia styraciflua ) [1] 2010 Altingiaceae Lobularia maritima Brassicaceae Lotus corniculatus Fabaceae Medicago truncatulata 124,033 Fabaceae Megaleranthis saniculifolia 159,924 Ranunculaceae Meliosma cuneifolia [1] 2010 Sabiaceae Nasturtium officinale Brassicaceae Olimarabidopsis pumila Brassicaceae Phoenix dactylifera Arecaceae Nerium oleander 154,903 Apocynaceae Nicotiana sylvestris 155,941 Solanaceae Nicotiana tomentosiformis 155,745 Solanaceae Oryza nivara 134,494 Poaceae Oxalis latifolia [1] 2010 Oxalidaceae Passiflora biflora [19] 2007 Passifloraceae Phoradendron leucarpum [1] 2010 Viscaceae Plumbago auriculata [1] 2010 Plumbaginaceae Populus trichocarpa [98] 2006 Salicaceae Quercus nigra [1] 2010 Fagaceae Rhododendron simsii [1] 2010 Ericaceae Scaevola aemula [19] 2007 Goodeniaceae Solanum bulbocastanum 155,371 Solanaceae Solanum lycopersicum 155,460 Solanaceae Staphylea colchica [1] 2010 Staphyleaceae Trithuria Hydatella unpublished Hydatellaceae Trochodendron aralioides [1] 2010 Trochodendraceae Ximenia americana 2010 Ximeniaceae [99]
Green algae [ edit ] Sequenced Plastomes Species Variety Size (bp ) Genes Reference Bryopsis plumosa 106,859 115 [100] Chaetosphaeridium globosum 131,183 124 [101] Chara vulgaris Chlamydomonas reinhardtii 203,395 99 Chlorella vulgaris 150,613 209 [102] Chlorokybus atmophyticus 201,763 70 [103] Dunaliella salina CCAP 19/18 269,044 102 [104] Emiliania huxleyi 105,309 150 Helicosporidium 37,454 54 [105] Leptosira terrestris 195,081 117 [106] Mesostigma viride 42,424 Monomastix 114,528 94 [107] Nephroselmis olivacea 200,799 127 [108] Oedogonium cardiacum 196,547 103 [109] Oltmannsiellopsis viridis 151,933 105 [110] Ostreococcus tauri 71,666 86 [111] Pseudendoclonium akinetum 195,867 105 [112] Pycnococcus provasolii 80,211 98 [107] Pyramimonas parkeae 101,605 110 [107] Scenedesmus obliquus 161,452 96 [113] Staurastrum punctulatum [114] Stigeoclonium helveticum 223,902 97 [115] Tydemania expeditionis 105,200 125 [100] Ulva sp.UNA00071828 99,983 102 [116] Volvox carteri 420,650 91 [117] Zygnema circumcarinatum
Sequenced Plastomes Species Variety Size (bp ) Genes Reference Year Taxon Notes Ahnfeltia plicata 190,451 205 (coding) [118] 2016 Ahnfeltiales Apophlaea sinclairii 182,437 189 (coding) [118] 2016 Hildenbrandiales Asparagopsis taxiformis 177,091 203 (coding) [118] 2016 Bangiopsis subsimplex 204,784 194 (coding) [118] 2016 Calliarthron tuberculosum 178,981 238 [119] 2013 Ceramium japonicum 171,634 199 (coding) [118] 2016 Chondrus crispus 180,086 240 [119] 2013 Gigartinales Cyanidioschyzon merolae 10D 149,987 243 [120] 2003 Cyanidium caldarium RK1 164,921 230 [121] 2000 Erythrotrichia carnea 210,691 191 (coding) [118] 2016 Galdieria sulphuraria 074W 167,741 233 [122] 2015 Gelidium elegans 174,748 234 [123] 2016 Gelidium sinicolaUC276620 177,095 232 [124] 2019 May be synonymous with G. coulteri Gelidium vagum 179,853 234 [123] 2016 Gracilaria changii 183,855 231 [125] 2018 Gracilariales Gracilaria chorda 182,459 201 (coding) [118] 2016 Gracilariales Gracilaria salicornia 179,757 235 [126] 2014 Gracilariales Gracilaria tenuistipitata var. liui 183,883 238 [127] 2004 Gracilariales Gracilaria vermiculophylla 180,254 239 unpublished Gracilariales Grateloupia filicina 195,990 265 unpublished Grateloupia taiwanensis 191,270 266 [128] 2013 Hildenbrandia rivularis 189,725 184 (coding) [118] 2016 Hildenbrandia rubra 180,141 190 (coding) [118] 2016 Kumanoa americana 184,025 234 [129] 2018 Palmaria palmata 192,960 245 [129] 2018 Plocamium cartilagineum 171,392 197 (coding) [118] 2016 Porphyra pulchra 194,175 251 [123] 2016 Bangiales Porphyra purpurea 191,028 253 [130] 1993 Bangiales Porphyra umbilicalis 190,173 250 [131] 2017 Bangiales Porphyridium purpureum NIES 2140 217,694 260 [132] 2014 Porphyridium sordidum 259,429 227 [118] 2016 Pyropia fucicola 187,282 [133] 2015 Partial genome Pyropia haitanensis PH 38 195,597 254 [134] 2013 Pyropia kanakaensis 189,931 [133] 2015 Partial genome Pyropia perforata 189,789 247 [133] 2015 Pyropia yezoensis 191,952 264 [134] 2013 Rhodochaete parvula 221,665 195 (coding) [118] 2016 Rhodymenia pseudopalmata 194,153 201 (coding) [118] 2016 Riquetophycus 180,384 202 (coding) [118] 2016 Schimmelmannia schousboei 181,030 202 (coding) [118] 2016 Schizymenia dubyi 183,959 204 (coding) [118] 2016 Sebdenia flabellata 192,140 205 (coding) [118] 2016 Sporolithon durum 191,464 239 [123] 2016 Thorea hispida 175,193 228 [129] 2018 Vertebrata lanosa 167,158 192 [135] 2015 Also assigned to genus Polysiphonia
Glaucophytes [ edit ] Meta-algae and apicomplexans [ edit ] Meta-algae are organisms with photosynthetic organelles of secondary or tertiary endosymbiotic origin, and their close non-photosynthetic, plastid-bearing, relatives. Apicomplexans are a secondarily non-photosynthetic group of chromalveoates which retain a reduced plastid organelle.
Photosynthetic chromalveolates [ edit ] Dinoflagellate plastid genomes are not organised into a single circular DNA molecule like other plastid genomes, but into an array of mini-circles.
Sequenced Plastomes Species Variety Size (bp ) Genes Reference Notes Chromera velia Chroomonas mesostigmaticaCCMP1168 139,403 189 [137] Chroomonas placoideaCCAP978/8 139,432 186 [137] Contains 3 annotated pseudogenes Cryptomonas curvataCNUKR 128,285 182 [137] Cryptomonas parameciumCCAP977/2a 77,717 115 [138] Emiliania huxleyi CCMP 373 105,309 154 [139] Guillardia theta 121,524 167 [140] Heterosigma akashiwo NIES 293 159,370 198 [141] Odontella sinensis 119,704 175 [142] Phaeodactylum tricornutum 117,369 170 [143] Rhodomonas salina CCMP1319 135,854 183 [144] Storeatula sp. CCMP1868 140,953 187 [137] Teleaulax amphioxeia HACCP-CR01 129,772 179 [145] Thalassiosira pseudonana 128,814 180 [143]
Chlorarachniophytes [ edit ] Apicomplexans [ edit ] Nucleomorph genomes [ edit ] In some photosynthetic organisms that ability was acquired via symbiosis with a unicellular green alga (chlorophyte ) or red alga (rhodophyte ). In some such cases not only does the chloroplast of the former unicellular alga retain its own genome, but a remnant of the alga is also retained. When this retains a nucleus and a nuclear genome it is termed a nucleomorph .
Cyanelle genomes [ edit ] The unicellular eukaryote Paulinella chromatophoracyanelle ) which represents an independent case of the acquisition of photosynthesis by cyanobacterial endosymbiosis. (Note: the term cyanelle is also applied to the plastids of glaucophytes.)
See also [ edit ] References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Moore MJ, Soltis PS, Bell CD, Burleigh JG, Soltis DE (March 2010). "Phylogenetic analysis of 83 plastid genes further resolves the early diversification of eudicots" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 107 (10): 4623–8. Bibcode :2010PNAS..107.4623M . doi :10.1073/pnas.0907801107 PMC 2842043 PMID 20176954 . ^ "Index of /refseq/release/plastid" . ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov . Retrieved 2017-01-08 .^ Wickett NJ, Zhang Y, Hansen SK, Roper JM, Kuehl JV, Plock SA, Wolf PG, DePamphilis CW, Boore JL, Goffinet B (February 2008). "Functional gene losses occur with minimal size reduction in the plastid genome of the parasitic liverwort Aneura mirabilis" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 25 (2): 393–401. doi :10.1093/molbev/msm267 PMID 18056074 . ^ Plastid genome evolution of the non-photosynthetic liverwort Aneura mirabilis (Malmb.) Wickett & Goffinet (Aneuraceae) ^ Kugita M, Kaneko A, Yamamoto Y, Takeya Y, Matsumoto T, Yoshinaga K (January 2003). "The complete nucleotide sequence of the hornwort (Anthoceros formosae) chloroplast genome: insight into the earliest land plants" . Nucleic Acids Research . 31 (2): 716–21. doi :10.1093/nar/gkg155 . PMC 140519 PMID 12527781 . ^ K Ohyama, Fukuzawa, H., Kohchi, T., Shirai, H., Sano, T., Chang Z, Aota SI, Inokuchi H, Ozeki H (2003). "Chloroplast gene organization deduced from complete sequence of liverwort Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast DNA". Nature . 322 (6079): 716–721. Bibcode :1986Natur.322..572O . doi :10.1038/322572a0 . S2CID 4311952 . ^ Villarreal JC, Forrest LL, Wickett N, Goffinet B (March 2013). "The plastid genome of the hornwort Nothoceros aenigmaticus (Dendrocerotaceae): phylogenetic signal in inverted repeat expansion, pseudogenization, and intron gain". American Journal of Botany . 100 (3): 467–77. doi :10.3732/ajb.1200429 . PMID 23416362 . ^ Grosche C, Funk HT, Maier UG, Zauner S (2012). "The chloroplast genome of Pellia endiviifolia: gene content, RNA-editing pattern, and the origin of chloroplast editing" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 4 (12): 1349–57. doi :10.1093/gbe/evs114 . PMC 3542565 PMID 23221608 . ^ Sugiura C, Kobayashi Y, Aoki S, Sugita C, Sugita M (September 2003). "Complete chloroplast DNA sequence of the moss Physcomitrella patens: evidence for the loss and relocation of rpoA from the chloroplast to the nucleus" . Nucleic Acids Research . 31 (18): 5324–31. doi :10.1093/nar/gkg726 . PMC 203311 PMID 12954768 . ^ Laura L. Forrest; Norman J. Wickett, Cymon J. Cox & Bernard Goffinet (2011). "Deep sequencing of Ptilidium (Ptilidiaceae) suggests evolutionary stasis in liverwort plastid genome structure" (PDF) . Plant Ecology and Evolution . 144 (1): 29–43. doi :10.5091/plecevo.2011.535 . hdl :10400.1/5518 ^ Oliver MJ, Murdock AG, Mishler BD, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Mandoli DF, Everett KD, Wolf PG, Duffy AM, Karol KG (February 2010). "Chloroplast genome sequence of the moss Tortula ruralis: gene content, polymorphism, and structural arrangement relative to other green plant chloroplast genomes" . BMC Genomics . 11 : 143. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-11-143 PMC 2841679 PMID 20187961 . ^ Wolf PG, Rowe CA, Sinclair RB, Hasebe M (April 2003). "Complete nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast genome from a leptosporangiate fern, Adiantum capillus-veneris L" . DNA Research . 10 (2): 59–65. doi :10.1093/dnares/10.2.59 PMID 12755170 . ^ Gao L, Yi X, Yang YX, Su YJ, Wang T (June 2009). "Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a tree fern Alsophila spinulosa: insights into evolutionary changes in fern chloroplast genomes" . BMC Evolutionary Biology . 9 : 130. doi :10.1186/1471-2148-9-130 PMC 2706227 PMID 19519899 . ^ Roper JM, Hansen SK, Wolf PG, Karol KG, Mandoli DF, Everett KD, Kuehl J, Boore JL (2007). "The Complete Plastid Genome Sequence of Angiopteris evecta (G. Forst.) Hoffm. (Marattiaceae)" . American Fern Journal . 97 (2): 95–106. doi :10.1640/0002-8444(2007)97[95:TCPGSO]2.0.CO;2 ^ Wolf PG, Karol KG, Mandoli DF, Kuehl J, Arumuganathan K, Ellis MW, Mishler BD, Kelch DG, Olmstead RG, Boore JL (May 2005). "The first complete chloroplast genome sequence of a lycophyte, Huperzia lucidula (Lycopodiaceae)" . Gene . 350 (2): 117–28. doi :10.1016/j.gene.2005.01.018 . PMID 15788152 . ^ Wakasugi, T (1998). "Complete nucleotide sequence of the plastid genome from a fern, Psilotum nudum " . Endocytobiology and Cell Research . 13 (Supplement): 147. External links below.^ Tsuji S, Ueda K, Nishiyama T, Hasebe M, Yoshikawa S, Konagaya A, Nishiuchi T, Yamaguchi K (March 2007). "The chloroplast genome from a lycophyte (microphyllophyte), Selaginella uncinata, has a unique inversion, transpositions and many gene losses". Journal of Plant Research . 120 (2): 281–90. doi :10.1007/s10265-006-0055-y . PMID 17297557 . S2CID 7691300 . ^ Hirao T, Watanabe A, Kurita M, Kondo T, Takata K (June 2008). "Complete nucleotide sequence of the Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. chloroplast genome and comparative chloroplast genomics: diversified genomic structure of coniferous species" . BMC Plant Biology . 8 : 70. doi :10.1186/1471-2229-8-70 PMC 2443145 PMID 18570682 . ^ a b c d e f Jansen RK, Cai Z, Raubeson LA, Daniell H, Depamphilis CW, Leebens-Mack J, Müller KF, Guisinger-Bellian M, Haberle RC, Hansen AK, Chumley TW, Lee SB, Peery R, McNeal JR, Kuehl JV, Boore JL (December 2007). "Analysis of 81 genes from 64 plastid genomes resolves relationships in angiosperms and identifies genome-scale evolutionary patterns" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 104 (49): 19369–74. Bibcode :2007PNAS..10419369J . doi :10.1073/pnas.0709121104 PMC 2148296 PMID 18048330 . ^ Wu CS, Wang YN, Liu SM, Chaw SM (June 2007). "Chloroplast genome (cpDNA) of Cycas taitungensis and 56 cp protein-coding genes of Gnetum parvifolium: insights into cpDNA evolution and phylogeny of extant seed plants" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 24 (6): 1366–79. doi :10.1093/molbev/msm059 PMID 17383970 . ^ a b Leebens-Mack J, Raubeson LA, Cui L, Kuehl JV, Fourcade MH, Chumley TW, Boore JL, Jansen RK, depamphilis CW (October 2005). "Identifying the basal angiosperm node in chloroplast genome phylogenies: sampling one's way out of the Felsenstein zone" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 22 (10): 1948–63. doi :10.1093/molbev/msi191 PMID 15944438 . ^ Lin, Diana; Coombe, Lauren; Jackman, Shaun D.; Gagalova, Kristina K.; Warren, René L.; Hammond, S. Austin; McDonald, Helen; Kirk, Heather; Pandoh, Pawan; Zhao, Yongjun; Moore, Richard A. (2019-06-13). Stajich, Jason E. (ed.). "Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of an Engelmann Spruce ( Picea engelmannii , Genotype Se404-851) from Western Canada" . Microbiology Resource Announcements . 8 (24): e00382–19, /mra/8/24/MRA.00382–19.atom. doi :10.1128/MRA.00382-19 . ISSN 2576-098X . PMC 6588038 PMID 31196920 . ^ Jackman, Shaun D.; Warren, René L.; Gibb, Ewan A.; Vandervalk, Benjamin P.; Mohamadi, Hamid; Chu, Justin; Raymond, Anthony; Pleasance, Stephen; Coope, Robin; Wildung, Mark R.; Ritland, Carol E. (January 2016). "Organellar Genomes of White Spruce ( Picea glauca ): Assembly and Annotation" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 8 (1): 29–41. doi :10.1093/gbe/evv244 . ISSN 1759-6653 . PMC 4758241 PMID 26645680 . ^ Lin, Diana; Coombe, Lauren; Jackman, Shaun D.; Gagalova, Kristina K.; Warren, René L.; Hammond, S. Austin; Kirk, Heather; Pandoh, Pawan; Zhao, Yongjun; Moore, Richard A.; Mungall, Andrew J. (2019-06-06). Rokas, Antonis (ed.). "Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of a White Spruce ( Picea glauca , Genotype WS77111) from Eastern Canada" . Microbiology Resource Announcements . 8 (23): e00381–19, /mra/8/23/MRA.00381–19.atom. doi :10.1128/MRA.00381-19 . ISSN 2576-098X . PMC 6554609 PMID 31171622 . ^ Coombe, Lauren; Warren, René L.; Jackman, Shaun D.; Yang, Chen; Vandervalk, Benjamin P.; Moore, Richard A.; Pleasance, Stephen; Coope, Robin J.; Bohlmann, Joerg; Holt, Robert A.; Jones, Steven J. M. (2016-09-15). Budak, Hikmet (ed.). "Assembly of the Complete Sitka Spruce Chloroplast Genome Using 10X Genomics' GemCode Sequencing Data" . PLOS ONE . 11 (9): e0163059. Bibcode :2016PLoSO..1163059C . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0163059 ISSN 1932-6203 . PMC 5025161 PMID 27632164 . ^ Wakasugi T, Tsudzuki J, Ito S, Nakashima K, Tsudzuki T, Sugiura M (October 1994). "Loss of all ndh genes as determined by sequencing the entire chloroplast genome of the black pine Pinus thunbergii" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 91 (21): 9794–8. Bibcode :1994PNAS...91.9794W . doi :10.1073/pnas.91.21.9794 PMC 44903 PMID 7937893 . ^ McCoy SR, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Raubeson LA (May 2008). "The complete plastid genome sequence of Welwitschia mirabilis: an unusually compact plastome with accelerated divergence rates" . BMC Evolutionary Biology . 8 : 130. doi :10.1186/1471-2148-8-130 PMC 2386820 PMID 18452621 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j Guisinger et al, Implications of the Plastid Genome Sequence of Typha (Typhaceae, Poales) for Understanding Genome Evolution in Poaceae, J Mol Evol 70: 149–166 (2010) ^ Yan M, Moore MJ, Meng A, Yao X, Wang H (2016-09-21). "The first complete plastome sequence of the basal asterid family Styracaceae (Ericales) reveals a large inversion". Plant Systematics and Evolution . 303 (1): 61–70. doi :10.1007/s00606-016-1352-0 . ISSN 0378-2697 . S2CID 25942874 . ^ a b Kim JS, Kim JH (2013-06-18). "Comparative genome analysis and phylogenetic relationship of order Liliales insight from the complete plastid genome sequences of two Lilies (Lilium longiflorum and Alstroemeria aurea)" . PLOS ONE . 8 (6): e68180. Bibcode :2013PLoSO...868180K . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0068180 PMC 3688979 PMID 23950788 . ^ Goremykin VV, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Wolfl S, Hellwig FH (September 2003). "Analysis of the Amborella trichopoda chloroplast genome sequence suggests that amborella is not a basal angiosperm" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 20 (9): 1499–505. doi :10.1093/molbev/msg159 PMID 12832641 . ^ Sato S, Nakamura Y, Kaneko T, Asamizu E, Tabata S (October 1999). "Complete structure of the chloroplast genome of Arabidopsis thaliana" . DNA Research . 6 (5): 283–90. doi :10.1093/dnares/6.5.283 PMID 10574454 . ^ Schmitz-Linneweber C, Regel R, Du TG, Hupfer H, Herrmann RG, Maier RM (September 2002). "The plastid chromosome of Atropa belladonna and its comparison with that of Nicotiana tabacum: the role of RNA editing in generating divergence in the process of plant speciation". Molecular Biology and Evolution . 19 (9): 1602–12. doi :10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004222 . PMID 12200487 . S2CID 1111063 . ^ a b c d Hansen DR, Dastidar SG, Cai Z, Penaflor C, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Jansen RK (November 2007). "Phylogenetic and evolutionary implications of complete chloroplast genome sequences of four early-diverging angiosperms: Buxus (Buxaceae), Chloranthus (Chloranthaceae), Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae), and Illicium (Schisandraceae)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution . 45 (2): 547–63. doi :10.1016/j.ympev.2007.06.004 . PMID 17644003 . ^ Goremykin V, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Wölfl S, Hellwig FH (2003). "The chloroplast genome of the basal angiosperm Calycanthus fertilis – structural and phylogenetic analyses". Plant Systematics and Evolution . 242 (1–4): 119–135. doi :10.1007/s00606-003-0056-4 . S2CID 44377635 . ^ Yang Y, Wang M, Lu Z, Xie X, Feng S (2017-01-04). "Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Carpinus tientaiensis ". Conservation Genetics Resources . 9 (2): 339–341. doi :10.1007/s12686-016-0668-y . ISSN 1877-7252 . S2CID 5184815 . ^ Bausher MG, Singh ND, Lee SB, Jansen RK, Daniell H (September 2006). "The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck var 'Ridge Pineapple': organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms" . BMC Plant Biology . 6 : 21. doi :10.1186/1471-2229-6-21 PMC 1599732 PMID 17010212 . ^ Huang YY, Matzke AJ, Matzke M (2013-08-30). "Complete sequence and comparative analysis of the chloroplast genome of coconut palm (Cocos nucifera)" . PLOS ONE . 8 (8): e74736. Bibcode :2013PLoSO...874736H . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0074736 PMC 3758300 PMID 24023703 . ^ Samson N, Bausher MG, Lee SB, Jansen RK, Daniell H (March 2007). "The complete nucleotide sequence of the coffee (Coffea arabica L.) chloroplast genome: organization and implications for biotechnology and phylogenetic relationships amongst angiosperms" . Plant Biotechnology Journal . 5 (2): 339–53. doi :10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00245.x . PMC 3473179 PMID 17309688 . ^ Leseberg CH, Duvall MR (October 2009). "The complete chloroplast genome of Coix lacryma-jobi and a comparative molecular evolutionary analysis of plastomes in cereals". Journal of Molecular Evolution . 69 (4): 311–8. Bibcode :2009JMolE..69..311L . doi :10.1007/s00239-009-9275-9 . PMID 19777151 . S2CID 24418374 . ^ Wicke S, Müller KF, de Pamphilis CW, Quandt D, Wickett NJ, Zhang Y, Renner SS, Schneeweiss GM (October 2013). "Mechanisms of functional and physical genome reduction in photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic parasitic plants of the broomrape family" . The Plant Cell . 25 (10): 3711–25. doi :10.1105/tpc.113.113373 . PMC 3877813 PMID 24143802 . ^ Plader W, Yukawa Y, Sugiura M, Malepszy S (2007). "The complete structure of the cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) chloroplast genome: its composition and comparative analysis" . Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters . 12 (4): 584–94. doi :10.2478/s11658-007-0029-7 . PMC 6275786 PMID 17607527 . ^ a b McNeal JR, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, de Pamphilis CW (October 2007). "Complete plastid genome sequences suggest strong selection for retention of photosynthetic genes in the parasitic plant genus Cuscuta" . BMC Plant Biology . 7 : 57. doi :10.1186/1471-2229-7-57 PMC 2216012 PMID 17956636 . ^ a b Funk HT, Berg S, Krupinska K, Maier UG, Krause K (August 2007). "Complete DNA sequences of the plastid genomes of two parasitic flowering plant species, Cuscuta reflexa and Cuscuta gronovii" . BMC Plant Biology . 7 : 45. doi :10.1186/1471-2229-7-45 PMC 2089061 PMID 17714582 . ^ Lin CS, Chen JJ, Huang YT, Chan MT, Daniell H, Chang WJ, Hsu CT, Liao DC, Wu FH, Lin SY, Liao CF, Deyholos MK, Wong GK, Albert VA, Chou ML, Chen CY, Shih MC (March 2015). "The location and translocation of ndh genes of chloroplast origin in the Orchidaceae family" . Scientific Reports . 5 : 9040. Bibcode :2015NatSR...5E9040L . doi :10.1038/srep09040 . PMC 4356964 PMID 25761566 . ^ Roquet C, Coissac É, Cruaud C, Boleda M, Boyer F, Alberti A, Gielly L, Taberlet P, Thuiller W, Van Es J, Lavergne S (July 2016). "Understanding the evolution of holoparasitic plants: the complete plastid genome of the holoparasite Cytinus hypocistis (Cytinaceae)" . Annals of Botany . 118 (5): 885–896. doi :10.1093/aob/mcw135 . PMC 5055816 PMID 27443299 . ^ Ruhlman T, Lee SB, Jansen RK, Hostetler JB, Tallon LJ, Town CD, Daniell H (August 2006). "Complete plastid genome sequence of Daucus carota: implications for biotechnology and phylogeny of angiosperms" . BMC Genomics . 7 : 222. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-7-222 PMC 1579219 PMID 16945140 . ^ a b c Cai Z, Penaflor C, Kuehl JV, Leebens-Mack J, Carlson JE, dePamphilis CW, Boore JL, Jansen RK (October 2006). "Complete plastid genome sequences of Drimys, Liriodendron, and Piper: implications for the phylogenetic relationships of magnoliids" . BMC Evolutionary Biology . 6 : 77. doi :10.1186/1471-2148-6-77 PMC 1626487 PMID 17020608 . ^ Wolfe KH, Morden CW, Palmer JD (November 1992). "Function and evolution of a minimal plastid genome from a nonphotosynthetic parasitic plant" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 89 (22): 10648–52. Bibcode :1992PNAS...8910648W . doi :10.1073/pnas.89.22.10648 PMC 50398 PMID 1332054 . ^ a b Schelkunov MI, Shtratnikova VY, Nuraliev MS, Selosse MA, Penin AA, Logacheva MD (January 2015). "Exploring the limits for reduction of plastid genomes: a case study of the mycoheterotrophic orchids Epipogium aphyllum and Epipogium roseum" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 7 (4): 1179–91. doi :10.1093/gbe/evv019 . PMC 4419786 PMID 25635040 . ^ a b Blazier JC, Jansen RK, Mower JP, Govindu M, Zhang J, Weng ML, Ruhlman TA (June 2016). "Variable presence of the inverted repeat and plastome stability in Erodium" . Annals of Botany . 117 (7): 1209–20. doi :10.1093/aob/mcw065 . PMC 4904181 PMID 27192713 . ^ a b c Guisinger MM, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Jansen RK (January 2011). "Extreme reconfiguration of plastid genomes in the angiosperm family Geraniaceae: rearrangements, repeats, and codon usage" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 28 (1): 583–600. doi :10.1093/molbev/msq229 PMID 20805190 . ^ Steane DA (2005). "Complete nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast genome from the Tasmanian blue gum, Eucalyptus globulus (Myrtaceae)" . DNA Research . 12 (3): 215–20. doi :10.1093/dnares/dsi006 PMID 16303753 . ^ Logacheva MD, Samigullin TH, Dhingra A, Penin AA (May 2008). "Comparative chloroplast genomics and phylogenetics of Fagopyrum esculentum ssp. ancestrale -a wild ancestor of cultivated buckwheat" . BMC Plant Biology . 8 : 59. doi :10.1186/1471-2229-8-59 PMC 2430205 PMID 18492277 . ^ Saski C, Lee SB, Daniell H, Wood TC, Tomkins J, Kim HG, Jansen RK (September 2005). "Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Glycine max and comparative analyses with other legume genomes". Plant Molecular Biology . 59 (2): 309–22. doi :10.1007/s11103-005-8882-0 . PMID 16247559 . S2CID 3332004 . ^ Ibrahim RI, Azuma J, Sakamoto M (October 2006). "Complete nucleotide sequence of the cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) chloroplast genome with a comparative analysis of sequences among 9 dicot plants" . Genes & Genetic Systems . 81 (5): 311–21. doi :10.1266/ggs.81.311 PMID 17159292 . ^ Lee SB, Kaittanis C, Jansen RK, Hostetler JB, Tallon LJ, Town CD, Daniell H (March 2006). "The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Gossypium hirsutum: organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms" . BMC Genomics . 7 : 61. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-7-61 PMC 1513215 PMID 16553962 . ^ a b Timme RE, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Jansen RK (March 2007). "A comparative analysis of the Lactuca and Helianthus (Asteraceae) plastid genomes: identification of divergent regions and categorization of shared repeats" . American Journal of Botany . 94 (3): 302–12. doi :10.3732/ajb.94.3.302 PMID 21636403 . ^ Naumann J, Der JP, Wafula EK, Jones SS, Wagner ST, Honaas LA, Ralph PE, Bolin JF, Maass E, Neinhuis C, Wanke S, dePamphilis CW (January 2016). "Detecting and Characterizing the Highly Divergent Plastid Genome of the Nonphotosynthetic Parasitic Plant Hydnora visseri (Hydnoraceae)" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 8 (2): 345–63. doi :10.1093/gbe/evv256 . PMC 4779604 PMID 26739167 . ^ Lee HL, Jansen RK, Chumley TW, Kim KJ (May 2007). "Gene relocations within chloroplast genomes of Jasminum and Menodora (Oleaceae) are due to multiple, overlapping inversions" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 24 (5): 1161–80. doi :10.1093/molbev/msm036 PMID 17329229 . ^ Hu Y, Woeste KE, Zhao P (2017-01-01). "Juglans and Their Contribution to Chloroplast Phylogeny" . Frontiers in Plant Science . 7 : 1955. doi :10.3389/fpls.2016.01955 PMC 5216037 PMID 28111577 . ^ Mardanov AV, Ravin NV, Kuznetsov BB, Samigullin TH, Antonov AS, Kolganova TV, Skyabin KG (June 2008). "Complete sequence of the duckweed (Lemna minor) chloroplast genome: structural organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms". Journal of Molecular Evolution . 66 (6): 555–64. Bibcode :2008JMolE..66..555M . doi :10.1007/s00239-008-9091-7 . PMID 18463914 . S2CID 10044367 . ^ Malé PJ, Bardon L, Besnard G, Coissac E, Delsuc F, Engel J, Lhuillier E, Scotti-Saintagne C, Tinaut A, Chave J (September 2014). "Genome skimming by shotgun sequencing helps resolve the phylogeny of a pantropical tree family". Molecular Ecology Resources . 14 (5): 966–75. doi :10.1111/1755-0998.12246 . PMID 24606032 . S2CID 26777683 . ^ Liang H, Carlson JE, Leebens-Mack JH, Wall PK, Mueller LA, Buzgo M, Landherr LL, Hu Y, DiLoreto DS, Ilut DC, Field D, Tanksley SD, Ma H, Claude (2008). "An EST database for Liriodendron tulipifera L. floral buds: the first EST resource for functional and comparative genomics in Liriodendron". Tree Genetics & Genomes . 4 (3): 419–433. doi :10.1007/s11295-007-0120-2 . S2CID 44266336 . ^ Kato T, Kaneko T, Sato S, Nakamura Y, Tabata S (December 2000). "Complete structure of the chloroplast genome of a legume, Lotus japonicus" . DNA Research . 7 (6): 323–30. doi :10.1093/dnares/7.6.323 PMID 11214967 . ^ Daniell H, Wurdack KJ, Kanagaraj A, Lee SB, Saski C, Jansen RK (March 2008). "The complete nucleotide sequence of the cassava (Manihot esculenta) chloroplast genome and the evolution of atpF in Malpighiales: RNA editing and multiple losses of a group II intron" . Theoretical and Applied Genetics . 116 (5): 723–37. doi :10.1007/s00122-007-0706-y . PMC 2587239 PMID 18214421 . ^ Ravin NV, Gruzdev EV, Beletsky AV, Mazur AM, Prokhortchouk EB, Filyushin MA, Kochieva EZ, Kadnikov VV, Mardanov AV, Skryabin KG (November 2016). "The loss of photosynthetic pathways in the plastid and nuclear genomes of the non-photosynthetic mycoheterotrophic eudicot Monotropa hypopitys" . BMC Plant Biology . 16 (Suppl 3): 238. doi :10.1186/s12870-016-0929-7 PMC 5123295 PMID 28105941 . ^ Ravi V, Khurana JP, Tyagi AK, Khurana P (2006). "The chloroplast genome of mulberry: complete nucleotide sequence, gene organization and comparative analysis". Tree Genetics & Genomes . 3 (1): 49–59. doi :10.1007/s11295-006-0051-3 . S2CID 22104273 . ^ Shetty SM, Md Shah MU, Makale K, Mohd-Yusuf Y, Khalid N, Othman RY (July 2016). "Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Corroborates Structural Heterogeneity of Inverted Repeats in Wild Progenitors of Cultivated Bananas and Plantains" . The Plant Genome . 9 (2). doi :10.3835/plantgenome2015.09.0089 PMID 27898825 . ^ a b Moore MJ, Dhingra A, Soltis PS, Shaw R, Farmerie WG, Folta KM, Soltis DE (August 2006). "Rapid and accurate pyrosequencing of angiosperm plastid genomes" . BMC Plant Biology . 6 : 17. doi :10.1186/1471-2229-6-17 PMC 1564139 PMID 16934154 . ^ Logacheva MD, Schelkunov MI, Penin AA (2011-01-01). "Sequencing and analysis of plastid genome in mycoheterotrophic orchid Neottia nidus-avis" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 3 : 1296–303. doi :10.1093/gbe/evr102 . PMC 3228488 PMID 21971517 . ^ Shinozaki K, Ohme M, Tanaka M, Wakasugi T, Hayashida N, Matsubayashi T, Zaita N, Chunwongse J, Obokata J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Ohto C, Torazawa K, Meng BY, Sugita M, Deno H, Kamogashira T, Yamada K, Kusuda J, Takaiwa F, Kato A, Tohdoh N, Shimada H, Sugiura M (September 1986). "The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression" . The EMBO Journal . 5 (9): 2043–2049. doi :10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x . PMC 1167080 PMID 16453699 . ^ a b Raubeson LA, Peery R, Chumley TW, Dziubek C, Fourcade HM, Boore JL, Jansen RK (June 2007). "Comparative chloroplast genomics: analyses including new sequences from the angiosperms Nuphar advena and Ranunculus macranthus" . BMC Genomics . 8 : 174. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-8-174 PMC 1925096 PMID 17573971 . ^ Goremykin VV, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Wölfl S, Hellwig FH (July 2004). "The chloroplast genome of Nymphaea alba: whole-genome analyses and the problem of identifying the most basal angiosperm" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 21 (7): 1445–54. doi :10.1093/molbev/msh147 PMID 15084683 . ^ a b c d e Greiner S, Wang X, Rauwolf U, Silber MV, Mayer K, Meurer J, Haberer G, Herrmann RG (April 2008). "The complete nucleotide sequences of the five genetically distinct plastid genomes of Oenothera, subsection Oenothera: I. sequence evaluation and plastome evolution" . Nucleic Acids Research . 36 (7): 2366–78. doi :10.1093/nar/gkn081 . PMC 2367718 PMID 18299283 . ^ a b Yu J, Wang J, Lin W, Li S, Li H, Zhou J, et al. (February 2005). "The Genomes of Oryza sativa: a history of duplications" . PLOS Biology . 3 (2): e38. doi :10.1371/journal.pbio.0030038 PMC 546038 PMID 15685292 . ^ Hiratsuka J, Shimada H, Whittier R, Ishibashi T, Sakamoto M, Mori M, Kondo C, Honji Y, Sun CR, Meng BY (June 1989). "The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals". Molecular & General Genetics . 217 (2–3): 185–94. doi :10.1007/BF02464880 . PMID 2770692 . S2CID 36458326 . ^ a b c Petersen G, Cuenca A, Seberg O (August 2015). "Plastome Evolution in Hemiparasitic Mistletoes" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 7 (9): 2520–32. doi :10.1093/gbe/evv165 . PMC 4607522 PMID 26319577 . ^ Kim KJ, Lee HL (August 2004). "Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants" . DNA Research . 11 (4): 247–61. doi :10.1093/dnares/11.4.247 PMID 15500250 . ^ Chumley TW, Palmer JD, Mower JP, Fourcade HM, Calie PJ, Boore JL, Jansen RK (November 2006). "The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Pelargonium x hortorum: organization and evolution of the largest and most highly rearranged chloroplast genome of land plants" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 23 (11): 2175–90. doi :10.1093/molbev/msl089 PMID 16916942 . ^ Logacheva MD, Schelkunov MI, Nuraliev MS, Samigullin TH, Penin AA (January 2014). "The plastid genome of mycoheterotrophic monocot Petrosavia stellaris exhibits both gene losses and multiple rearrangements" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 6 (1): 238–46. doi :10.1093/gbe/evu001 . PMC 3914687 PMID 24398375 . ^ Chang CC, Lin HC, Lin IP, Chow TY, Chen HH, Chen WH, Cheng CH, Lin CY, Liu SM, Chang CC, Chaw SM (February 2006). "The chloroplast genome of Phalaenopsis aphrodite (Orchidaceae): comparative analysis of evolutionary rate with that of grasses and its phylogenetic implications" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 23 (2): 279–91. doi :10.1093/molbev/msj029 PMID 16207935 . ^ Guo X, Castillo-Ramírez S, González V, Bustos P, Fernández-Vázquez JL, Santamaría RI, Arellano J, Cevallos MA, Dávila G (July 2007). "Rapid evolutionary change of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L) plastome, and the genomic diversification of legume chloroplasts" . BMC Genomics . 8 : 228. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-8-228 PMC 1940014 PMID 17623083 . ^ a b Bellot S, Renner SS (December 2015). "The Plastomes of Two Species in the Endoparasite Genus Pilostyles (Apodanthaceae) Each Retain Just Five or Six Possibly Functional Genes" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 8 (1): 189–201. doi :10.1093/gbe/evv251 . PMC 4758247 PMID 26660355 . ^ Okumura S, Sawada M, Park YW, Hayashi T, Shimamura M, Takase H, Tomizawa K (October 2006). "Transformation of poplar (Populus alba) plastids and expression of foreign proteins in tree chloroplasts". Transgenic Research . 15 (5): 637–46. doi :10.1007/s11248-006-9009-3 . PMID 16952016 . S2CID 39294451 . ^ Delannoy E, Fujii S, Colas des Francs-Small C, Brundrett M, Small I (July 2011). "Rampant gene loss in the underground orchid Rhizanthella gardneri highlights evolutionary constraints on plastid genomes" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 28 (7): 2077–86. doi :10.1093/molbev/msr028 . PMC 3112369 PMID 21289370 . ^ Lam VK, Soto Gomez M, Graham SW (July 2015). "The Highly Reduced Plastome of Mycoheterotrophic Sciaphila (Triuridaceae) Is Colinear with Its Green Relatives and Is under Strong Purifying Selection" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 7 (8): 2220–36. doi :10.1093/gbe/evv134 . PMC 4558852 PMID 26170229 . ^ Chung HJ, Jung JD, Park HW, Kim JH, Cha HW, Min SR, Jeong WJ, Liu JR (December 2006). "The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Solanum tuberosum and comparative analysis with Solanaceae species identified the presence of a 241-bp deletion in cultivated potato chloroplast DNA sequence". Plant Cell Reports . 25 (12): 1369–79. doi :10.1007/s00299-006-0196-4 . PMID 16835751 . S2CID 24055793 . ^ Schmitz-Linneweber C, Maier RM, Alcaraz JP, Cottet A, Herrmann RG, Mache R (February 2001). "The plastid chromosome of spinach (Spinacia oleracea): complete nucleotide sequence and gene organization". Plant Molecular Biology . 45 (3): 307–15. doi :10.1023/A:1006478403810 . PMID 11292076 . S2CID 28271437 . ^ Haberle RC, Fourcade HM, Boore JL, Jansen RK (April 2008). "Extensive rearrangements in the chloroplast genome of Trachelium caeruleum are associated with repeats and tRNA genes". Journal of Molecular Evolution . 66 (4): 350–61. Bibcode :2008JMolE..66..350H . CiteSeerX 10.1.1.174.5498 doi :10.1007/s00239-008-9086-4 . PMID 18330485 . S2CID 18228097 . ^ Cai Z, et al. (2008). "Extensive Reorganization of the Plastid Genome of Trifolium subterraneum (Fabaceae) Is Associated with Numerous Repeated Sequences and Novel DNA Insertions". J Mol Evol . 67 (6): 696–704. Bibcode :2008JMolE..67..696C . doi :10.1007/s00239-008-9180-7 . PMID 19018585 . S2CID 36486188 . ^ Ogihara Y, Isono K, Kojima T, Endo A, Hanaoka M, Shiina T, et al. (2000). "Chinese Spring Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Chloroplast Genome: Complete Sequence and Contig Clones". Plant Molecular Biology Reporter . 18 (3): 243–253. doi :10.1007/BF02823995 . S2CID 41773993 . ^ Ogihara Y, Isono K, Kojima T, Endo A, Hanaoka M, Shiina T, Terachi T, Utsugi S, Murata M, Mori N, Takumi S, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Murai R, Murai K, Matsuoka Y, Ohnishi Y, Tajiri H, Tsunewaki K (January 2002). "Structural features of a wheat plastome as revealed by complete sequencing of chloroplast DNA". Molecular Genetics and Genomics . 266 (5): 740–6. doi :10.1007/s00438-001-0606-9 . PMID 11810247 . S2CID 22434780 . ^ Fajardo D, Senalik D, Ames M, Zhu H, Steffan SA, Harbut R, Polashock J, Vorsa N, Gillespie E, Kron K, Zalapa JE (2013). "Complete plastid genome sequence of Vaccinium macrocarpon: structure, gene content, and rearrangements revealed by next generation sequencing". Tree Genetics & Genomes . 9 (2): 489–498. doi :10.1007/s11295-012-0573-9 . S2CID 17130517 . ^ Jansen RK, Kaittanis C, Saski C, Lee SB, Tomkins J, Alverson AJ, Daniell H (April 2006). "Phylogenetic analyses of Vitis (Vitaceae) based on complete chloroplast genome sequences: effects of taxon sampling and phylogenetic methods on resolving relationships among rosids" . BMC Evolutionary Biology . 6 : 32. doi :10.1186/1471-2148-6-32 PMC 1479384 PMID 16603088 . ^ Maier RM, Neckermann K, Igloi GL, Kössel H (September 1995). "Complete sequence of the maize chloroplast genome: gene content, hotspots of divergence and fine tuning of genetic information by transcript editing". Journal of Molecular Biology . 251 (5): 614–28. doi :10.1006/jmbi.1995.0460 . PMID 7666415 . ^ Moore MJ, Bell CD, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (December 2007). "Using plastid genome-scale data to resolve enigmatic relationships among basal angiosperms" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 104 (49): 19363–8. Bibcode :2007PNAS..10419363M . doi :10.1073/pnas.0708072104 PMC 2148295 PMID 18048334 . ^ Gerald A. Tuskan, et alii (110 authors). 2006. "The genome of Black Cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray)". Science 313 (5793):1596-1604. ^ Nickrent DL, Malécot V, Vidal-Russell R, Der JP (2010). "A revised classification of Santalales". Taxon . 59 (2): 538–558. doi :10.1002/tax.592019 . S2CID 85950875 . ^ a b Leliaert F, Lopez-Bautista JM (March 2015). "The chloroplast genomes of Bryopsis plumosa and Tydemania expeditiones (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta): compact genomes and genes of bacterial origin" . BMC Genomics . 16 (1): 204. doi :10.1186/s12864-015-1418-3 PMC 4487195 PMID 25879186 . ^ Turmel M, Otis C, Lemieux C (August 2002). "The chloroplast and mitochondrial genome sequences of the charophyte Chaetosphaeridium globosum: insights into the timing of the events that restructured organelle DNAs within the green algal lineage that led to land plants" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 99 (17): 11275–80. Bibcode :2002PNAS...9911275T . doi :10.1073/pnas.162203299 PMC 123247 PMID 12161560 . ^ Wakasugi T, Nagai T, Kapoor M, Sugita M, Ito M, Ito S, Tsudzuki J, Nakashima K, Tsudzuki T, Suzuki Y, Hamada A, Ohta T, Inamura A, Yoshinaga K, Sugiura M (May 1997). "Complete nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast genome from the green alga Chlorella vulgaris: the existence of genes possibly involved in chloroplast division" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 94 (11): 5967–72. Bibcode :1997PNAS...94.5967W . doi :10.1073/pnas.94.11.5967 PMC 20890 PMID 9159184 . ^ Turmel M, Otis C, Lemieux C (May 2007). "An unexpectedly large and loosely packed mitochondrial genome in the charophycean green alga Chlorokybus atmophyticus" . BMC Genomics . 8 : 137. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-8-137 PMC 1894977 PMID 17537252 . ^ Smith DR, et al. (May 2010). "The Dunaliella salina organelle genomes: large sequences, inflated with intronic and intergenic DNA" . BMC Plant Biology . 10 : 83. doi :10.1186/1471-2229-10-83 PMC 3017802 PMID 20459666 . ^ de Koning AP, Keeling PJ (April 2006). "The complete plastid genome sequence of the parasitic green alga Helicosporidium sp. is highly reduced and structured" . BMC Biology . 4 : 12. doi :10.1186/1741-7007-4-12 PMC 1463013 PMID 16630350 . ^ de Cambiaire JC, Otis C, Turmel M, Lemieux C (July 2007). "The chloroplast genome sequence of the green alga Leptosira terrestris: multiple losses of the inverted repeat and extensive genome rearrangements within the Trebouxiophyceae" . BMC Genomics . 8 : 213. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-8-213 PMC 1931444 PMID 17610731 . ^ a b c Turmel M, Gagnon MC, O'Kelly CJ, Otis C, Lemieux C (March 2009). "The chloroplast genomes of the green algae Pyramimonas, Monomastix, and Pycnococcus shed new light on the evolutionary history of prasinophytes and the origin of the secondary chloroplasts of euglenids" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 26 (3): 631–48. doi :10.1093/molbev/msn285 PMID 19074760 . ^ Turmel M, Otis C, Lemieux C (August 1999). "The complete chloroplast DNA sequence of the green alga Nephroselmis olivacea: insights into the architecture of ancestral chloroplast genomes" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 96 (18): 10248–53. Bibcode :1999PNAS...9610248T . doi :10.1073/pnas.96.18.10248 PMC 17874 PMID 10468594 . ^ Brouard JS, Otis C, Lemieux C, Turmel M (June 2008). "Chloroplast DNA sequence of the green alga Oedogonium cardiacum (Chlorophyceae): unique genome architecture, derived characters shared with the Chaetophorales and novel genes acquired through horizontal transfer" . BMC Genomics . 9 : 290. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-9-290 PMC 2442088 PMID 18558012 . ^ Pombert JF, Lemieux C, Turmel M (February 2006). "The complete chloroplast DNA sequence of the green alga Oltmannsiellopsis viridis reveals a distinctive quadripartite architecture in the chloroplast genome of early diverging ulvophytes" . BMC Biology . 4 : 3. doi :10.1186/1741-7007-4-3 PMC 1402334 PMID 16472375 . ^ Robbens S, Derelle E, Ferraz C, Wuyts J, Moreau H, Van de Peer Y (April 2007). "The complete chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA sequence of Ostreococcus tauri: organelle genomes of the smallest eukaryote are examples of compaction" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 24 (4): 956–68. doi :10.1093/molbev/msm012 PMID 17251180 . ^ Pombert JF, Otis C, Lemieux C, Turmel M (September 2005). "The chloroplast genome sequence of the green alga Pseudendoclonium akinetum (Ulvophyceae) reveals unusual structural features and new insights into the branching order of chlorophyte lineages" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 22 (9): 1903–18. doi :10.1093/molbev/msi182 PMID 15930151 . ^ de Cambiaire JC, Otis C, Lemieux C, Turmel M (April 2006). "The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the chlorophycean green alga Scenedesmus obliquus reveals a compact gene organization and a biased distribution of genes on the two DNA strands" . BMC Evolutionary Biology . 6 : 37. doi :10.1186/1471-2148-6-37 PMC 1513399 PMID 16638149 . ^ Turmel M, Otis C, Lemieux C (October 2005). "The complete chloroplast DNA sequences of the charophycean green algae Staurastrum and Zygnema reveal that the chloroplast genome underwent extensive changes during the evolution of the Zygnematales" . BMC Biology . 3 : 22. doi :10.1186/1741-7007-3-22 PMC 1277820 PMID 16236178 . ^ Bélanger AS, Brouard JS, Charlebois P, Otis C, Lemieux C, Turmel M (November 2006). "Distinctive architecture of the chloroplast genome in the chlorophycean green alga Stigeoclonium helveticum". Molecular Genetics and Genomics . 276 (5): 464–77. doi :10.1007/s00438-006-0156-2 . PMID 16944205 . S2CID 19489840 . ^ Melton JT, Leliaert F, Tronholm A, Lopez-Bautista JM (2015). "The complete chloroplast and mitochondrial genomes of the green macroalga Ulva sp. UNA00071828 (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta)" . PLOS ONE . 10 (4): e0121020. Bibcode :2015PLoSO..1021020M . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0121020 PMC 4388391 PMID 25849557 . ^ Smith DR, Lee RW (March 2009). "The mitochondrial and plastid genomes of Volvox carteri: bloated molecules rich in repetitive DNA" . BMC Genomics . 10 (132): 132. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-10-132 PMC 2670323 PMID 19323823 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Lee J, Cho CH, Park SI, Choi JW, Song HS, West JA, Bhattacharya D, Yoon HS (September 2016). "Parallel evolution of highly conserved plastid genome architecture in red seaweeds and seed plants" . BMC Biology . 14 (1): 75. doi :10.1186/s12915-016-0299-5 PMC 5010701 PMID 27589960 . ^ a b Janouškovec J, Liu SL, Martone PT, Carré W, Leblanc C, Collén J, Keeling PJ (2013-03-25). Bhattacharya D (ed.). "Evolution of red algal plastid genomes: ancient architectures, introns, horizontal gene transfer, and taxonomic utility of plastid markers" . PLOS ONE . 8 (3): e59001. Bibcode :2013PLoSO...859001J . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0059001 PMC 3607583 PMID 23536846 . ^ Ohta N, Matsuzaki M, Misumi O, Miyagishima SY, Nozaki H, Tanaka K, Shin-I T, Kohara Y, Kuroiwa T (April 2003). "Complete sequence and analysis of the plastid genome of the unicellular red alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae" . DNA Research . 10 (2): 67–77. doi :10.1093/dnares/10.2.67 PMID 12755171 . ^ Glöckner G, Rosenthal A, Valentin K (October 2000). "The structure and gene repertoire of an ancient red algal plastid genome". Journal of Molecular Evolution . 51 (4): 382–90. Bibcode :2000JMolE..51..382G . CiteSeerX 10.1.1.566.2529 doi :10.1007/s002390010101 . PMID 11040290 . S2CID 23064129 . ^ Jain K, Krause K, Grewe F, Nelson GF, Weber AP, Christensen AC, Mower JP (December 2014). "Extreme features of the Galdieria sulphuraria organellar genomes: a consequence of polyextremophily?" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 7 (1): 367–80. doi :10.1093/gbe/evu290 . PMC 4316638 PMID 25552531 . ^ a b c d Lee J, Kim KM, Yang EC, Miller KA, Boo SM, Bhattacharya D, Yoon HS (March 2016). "Reconstructing the complex evolutionary history of mobile plasmids in red algal genomes" . Scientific Reports . 6 (1): 23744. Bibcode :2016NatSR...623744L . doi :10.1038/srep23744 . PMC 4814812 PMID 27030297 . ^ Boo GH, Hughey JR (February 2019). "Phylogenomics and multigene phylogenies decipher two new cryptic marine algae from California, Gelidium gabrielsonii and G. kathyanniae (Gelidiales, Rhodophyta)" . Journal of Phycology . 55 (1): 160–172. doi :10.1111/jpy.12802 PMID 30341779 . ^ Ho CL, Lee WK, Lim EL (March 2018). "Unraveling the nuclear and chloroplast genomes of an agar producing red macroalga, Gracilaria changii (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales)" . Genomics . 110 (2): 124–133. doi :10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.09.003 PMID 28890206 . ^ Campbell, Matthew A.; Presting, Gernot; Bennett, Matthew S.; Sherwood, Alison R. (2014-02-21). "Highly conserved organellar genomes in the Gracilariales as inferred using new data from the Hawaiian invasive alga Gracilaria salicornia (Rhodophyta". Phycologia . 53 (2): 109–116. doi :10.2216/13-222.1 . S2CID 85867132 . ^ Hagopian JC, Reis M, Kitajima JP, Bhattacharya D, de Oliveira MC (October 2004). "Comparative analysis of the complete plastid genome sequence of the red alga Gracilaria tenuistipitata var. liui provides insights into the evolution of rhodoplasts and their relationship to other plastids". Journal of Molecular Evolution . 59 (4): 464–77. Bibcode :2004JMolE..59..464H . CiteSeerX 10.1.1.614.9150 doi :10.1007/s00239-004-2638-3 . PMID 15638458 . S2CID 19135480 . ^ DePriest MS, Bhattacharya D, López-Bautista JM (2013-07-19). "The plastid genome of the red macroalga Grateloupia taiwanensis (Halymeniaceae)" . PLOS ONE . 8 (7): e68246. Bibcode :2013PLoSO...868246D . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0068246 PMC 3716797 PMID 23894297 . ^ a b c Cho CH, Choi JW, Lam DW, Kim KM, Yoon HS (2018-05-08). "Plastid genome analysis of three Nemaliophycidae red algal species suggests environmental adaptation for iron limited habitats" . PLOS ONE . 13 (5): e0196995. Bibcode :2018PLoSO..1396995C . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0196995 PMC 5940233 PMID 29738547 . ^ Reith M, Munholland J (April 1993). "A High-Resolution Gene Map of the Chloroplast Genome of the Red Alga Porphyra purpurea" . The Plant Cell . 5 (4): 465–475. doi :10.1105/tpc.5.4.465 . PMC 160285 PMID 12271072 . ^ Brawley SH, Blouin NA, Ficko-Blean E, Wheeler GL, Lohr M, Goodson HV, et al. (August 2017). "Porphyra umbilicalis (Bangiophyceae, Rhodophyta)" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 114 (31): E6361–E6370. doi :10.1073/pnas.1703088114 PMC 5547612 PMID 28716924 . ^ Tajima N, Sato S, Maruyama F, Kurokawa K, Ohta H, Tabata S, Sekine K, Moriyama T, Sato N (May 2014). "Analysis of the complete plastid genome of the unicellular red alga Porphyridium purpureum". Journal of Plant Research . 127 (3): 389–97. doi :10.1007/s10265-014-0627-1 . PMID 24595640 . S2CID 1420996 . ^ a b c Hughey JR, Gabrielson PW, Rohmer L, Tortolani J, Silva M, Miller KA, Young JD, Martell C, Ruediger E (June 2014). "Minimally destructive sampling of type specimens of Pyropia (Bangiales, Rhodophyta) recovers complete plastid and mitochondrial genomes" . Scientific Reports . 4 (1): 5113. Bibcode :2014NatSR...4E5113H . doi :10.1038/srep05113 . PMC 4044621 PMID 24894641 . ^ a b Wang L, Mao Y, Kong F, Li G, Ma F, Zhang B, Sun P, Bi G, Zhang F, Xue H, Cao M (2013-05-29). "Complete sequence and analysis of plastid genomes of two economically important red algae: Pyropia haitanensis and Pyropia yezoensis" . PLOS ONE . 8 (5): e65902. Bibcode :2013PLoSO...865902W . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0065902 PMC 3667073 PMID 23734264 . ^ Salomaki ED, Nickles KR, Lane CE (April 2015). "The ghost plastid of Choreocolax polysiphoniae". Journal of Phycology . 51 (2): 217–21. doi :10.1111/jpy.12283 . PMID 26986516 . S2CID 30670447 . ^ Löffelhardt W, Bohnert HJ, Bryant DA (1997). "The complete sequence of the Cyanophora paradoxa cyanelle genome (Glaucocystophyceae)". Plant Systematics and Evolution . Vol. 11. Springer Vienna. pp. 149–162. doi :10.1007/978-3-7091-6542-3_8 . ISBN 9783211830352 ^ a b c d Kim JI, Moore CE, Archibald JM, Bhattacharya D, Yi G, Yoon HS, Shin W (July 2017). "Evolutionary Dynamics of Cryptophyte Plastid Genomes" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 9 (7): 1859–1872. doi :10.1093/gbe/evx123 . PMC 5534331 PMID 28854597 . ^ Donaher N, Tanifuji G, Onodera NT, Malfatti SA, Chain PS, Hara Y, Archibald JM (November 2009). "The complete plastid genome sequence of the secondarily nonphotosynthetic alga Cryptomonas paramecium: reduction, compaction, and accelerated evolutionary rate" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 1 : 439–48. doi :10.1093/gbe/evp047 . PMC 2839278 PMID 20333213 . ^ Sánchez Puerta MV, Bachvaroff TR, Delwiche CF (2005-01-01). "The complete plastid genome sequence of the haptophyte Emiliania huxleyi: a comparison to other plastid genomes" . DNA Research . 12 (2): 151–6. doi :10.1093/dnares/12.2.151 PMID 16303746 . ^ Douglas SE, Penny SL (February 1999). "The plastid genome of the cryptophyte alga, Guillardia theta: complete sequence and conserved synteny groups confirm its common ancestry with red algae". Journal of Molecular Evolution . 48 (2): 236–44. Bibcode :1999JMolE..48..236D . doi :10.1007/PL00006462 . PMID 9929392 . S2CID 2005223 . ^ Cattolico RA, Jacobs MA, Zhou Y, Chang J, Duplessis M, Lybrand T, McKay J, Ong HC, Sims E, Rocap G (May 2008). "Chloroplast genome sequencing analysis of Heterosigma akashiwo CCMP452 (West Atlantic) and NIES293 (West Pacific) strains" . BMC Genomics . 9 (1): 211. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-9-211 PMC 2410131 PMID 18462506 . ^ Kowallik KV, Stoebe B, Schaffran I, Kroth-Pancic P, Freier U (December 1995). "The chloroplast genome of a chlorophylla+c-containing alga,Odontella sinensis". Plant Molecular Biology Reporter . 13 (4): 336–342. doi :10.1007/BF02669188 . ISSN 0735-9640 . S2CID 1515475 . ^ a b Oudot-Le Secq MP, Grimwood J, Shapiro H, Armbrust EV, Bowler C, Green BR (April 2007). "Chloroplast genomes of the diatoms Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Thalassiosira pseudonana: comparison with other plastid genomes of the red lineage". Molecular Genetics and Genomics . 277 (4): 427–39. doi :10.1007/s00438-006-0199-4 . PMID 17252281 . S2CID 23192934 . ^ Khan H, Parks N, Kozera C, Curtis BA, Parsons BJ, Bowman S, Archibald JM (August 2007). "Plastid genome sequence of the cryptophyte alga Rhodomonas salina CCMP1319: lateral transfer of putative DNA replication machinery and a test of chromist plastid phylogeny" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 24 (8): 1832–42. doi :10.1093/molbev/msm101 PMID 17522086 . ^ Kim JI, Yoon HS, Yi G, Kim HS, Yih W, Shin W (2015-06-05). Przyborski JM (ed.). "The Plastid Genome of the Cryptomonad Teleaulax amphioxeia" . PLOS ONE . 10 (6): e0129284. Bibcode :2015PLoSO..1029284K . doi :10.1371/journal.pone.0129284 PMC 4457928 PMID 26047475 . ^ Rogers MB, Gilson PR, Su V, McFadden GI, Keeling PJ (January 2007). "The complete chloroplast genome of the chlorarachniophyte Bigelowiella natans: evidence for independent origins of chlorarachniophyte and euglenid secondary endosymbionts" . Molecular Biology and Evolution . 24 (1): 54–62. doi :10.1093/molbev/msl129 PMID 16990439 . ^ a b c Suzuki S, Hirakawa Y, Kofuji R, Sugita M, Ishida KI (July 2016). "Plastid genome sequences of Gymnochlora stellata, Lotharella vacuolata, and Partenskyella glossopodia reveal remarkable structural conservation among chlorarachniophyte species". Journal of Plant Research . 129 (4): 581–590. doi :10.1007/s10265-016-0804-5 . PMID 26920842 . S2CID 3463713 . ^ Tanifuji G, Onodera NT, Brown MW, Curtis BA, Roger AJ, Ka-Shu Wong G, Melkonian M, Archibald JM (May 2014). "Nucleomorph and plastid genome sequences of the chlorarachniophyte Lotharella oceanica: convergent reductive evolution and frequent recombination in nucleomorph-bearing algae" . BMC Genomics . 15 (1): 374. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-15-374 PMC 4035089 PMID 24885563 . ^ Hallick RB, Hong L, Drager RG, Favreau MR, Monfort A, Orsat B, Spielmann A, Stutz E (July 1993). "Complete sequence of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA" . Nucleic Acids Research . 21 (15): 3537–44. doi :10.1093/nar/21.15.3537 . PMC 331456 PMID 8346031 . ^ Cai X, Fuller AL, McDougald LR, Zhu G (December 2003). "Apicoplast genome of the coccidian Eimeria tenella". Gene . 321 : 39–46. doi :10.1016/j.gene.2003.08.008 . PMID 14636990 . ^ a b Suzuki S, Shirato S, Hirakawa Y, Ishida KI (2015). "Nucleomorph Genome Sequences of Two Chlorarachniophytes, Amorphochlora amoebiformis and Lotharella vacuolata" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 7 (6): 1533–1545. doi :10.1093/gbe/evv096 PMC 4494063 PMID 26002880 . ^ Gilson PR, Su V, Slamovits CH, Reith ME, Keeling PJ, McFadden GI (June 2006). "Complete nucleotide sequence of the chlorarachniophyte nucleomorph: nature's smallest nucleus" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 103 (25): 9566–71. Bibcode :2006PNAS..103.9566G . doi :10.1073/pnas.0600707103 PMC 1480447 PMID 16760254 . ^ Curtis BA, Tanifuji G, Burki F, Gruber A, Irimia M, Maruyama S, et al. (December 2012). "Algal genomes reveal evolutionary mosaicism and the fate of nucleomorphs" (PDF) . Nature . 492 (7427): 59–65. Bibcode :2012Natur.492...59C . doi :10.1038/nature11681 PMID 23201678 . ^ Moore CE, Curtis B, Mills T, Tanifuji G, Archibald JM (2012). "Nucleomorph genome sequence of the cryptophyte alga Chroomonas mesostigmatica CCMP1168 reveals lineage-specific gene loss and genome complexity" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 4 (11): 1162–75. doi :10.1093/gbe/evs090 . PMC 3514955 PMID 23042551 . ^ Tanifuji G, Onodera NT, Wheeler TJ, Dlutek M, Donaher N, Archibald JM (2011). "Complete nucleomorph genome sequence of the nonphotosynthetic alga Cryptomonas paramecium reveals a core nucleomorph gene set" . Genome Biology and Evolution . 3 : 44–54. doi :10.1093/gbe/evq082 . PMC 3017389 PMID 21147880 . ^ Douglas S, Zauner S, Fraunholz M, Beaton M, Penny S, Deng LT, Wu X, Reith M, Cavalier-Smith T, Maier UG (April 2001). "The highly reduced genome of an enslaved algal nucleus" . Nature . 410 (6832): 1091–6. Bibcode :2001Natur.410.1091D . doi :10.1038/35074092 PMID 11323671 . ^ Lane CE, van den Heuvel K, Kozera C, Curtis BA, Parsons BJ, Bowman S, Archibald JM (December 2007). "Nucleomorph genome of Hemiselmis andersenii reveals complete intron loss and compaction as a driver of protein structure and function" . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 104 (50): 19908–13. Bibcode :2007PNAS..10419908L . doi :10.1073/pnas.0707419104 PMC 2148396 PMID 18077423 . ^ Tanifuji G, Onodera NT, Brown MW, Curtis BA, Roger AJ, Ka-Shu Wong G, Melkonian M, Archibald JM (May 2014). "Nucleomorph and plastid genome sequences of the chlorarachniophyte Lotharella oceanica: convergent reductive evolution and frequent recombination in nucleomorph-bearing algae" . BMC Genomics . 15 (1): 374. doi :10.1186/1471-2164-15-374 PMC 4035089 PMID 24885563 . ^ Nowack EC, Melkonian M , Glöckner G (March 2008). "Chromatophore genome sequence of Paulinella sheds light on acquisition of photosynthesis by eukaryotes" . Current Biology . 18 (6): 410–8. doi :10.1016/j.cub.2008.02.051 PMID 18356055 . External links [ edit ] ^ Dennis, R. D. (January 1976). "Insect morphogenetic hormones and developmental mechanisms in the nematode, Nematospiroides dubius". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. A, Comparative Physiology . 53 (1): 53–56. doi :10.1016/s0300-9629(76)80009-6 . ISSN 0300-9629 . PMID 184 . 



 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch