Foreign relations of Italy
| Part of the Politics series |
 |
|---|
| |
The foreign relations of the Italian Republic are the Italian government's external relations with the outside world. Located in Europe, Italy has been considered a major Western power since its unification in 1860.[1] Its main allies are the NATO countries and the EU states, two entities of which Italy is a founding member. Italy was admitted to the United Nations in 1955, and it is a member and a strong supporter of a wide number of international organisations, such as the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and World Trade Organization (GATT and WTO), the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), the Council of Europe, and the Central European Initiative.
Its turns in the rotating presidency of international organisations include the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the G7 and the EU Council. Italy is also a recurrent non-permanent member of the UN Security Council. Italy is an important actor in the Mediterranean region and has close relations with the Romance-speaking countries in Europe and Latin America. Although it is a secular state,[2] Rome hosts the Pope and the headquarters of the Catholic Church, which operates a large diplomatic system of its own. Italy is currently commanding various multinational forces and has significant troops deployed all over the world for peacekeeping missions, and for combating organized crime, illegal drug trade, human trafficking, piracy and terrorism.[3]
History[edit]
National unification[edit]

The Risorgimento was the era from 1829 to 1871 that saw the emergence of a national consciousness. The Northern Italy monarchy of the House of Savoy in the Kingdom of Sardinia, whose government was led by Camillo Benso, Count of Cavour, had ambitions of establishing a united Italian state. In the context of the 1848 liberal revolutions that swept through Europe, an unsuccessful first war of independence was declared on Austria. In 1855, the Kingdom of Sardinia became an ally of Britain and France in the Crimean War, giving Cavour's diplomacy legitimacy in the eyes of the great powers.[4][5] The Kingdom of Sardinia again attacked the Austrian Empire in the Second Italian War of Independence of 1859, with the aid of France, resulting in liberating Lombardy. On the basis of the Plombières Agreement, the Kingdom of Sardinia ceded Savoy and Nice to France, an event that caused the Niçard exodus, that was the emigration of a quarter of the Niçard Italians to Italy,[6] and the Niçard Vespers.
In 1860–1861, Giuseppe Garibaldi led the drive for unification in Naples and Sicily conquering the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies (the Expedition of the Thousand),[7] while the House of Savoy troops occupied the central territories of the Italian peninsula, except Rome and part of Papal States. This allowed the Sardinian government to declare a united Italian kingdom on 17 March 1861.[8] In 1866, Italy allied with Prussia during the Austro-Prussian War, waging the Third Italian War of Independence which allowed Italy to annex Venetia. Finally, in 1870, as France abandoned its garrisons in Rome during the disastrous Franco-Prussian War to keep the large Prussian Army at bay, the Italians rushed to fill the power gap by taking over the Papal States. Italian unification was completed and shortly afterwards Italy's capital was moved to Rome. Later Italy formed the Triple Alliance (1882) with Germany and Austria.
World War I[edit]
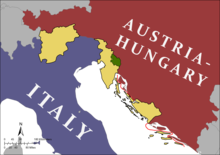
Italy defeated the Ottoman Empire in 1911–1912.[9] By 1915, Italy had acquired in Africa a colony on the Red Sea coast (Eritrea), a large protectorate in Somalia and administrative authority in formerly Turkish Libya. Outside of Africa, Italy possessed a small concession in Tientsin in China (following the Boxer Rebellion) and the Dodecanese Islands off the coast of Turkey.
Austria took the offensive against the terms of the alliance and Italy decided to take part in World War I as a principal allied power with France and Great Britain. Two leaders, Prime Minister Antonio Salandra and Foreign Minister Sidney Sonnino made the decisions; their primary motivation was seizure of territory from Austria, as secretly promised by Britain and France in the Treaty of London of 1915. Also, Italy occupied southern Albania and established a protectorate over Albania, which remained in place until 1920.[10]
The Allies defeated the Austrian Empire in 1918 and Italy became one of the main winners of the war. At the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, Prime Minister Vittorio Emanuele Orlando focused almost exclusively on territorial gains, but he got far less than he wanted, and Italians were bitterly resentful when they were denied control of the city of Fiume. The conference, under the control of Britain, France and the United States refused to assign Dalmatia and Albania to Italy as had been promised in the Treaty of London. Britain, France and Japan divided the German overseas colonies into mandates of their own, excluding Italy. Italy also gained no territory from the breakup of the Ottoman Empire.
Italy did not receive other territories promised by the Treaty of London, so this outcome was denounced as a Mutilated victory. The rhetoric of Mutilated victory was adopted by Benito Mussolini and led to the rise of Italian fascism, becoming a key point in the propaganda of Fascist Italy. Historians regard Mutilated victory as a "political myth", used by fascists to fuel Italian imperialism and obscure the successes of liberal Italy in the aftermath of World War I.[11] Italy also gained a permanent seat in the League of Nations's executive council.
Fascism and World War II[edit]
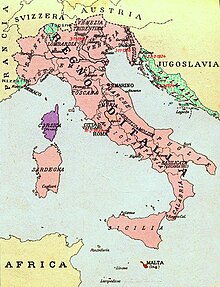
The Fascist government that came to power with Benito Mussolini in 1922 sought to increase the size of the Italian empire and to satisfy the claims of Italian irredentists. Italian Fascism is based upon Italian nationalism and imperialism, and in particular seeks to complete what it considers as the incomplete project of the unification of Italy by incorporating Italia Irredenta (unredeemed Italy) into the state of Italy.[12][13] To the east of Italy, the Fascists claimed that Dalmatia was a land of Italian culture whose Italians, including those of Italianized South Slavic descent, had been driven out of Dalmatia and into exile in Italy, and supported the return of Italians of Dalmatian heritage.[14] Mussolini identified Dalmatia as having strong Italian cultural roots for centuries, similarly to Istria, via the Roman Empire and the Republic of Venice.[15] To the south of Italy, the Fascists claimed Malta, which belonged to the United Kingdom, and Corfu, which instead belonged to Greece; to the north claimed Italian Switzerland, while to the west claimed Corsica, Nice, and Savoy, which belonged to France.[16][17] The Fascist regime produced literature on Corsica that presented evidence of the island's italianità.[18] The Fascist regime produced literature on Nice that justified that Nice was an Italian land based on historic, ethnic, and linguistic grounds.[18]

Mussolini promised to bring Italy back as a great power in Europe, building a "New Roman Empire"[19] and holding power over the Mediterranean Sea. In propaganda, Fascists used the ancient Roman motto "Mare Nostrum" (Latin for "Our Sea") to describe the Mediterranean. For this reason the Fascist regime engaged in interventionist foreign policy. In 1923, the Greek island of Corfu was briefly occupied by Italy, after the assassination of General Tellini in Greek territory. In 1925, Italy forced Albania to become a de facto protectorate. In 1935, Mussolini invaded Ethiopia and founded Italian East Africa, resulting in an international alienation and leading to Italy's withdrawal from the League of Nations; Italy allied with Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan and strongly supported Francisco Franco in the Spanish Civil War. In 1939, Italy formally annexed Albania. Italy entered World War II on 10 June 1940. The Italians initially advanced in British Somaliland, Egypt, the Balkans (establishing the Governorate of Dalmatia and Montenegro, the Province of Ljubljana, and the puppet states Independent State of Croatia and Hellenic State), and eastern fronts. They were, however, subsequently defeated on the Eastern Front as well as in the East African campaign and the North African campaign, losing as a result their territories in Africa and in the Balkans.
An Allied invasion of Sicily began in July 1943, leading to the collapse of the Fascist regime and the fall of Mussolini on 25 July. In the north, the Germans set up the Italian Social Republic (RSI), a Nazi puppet state with Mussolini installed as leader after he was rescued by German paratroopers. Some Italian troops in the south were organised into the Italian Co-belligerent Army, which fought alongside the Allies for the rest of the war, while other Italian troops, loyal to Mussolini and his RSI, continued to fight alongside the Germans in the National Republican Army. Also, the post-armistice period saw the rise of a large anti-fascist resistance movement, the Resistenza.[20] As result, the country descended into civil war;[21][22] the Italian resistance fought a guerrilla war against the Nazi German occupiers and Italian Fascist forces,[20] while clashes between the Fascist RSI Army and the Royalist Italian Co-Belligerent Army were rare.[23] In late April 1945, with total defeat looming, Mussolini attempted to escape north,[24] but was captured and summarily executed near Lake Como by Italian partisans. His body was then taken to Milan, where it was hung upside down at a service station for public viewing and to provide confirmation of his demise.[25] Hostilities ended on 29 April 1945, when the German forces in Italy surrendered.
Republican era[edit]

Italy became a republic after the 1946 Italian institutional referendum[26] held on 2 June 1946, a day celebrated since as Festa della Repubblica. This was the first time that Italian women voted at the national level, and the second time overall considering the local elections that were held a few months earlier in some cities.[27][28] Under the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947, Istria, Kvarner, most of the Julian March as well as the Dalmatian city of Zara was annexed by Yugoslavia causing the Istrian-Dalmatian exodus, which led to the emigration of between 230,000 and 350,000 of local ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians), the others being ethnic Slovenians, ethnic Croatians, and ethnic Istro-Romanians, choosing to maintain Italian citizenship.[29] Later, the Free Territory of Trieste was divided between the two states. Italy also lost all of its colonial possessions, formally ending the Italian Empire. In 1950, Italian Somaliland was made a United Nations Trust Territory under Italian administration until 1 July 1960. The Italian border that applies today has existed since 1975, when Trieste was formally re-annexed to Italy.
in 1949 Italy became a member of NATO. The Marshall Plan helped to revive the Italian economy which, until the late 1960s, enjoyed a period of sustained economic growth commonly called the "Economic Miracle". In the 1950s, Italy became one of the six founding countries of the European Communities, following the 1952 establishment of the European Coal and Steel Community, and subsequent 1958 creations of the European Economic Community and European Atomic Energy Community. In 1993, the former two of these were incorporated into the European Union.
Diplomatic relations[edit]
List of countries which Italy maintains diplomatic relations with:
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| # | Country | Date |
| 1 | 24 February 1851[30] | |
| 2 | 22 March 1854[31] | |
| 3 | 5 May 1856[30] | |
| 4 | 5 May 1856[32] | |
| 5 | 5 May 1856[33] | |
| 6 | 25 September 1856[34] | |
| 7 | 25 September 1856[33] | |
| 8 | 13 April 1859[35] | |
| 9 | 15 September 1859[36] | |
| 10 | 6 November 1859[37] | |
| 11 | 23 December 1859[38] | |
| 12 | 12 February 1860[33] | |
| 13 | 24 October 1860[34] | |
| 14 | 11 April 1861[39] | |
| 15 | 16 June 1861[36] | |
| 16 | 10 August 1861[35] | |
| 17 | 2 September 1861[40] | |
| 18 | 25 February 1864[37] | |
| 19 | 25 February 1864[37] | |
| 20 | 25 February 1864[35] | |
| 21 | 25 February 1864[35] | |
| 22 | 25 February 1864[41] | |
| 23 | 25 February 1864[36] | |
| 24 | 25 February 1864[36] | |
| 25 | 25 February 1864[36] | |
| 26 | 25 February 1864[34] | |
| 27 | 13 March 1864[37] | |
| 28 | 13 March 1864[33] | |
| 29 | 28 December 1864[36] | |
| 30 | 25 August 1866[42] | |
| 31 | 27 January 1867[30] | |
| 32 | 21 July 1867[34] | |
| 33 | 3 October 1868[43] | |
| 34 | 20 April 1871[44] | |
| 35 | 25 April 1875[45] | |
| 36 | 18 January 1879[46] | |
| 37 | 25 July 1879[47] | |
| 38 | 26 December 1879[48] | |
| 39 | 18 February 1886[49] | |
| 40 | 7 February 1891[50] | |
| 41 | 24 June 1897[51] | |
| 42 | 24 February 1898[52] | |
| 43 | 4 February 1903[53] | |
| 44 | 15 January 1904[54] | |
| 45 | 22 March 1906[55] | |
| 46 | 21 February 1914[56] | |
| 47 | 16 October 1918[57] | |
| 48 | 27 February 1919[58] | |
| 49 | 6 September 1919[59] | |
| 50 | 21 November 1920[60] | |
| 51 | 3 June 1921[61] | |
| 52 | 30 April 1922[62] | |
| 53 | 2 September 1926[63] | |
| — | 24 June 1929[64] | |
| 54 | 31 October 1929[60] | |
| 55 | 10 February 1932[65] | |
| 56 | 27 September 1937[66] | |
| 57 | 15 August 1945[67] | |
| 58 | 3 November 1946[68] | |
| 59 | 20 November 1946[69] | |
| 60 | 13 August 1947[70] | |
| 61 | 27 September 1947[71] | |
| 62 | 25 March 1948[72] | |
| 63 | 7 April 1948[73] | |
| 64 | 13 July 1949[74] | |
| 65 | 24 November 1949[75] | |
| 66 | 29 December 1949[76] | |
| 67 | 7 March 1950[77] | |
| 68 | 18 April 1950[78] | |
| 69 | 22 August 1950[79] | |
| 70 | 24 November 1950[80] | |
| 71 | 27 July 1951[81] | |
| 72 | 5 October 1951[82] | |
| 73 | 21 February 1952[83] | |
| — | 12 June 1956[84] | |
| 74 | 20 June 1956[85] | |
| 75 | 1 October 1956[86] | |
| 76 | 31 October 1956[87] | |
| 77 | 24 November 1956[88] | |
| 78 | 31 August 1957[89] | |
| 79 | 31 August 1959[90] | |
| 80 | 5 December 1959[91] | |
| 81 | 1 July 1960[92] | |
| 82 | 21 July 1960[93] | |
| 83 | 1 March 1961[94] | |
| 84 | 18 June 1961[95] | |
| 85 | 12 September 1961[96] | |
| 86 | 23 September 1961[97] | |
| 87 | 30 November 1961[98] | |
| 88 | 9 December 1961[99] | |
| 89 | 1961[100] | |
| 90 | 1961[101] | |
| 91 | 28 February 1962[102] | |
| 92 | 27 April 1962[103] | |
| 93 | 16 June 1962[104] | |
| 94 | 1 October 1962[105] | |
| 95 | 1962[106] | |
| 96 | 6 February 1963[107] | |
| 97 | 14 February 1963[108] | |
| 98 | 25 February 1963[109] | |
| 99 | 4 January 1964[110] | |
| 100 | 15 January 1964[111] | |
| 101 | 13 February 1964[112] | |
| 102 | June 1964[113] | |
| 103 | 5 July 1964[114] | |
| 104 | 21 September 1964[115] | |
| 105 | 8 November 1964[116] | |
| 106 | 20 April 1965[117] | |
| 107 | 5 May 1965[118] | |
| 108 | 28 October 1965[119] | |
| 109 | 30 October 1965[120] | |
| 110 | 7 December 1965[121] | |
| 111 | 10 May 1966[122] | |
| 112 | 20 September 1966[123] | |
| 113 | 1966[124] | |
| 114 | 12 April 1967[125] | |
| 115 | 1967[126] | |
| 116 | 8 April 1970[127] | |
| 117 | 29 June 1970[128] | |
| 118 | 6 November 1970[129] | |
| 119 | 1970[130] | |
| 120 | 1971[131] | |
| 121 | 26 January 1972[132] | |
| 122 | 13 October 1972[133] | |
| 123 | 18 January 1973[134] | |
| 124 | 15 February 1973[135] | |
| 125 | 23 March 1973[136] | |
| 126 | 16 December 1973[137] | |
| 127 | 25 June 1975[138] | |
| 128 | 4 June 1976[139] | |
| 129 | 29 June 1976[140] | |
| 130 | 1 November 1976[141] | |
| 131 | 18 November 1976[142] | |
| 132 | 23 August 1977[143] | |
| 133 | 24 November 1977[144] | |
| 134 | 7 July 1978[145] | |
| 135 | 1978[146] | |
| 136 | July 1979[147] | |
| 137 | 1979[148] | |
| 138 | 18 April 1980[149] | |
| 139 | 22 October 1980[150] | |
| 140 | 26 November 1981[151] | |
| 141 | 1 October 1982[152] | |
| 142 | 30 October 1982[153] | |
| 143 | 15 December 1982[154] | |
| 144 | 20 August 1985[155] | |
| 145 | 1 March 1987[156] | |
| 146 | 25 May 1987[157] | |
| 147 | 1 August 1988[158] | |
| 148 | 24 December 1988[158] | |
| 149 | 2 November 1989[159] | |
| 150 | 20 April 1990[160] | |
| 151 | 30 August 1991[161] | |
| 152 | 30 August 1991[162] | |
| 153 | 31 August 1991[163] | |
| 154 | 17 January 1992[164] | |
| 155 | 17 January 1992[165] | |
| 156 | 21 February 1992[166] | |
| 157 | 29 January 1992[167] | |
| 158 | 17 March 1992[168] | |
| 159 | 24 March 1992[169] | |
| 160 | 24 March 1992[170] | |
| 161 | 13 April 1992[171] | |
| 162 | 8 May 1992[172] | |
| 163 | 11 May 1992[173] | |
| 164 | 19 May 1992[174] | |
| 165 | 9 June 1992[175] | |
| 166 | 21 August 1992[176] | |
| 167 | 27 November 1992[177] | |
| 168 | 1 January 1993[178] | |
| 169 | 5 January 1993[158] | |
| 170 | 1 February 1993[179] | |
| 171 | 24 May 1993[180] | |
| 172 | 24 September 1993[145] | |
| 173 | 16 December 1993[181] | |
| 174 | 1 February 1995[182] | |
| 175 | 7 December 1995[158] | |
| 176 | 11 December 1995[158] | |
| 177 | 7 January 1996[158] | |
| 178 | 27 February 1997[183] | |
| 179 | 22 January 1998[158] | |
| 180 | 22 January 1998[158] | |
| 181 | 4 January 2000[184] | |
| 182 | 22 March 2002[185] | |
| — | 9 October 2003[186] | |
| 183 | 24 November 2003[187] | |
| 184 | 14 June 2006[188] | |
| — | 15 May 2008[189] | |
| 185 | 23 May 2012[190] | |
| — | 12 September 2015[191] | |
| 186 | Unknown | |
| 187 | Unknown | |
| 188 | Unknown | |
| 189 | Unknown | |
| 190 | Unknown | |
| 191 | Unknown | |
Bilateral relations by country[edit]
Africa[edit]
| Country | Beginning of formal relations | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 October 1962 | See Algeria–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 October 1962.[192]
| |
| 4 June 1976[193] | See Angola–Italy relations
| |
| 16 June 1962 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 16 June 1962 when Mr. Renzo Luigi Romanelli, the first Italian Ambassador to Upper Volta, has presented his letters of credence to President Maurice Yameogo.[104] | |
| 1 November 1976 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 November 1976[196] | |
| 21 July 1960 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 July 1960 when accredited first Ambassador of Italy to Congo (Leopoldville) Mr. Pietro Franca[93]
| |
| 30 April 1922 | See Egypt–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 30 April 1922 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Egypt Mr Lazzaro Negrotto Cambiaso.[201] Relations between both countries were established during the period of the Roman Empire. However, in World War II, relations were strained as Italy invaded Egypt. However, after the war, relations were re-established and are close. Egypt has representations in Rome and Milan, while Italy has representations in Cairo and Alexandria, also the two nations are members of the Union for the Mediterranean. Relations deteriorated after the abduction and killing of Italian student Giulio Regeni. Egypt has been accused by Italian authorities and public opinion of lacking of transparence.
| |
| 24 May 1993 | See Eritrea–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 May 1993.[180]
| |
| 24 June 1897 | See Ethiopia–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 June 1897.[51]
| |
| 1963 | See Italy–Kenya relations | |
| 21 February 1952 | See Italy–Libya relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 February 1952 when has been accredited first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Libya Mr. Mario Conti.[202]
| |
| 25 February 1963 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1963 when first Ambassador of Mauritania to Italy (resident in Paris) Mr. Bakar Ould Ahmedou presented his credentials to President Antonio Segni.[109] | |
| 1 October 1956 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 October 1956[86] | |
| ||
| 5 May 1965 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 5 May 1965 when Ambassador of Rwanda to Italy Mr. Emanuele Kaberuka presented his credentials to President Giuseppe Saragat.[118] | |
| 1 March 1961 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 March 1961.[94] | |
| 1 July 1960 | See Italy–Somalia relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 July 1960.[92]
| |
| 31 October 1929 | See Italy–South Africa relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 31 October 1929 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Union of South Africa Natale Labia.[60]
| |
| 23 May 2012 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 23 May 2012.[190] | |
| 31 October 1956 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 31 October 1956 when Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Sudan to Italy Mr. Omer Abedel Hanid Adeel has presented his credentials to President Giovanni Gronchi.[87] | |
| 9 December 1961 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 9 December 1961 when open Embassy of Italy in Dar es Salaam with accredited Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Tanganyika Mr. Luciano Falco[99] | |
| 20 June 1956 | See Italy–Tunisia relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 20 June 1956.[85]
| |
| 5 July 1964 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 5 July 1964[114] | |
| 18 April 1980 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 18 April 1980.[211] |
Americas[edit]
| Country | Beginning of formal relations | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 5 May 1856 | See Argentina–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 5 May 1856 when has been accredited first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Argentina Marcello Cerruti.[30]
| |
| 1 October 1982 |
| |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Bolivia Antonio Maria Migliorati.[37]
| |
| 6 November 1859 | See Brazil–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 6 November 1859 when has been appointed first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Brazil Gabriele Galateri di Genola.[37]
| |
| 13 August 1947 | See Canada–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 13 August 1947 when has been established Legation of Canada in Italy.[226]
| |
| 25 February 1864 | See Chile–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Chile Antonio Maria Migliorati.[37]
| |
| 13 March 1864 | See Colombia–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Colombia Antonio Maria Migliorati.[37]
| |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Ecuador Antonio Maria Migliorati.[35]
| |
| 4 February 1903 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 4 February 1903.[53]
| |
| 24 February 1898 | See Dominican Republic-Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 February 1898 when has been accredited Minister Resident of Italy to Dominican Republic Chicco Enrico.[239]
| |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Ecuador Antonio Maria Migliorati.[35] | |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to El Salvador Antonio Maria Migliorati.[41]
| |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Guatemala Antonio Maria Migliorati.[36] | |
| 24 February 1898 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 February 1898 when has been accredited Minister Resident of Italy to Haiti Chicco Enrico.[241] | |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Honduras Antonio Maria Migliorati.[36] | |
| 14 February 1963 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 14 February 1963.[108] | |
| 28 December 1864 | See Italy–Mexico relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 28 December 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Mexico Vittorio Sallier de la Tour.[36]
| |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Nicaragua Antonio Maria Migliorati.[36] | |
| 15 January 1904 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 January 1904[245] | |
| 21 July 1867 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 July 1867 when has been appointed first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Paraguay Luigi Joannini Ceva di San Michele.[34]
| |
| 25 February 1864 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 February 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Peru Giovanni Antonio Migliorati.[34]
| |
| 4 January 1964 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 4 January 1964.[110] | |
| 11 April 1861 | See Italy–United States relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 11 April 1861.[250] The United States enjoys a peculiar and friendly relation with Italy, as the latter, defeated in WWII, has been a secret battlefield of the Cold War. Italy and the US are NATO allies and cooperate in the United Nations, in various regional organizations, and bilaterally. Italy has worked closely with the United States and with other nations on such issues as NATO and UN operations as well as with assistance to Russia and the New Independent States; the Middle East peace process; multilateral talks. Under longstanding bilateral agreements flowing from NATO membership, Italy hosts important U.S. military forces at Vicenza and Pisa (army); Aviano (air force); and Sigonella, Gaeta, and Naples- home port for the U.S. Navy Sixth Fleet. The United States still has about 16,000 military personnel stationed in Italy. The NATO War College is situated at Cecchignola, a neighborhood of Rome.
| |
| 5 May 1856 | See Italy–Uruguay relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 5 May 1856 when has been appointed first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Uruguay Marcello Cerruti.[33]
| |
| 13 March 1864 | See Italy–Venezuela relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 13 March 1864 when has been appointed first Minister Resident of Italy to Venezuela Antonio Maria Migliorati.[33]
|
Asia[edit]
| Country | Beginning of formal relations | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 3 June 1921 | See Afghanistan–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 June 1921.[61]
| |
| 17 March 1992 | See Armenia–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 17 March 1992.[257]
| |
| 8 May 1992 | See Azerbaijan–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 8 May 1992.[172] | |
| 16 December 1973 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 16 December 1973.[137] | |
| 18 January 1973 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 18 January 1973 when first Ambassador of Bangladesh to Italy Mr.Ikbal Athar presented his credentials to President Giovanni Leone.[134] Relations between two countries have been wonderful. Bangladesh is a huge import market for Italy. Italy has an embassy in Dhaka. Bangladesh has an embassy in Rome. | |
| 6 November 1970 | See People's Republic of China – Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 6 November 1970.[129] In 2005, Italy and the People's Republic of China have celebrated the 35th anniversary of the establishment of diplomatic relations between the two nations. However, China's massive exports of textile and footwear into Italy are said to be a rising concern to Italy's economy and productivity.[262] | |
| 11 May 1992 | See Georgia–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 11 May 1992.[173] | |
| 25 March 1948 | See India–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 March 1948.[72]
In 2012, relations deteriorated following the Enrica Lexie Case
| |
| 25 June 1950 | See Indonesia–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 June 1950.[4]
| |
| 18 February 1886 | See Iran–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 18 February 1886 when has been appointed first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Persia Alessandro De Rege Di Donato.[49] In 2005, Italy was the third largest trading partner of Iran with 7.5% of all exports to Iran.[271] Italy was the top trading partner of Iran in the European Union in early 2006.[272] Commercial exchanges hit 6 billion euros in 2008.[273] | |
| See Iraq–Italy relations Iraq has an embassy in Rome and Italy has an embassy in Baghdad and a consulate-general in Basra. | ||
| 13 July 1949 | See Israel–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 13 July 1949 when has been accredited first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Israel to Italy Mr. Shlomo Ginossar.[274]
| |
| 25 August 1866 | See Italy–Japan relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 August 1866.[42]
| |
| 7 March 1950 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 7 March 1950 when has been accredited first Chargé d'Affaires of Jordan to Italy Mr. Edmond Roch Bey.[282] | |
| 21 August 1992 | See Italy-Kazakhstan relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 August 1992.[176]
| |
| 24 March 1992 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 March 1992.[169] | |
| 20 November 1946 | See Italy–Lebanon relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 20 November 1946 when has been accredited first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Lebanon Mr. Adolfo Alessandrini.[284]
| |
| 1966 | Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1966.[288] | |
| 31 August 1957 | See Italy–Malaysia relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 31 August 1957.[89]
| |
| 24 November 1950 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 November 1950.[80] | |
| 31 August 1959 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 31 August 1959.[90] | |
| 4 January 2000[291] | See Italy–North Korea relations | |
| 26 January 1972 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 26 January 1972[132] | |
| 7 April 1948 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 7 April 1948.[292]
| |
| 3 November 1946 | See Italy–Philippines relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 November 1946 when has been accredited first interim Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Philippines Mr. Vittorio Strigari.[295]
| |
| 15 February 1973 | See Italy–Qatar relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 February 1973[135] | |
| 10 February 1932 | See Italy–Saudi Arabia relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 10 February 1932.[65] | |
| 28 October 1965 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 28 October 1965.[297] | |
| 24 November 1956 | See Italy–South Korea relations The establishment of diplomatic relations between the kingdom of Italy and the kingdom of Korea began on 26 June 1884 and the Re establishment of Diplomatic Relations between the Italian republic the Republic of Korea was on November 24, 1956.[88]
| |
| 18 April 1950 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 18 April 1950.[78] Italy and Sri Lanka maintain a strong relationship dated back from 1st century.[304] | |
| 19 May 1992 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 19 May 1992.[174] | |
| 3 October 1868 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 October 1868.[43]
| |
| 24 November 2003 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 November 2003.[187] | |
| 25 September 1856 | See Italy–Turkey relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 September 1856 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Turkey Giacomo Durando.[33]
| |
| 9 June 1992 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 9 June 1992.[175] | |
| ||
| 24 March 1992 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 March 1992.[170] | |
| 23 March 1973 | See Italy–Vietnam relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 23 March 1973.[136]
|
Europe[edit]
| Country | Beginning of formal relations | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 21 February 1914 | See Albania–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 February 1914 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Albania Carlo Aliotti.[56] The Kingdom of Italy supported Albanian Declaration of Independence in 1912.
| |
| 1 February 1995 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 February 1995.[313] Italy is represented in Andorra through its embassy in Madrid (Spain) and an honorary consulate in Andorra La Vella. | |
| 27 January 1867 | See Austria–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 27 January 1867 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Austro-Hungary Giulio Camillo De Barral De Monteauvrard.[30]
| |
| 13 April 1992 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 13 April 1992.[171] | |
| 24 February 1851 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 February 1851 when has been appointed Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Belgium Alberto Lupi Di Montalto.[30]
| |
| 1 February 1993 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 February 1993.[179]
| |
| 25 July 1879 | See Bulgaria–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 July 1879.[322][47]
| |
| 17 January 1992 | See Croatia–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 17 January 1992.[164]
| |
| 12 September 1961 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 12 September 1961 when the first Ambassador of Italy to Cyprus, Pietro Solari presentation of credentials.[326]
| |
| 24 October 1918 | See Czech Republic–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 October 1918.[328]
| |
| 23 December 1859 | See Denmark–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 23 December 1859 when has been appointed first interim chargé d'affaires Giovanni Antonio Migliorati.[35]
| |
| 31 August 1991 | Both countries re-established diplomatic relations on 31 August 1991.[163]
| |
| 6 September 1919 | See Finland–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 6 September 1919.[59]
| |
| 25 July 1861 | See France–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 July 1861 when has been appointed Envoy Extraordinary and minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to France Costantino Nigra.[35]
| |
| 20 April 1871 | See Germany–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 20 April 1871 when has been appointed first Ambassador Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Germany Edoardo De Launay.[44]
| |
| 16 June 1861 | See Greece–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 16 June 1861 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Greece Terenzio Mamiani della Rovere.[36]
| |
| 24 June 1929 | See Holy See – Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 June 1929.[338] Due to the size of the Vatican City State, embassies accredited to the Holy See are based on Italian territory. Treaties signed between Italy and the Vatican City State permit such embassages. The Embassy of Italy to the Holy See is unique amongst foreign embassages in that it is the only embassy based on its home territory. The Holy See maintains formal diplomatic relations with 176 sovereign states, the European Union, and the Order of Malta; 69 of the diplomatic missions accredited to the Holy See are situated in Rome, though those countries than have two embassies in the same city, since, by agreement between the Holy See and Italy, the same person cannot be accredited simultaneously to both. This is shown clearly by the fact that Italy recognizes the People's Republic of China, and as such, the Chinese Embassy is in Rome. However, the Vatican City State recognizes the Taiwan, and as such, Taiwan's embassy to the Holy See is also in Rome. As Italy was the first country to recognize the Holy See as a sovereign nation, their embassy was the first one established. | |
| 21 November 1920 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 November 1920 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Hungary Gaetano Caracciolo Di Castagneto.[60]
| |
| 15 August 1945 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 August 1945.[67]
| |
| 27 September 1937 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 27 September 1937 when has been accredited first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Ireland Mr. Romano Lodi Fe.[344]
| |
| 15 May 2008 | See Italy–Kosovo relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 May 2008.[189] Italy recognized Kosovo on 21 February 2008.[347][348] Italy has an embassy in Pristina since 15 May 2008.[349] Kosovo will open an embassy in Rome.
| |
| 30 August 1991 | Both countries re-established diplomatic relations on 30 August 1991.[161]
| |
| 11 December 1995 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 11 December 1995 when has been appointed Ambassador of Italy to Liechtenstein with residence in Berne Mr. Arduino Fornara.[158]
| |
| 30 August 1991 | Both countries re-established diplomatic relations on 30 August 1991.[162]
| |
| 7 February 1891 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 7 February 1891.[50]
| |
| 21 September 1964 | See Italy–Malta relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 September 1964.[356]
| |
| 21 February 1992 | See Italy-Moldova relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 February 1992.[166]
| |
| 25 April 1875 | See Italy-Monaco relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 April 1875.[357]
| |
| 14 June 2006 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 14 June 2006.[188]
| |
| 15 September 1859 | See Italy–Netherlands relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 September 1859 when has been appointed first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to the Netherlands Andrea Taliacarne.[36]
| |
| 16 December 1993 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 16 December 1993.[181]
| |
| 22 March 1906 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 22 March 1906.[363] | |
| 27 February 1919 | See Italy–Poland relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 27 February 1919.[58]
| |
| 24 October 1860 | See Italy–Portugal relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 October 1860 when has been appointed first Chargé d'Affaires of Italy to Portugal Minerva Domenico Pes Di San Vittorio.[34] | |
| 26 December 1879 | See Italy–Romania relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 26 December 1879.[367]
| |
| 25 September 1856 | See Italy–Russia relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 25 September 1856 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Russia Francesco Maria Sauli.[34] Russia has an embassy in Rome and consulates in Genoa, Milan and Palermo, and Italy has an embassy in Moscow, a consulate in Saint Petersburg, two consulte generals (in Ekaterinburg and Kaliningrad), and two embassy branches in (Samara and Volgograd). Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. In 2006, Russia and Italy have signed a protocol of cooperation for fighting crime and defending civil liberties. The relationship between Russia and Italy goes back a long way. Already in the 1960s, Italy's FIAT built a car-assembling plant in the Soviet city of Tolyatti (a city named after the Italian Communist Party's secretary Palmiro Togliatti). In the past, Russians visited Italy in great numbers. Many Russian students came to Italy each year to study in Italian universities.[372] The Silvio Berlusconi Government (2001–2006) strengthened Italy's ties with Russia, due to his personal friendship with President Vladimir Putin. Cooperation extended also to the aviation sector, between Italy's Alenia and Russia's Sukhoi. Finally, for a long time Italy had the largest communist party in the Western world, with over 2 million members. .[373] Good relations ended in 2022 after the invasion of Russia in Ukraine. | |
See Italy–San Marino relations
| ||
| 18 January 1879 | See Italy–Serbia relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 18 January 1879.[46]
| |
| 1 January 1993 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 January 1993.[178]
| |
| 17 January 1992 | See Italy–Slovenia relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 17 January 1992.[165]
| |
| 5 May 1856 | See Italy–Spain relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 5 May 1856 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Spain barone Romualdo Tecco.[32] Both countries established diplomatic relations after the unification of Italy. Relations between Italy Spain have remained strong and affable for centuries owing to various political, cultural, and historical connections between the two nations.
| |
| 23 December 1859 | See Italy–Sweden relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 23 December 1859 when has been appointed first interim Chargé d'Affaires Giov. Antonio Migliorati.[38]
| |
| 12 February 1860 | See Italy–Switzerland relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 12 February 1860 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Switzerland Alessandro Jocteau.[33]
| |
| 29 January 1992 | See Italy–Ukraine relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 29 January 1992.[167]
| |
| 13 April 1859 | See Italy–United Kingdom relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 13 April 1859 when has been appointed first Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Italy to Great Britain Roberto Taparelli d'Azeglio.[35] Although enemies during World War II, the United Kingdom and Italy have generally enjoyed a warm and friendly relationship throughout history. Both states embrace membership of the NATO, OSCE and the G7[380] Between 4 and 5 million British tourists visit Italy every year, while 1 million Italian tourists visit the UK.[381] There are about 30,000 British nationals living in Italy (see British in Italy), and 200,000 Italians living in the UK.[382]
|
Oceania[edit]
| Country | Beginning of formal relations | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 4 February 1949 | See Australia–Italy relations Both countries established diplomatic relations on 4 February 1949.[6]
| |
| 13 October 1972 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 13 October 1972.[387] | |
| 22 August 1950 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 22 August 1950.[2]
| |
International institutions[edit]
Italy is part of the UN, EU, NATO, the OECD, the OSCE, the DAC, the WTO, the G7, the G20, the Union for the Mediterranean, the Latin Union, the Council of Europe, the Central European Initiative, the ASEM, the MEF, the ISA, the Uniting for Consensus and several Contact Groups.
See also[edit]
- Diplomatic history of World War II#Italy
- International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919)
- List of diplomatic missions in Italy
- List of diplomatic missions of Italy
- Treaty of Osimo, 1975 with Yugoslavia
- Treaty of Rapallo, 1920
- Visa requirements for Italian citizens
- List of international trips made by prime ministers of Italy
References[edit]
- ^ française, La Documentation. "L'Italie : un destin européen". www.ladocumentationfrancaise.fr.
- ^ a b Articles 3, 7, 8, 19, 20 of the Constitution of Italy; Constitutional Court's Decision n. 203/1989
- ^ (in Italian) Documento programmatico pluriennale per la Difesa per il triennio 2014-2016. Italian Ministry of Defence, August 2014.
- ^ a b Enrico Dal Lago, "Lincoln, Cavour, and National Unification: American Republicanism and Italian Liberal Nationalism in Comparative Perspective." The Journal of the Civil War Era 3#1 (2013): 85–113.
- ^ William L. Langer, ed., An Encyclopedia of World Cup History. 4th ed. 1968. pp 704–7.
- ^ a b ""Un nizzardo su quattro prese la via dell'esilio" in seguito all'unità d'Italia, dice lo scrittore Casalino Pierluigi" (in Italian). 28 August 2017. Retrieved 14 May 2021.
- ^ Mack Smith, Denis (1997). Modern Italy; A Political History. Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-10895-6
- ^ "Everything you need to know about March 17th, Italy's Unity Day". 17 March 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ^ Charles Stevenson, A Box of Sand: The Italo-Ottoman War 1911–1912: The First Land, Sea and Air War (2014)
- ^ Nigel Thomas. Armies in the Balkans 1914–18. Osprey Publishing, 2001, p. 17.
- ^ G.Sabbatucci, La vittoria mutilata, in AA.VV., Miti e storia dell'Italia unita, Il Mulino, Bologna 1999, pp.101–106
- ^ Aristotle A. Kallis. Fascist ideology: territory and expansionism in Italy and Germany, 1922–1945. London, England, UK; New York City, USA: Routledge, 2000, pp. 41.
- ^ Terence Ball, Richard Bellamy. The Cambridge History of Twentieth-Century Political Thought. Pp. 133
- ^ Jozo Tomasevich. War and Revolution in Yugoslavia 1941–1945: Occupation and Collaboration. Stanford, California, USA: Stanford University Press, 2001. P. 131.
- ^ Larry Wolff. Venice And the Slavs: The Discovery of Dalmatia in the Age of Enlightenment. Stanford, California, USA: Stanford University Press, P. 355.
- ^ Aristotle A. Kallis. Fascist Ideology: Expansionism in Italy and Germany 1922–1945. London, England; UK; New York, New York, USA: Routledge, 2000. P. 118.
- ^ Mussolini Unleashed, 1939–1941: Politics and Strategy in Fascist Italy's Last War. Cambridge, England, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1986, 1999. P. 38.
- ^ a b Davide Rodogno. Fascism's European Empire: Italian Occupation during the Second World War. Cambridge, England, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2006. P. 88.
- ^ Stephen J. Lee (2008). European Dictatorships, 1918–1945. Routledge. pp. 157–58. ISBN 978-0-415-45484-1.
- ^ a b G. Bianchi, La Resistenza, in: AA.VV., Storia d'Italia, vol. 8, pp. 368-369.
- ^ Storia della guerra civile in Italia
- ^ See the books from Italian historian Giorgio Pisanò Storia della guerra civile in Italia, 1943–1945, 3 voll., Milano, FPE, 1965 and the book L'Italia della guerra civile ("Italy of civil war"), published in 1983 by the Italian writer and journalist Indro Montanelli as the fifteen volume of the Storia d'Italia ("History of Italy") by the same author.
- ^ Pavone, Claudio (1991). Una guerra civile. Saggio storico sulla moralità della Resistenza (in Italian). Torino: Bollati Boringhieri. p. 238. ISBN 88-339-0629-9.
- ^ Viganò, Marino (2001), "Un'analisi accurata della presunta fuga in Svizzera", Nuova Storia Contemporanea (in Italian), 3
- ^ "1945: Italian partisans kill Mussolini". BBC News. 28 April 1945. Archived from the original on 26 November 2011. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ Damage Foreshadows A-Bomb Test, 1946/06/06 (1946). Universal Newsreel. 1946. Retrieved 22 February 2012.
- ^ "Italia 1946: le donne al voto, dossier a cura di Mariachiara Fugazza e Silvia Cassamagnaghi" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 May 2011. Retrieved 30 May 2011.
- ^ "La prima volta in cui le donne votarono in Italia, 75 anni fa". Il Post (in Italian). 10 March 2021. Retrieved 24 August 2021.
- ^ Tobagi, Benedetta. "La Repubblica italiana | Treccani, il portale del sapere". Treccani.it. Retrieved 28 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 53. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ Mario J. Gallego, Cosme (2014). "CONTEXTO HISTÓRICO E INTERNACIONAL DE LAS RELACIONES DIPLOMÁTICAS DE LA REPÚBLICA DOMINICANA CON ESPAÑA DURANTE LA SEGUNDA MITAD DEL SIGLO XIX1" (PDF) (in Spanish): 12.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1865. p. 58. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 59. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 57. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 55. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 56. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 54. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 58. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ "All Countries". Office of the Historian. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ "L'Italia celebra i primi 150 anni - I documenti ufficiali relativi al riconoscimento dell'Italia quale nuovo Stato nazionale". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Italy (in Italian). 28 September 2011. Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- ^ a b Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1886. p. 58. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Italia-Giappone: 150 anni di amicizia costante". Ambasciata del Giappone (in Italian). Retrieved 29 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Ambassador of Italy to Thailand paid an introductory call on Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Kingdom of Thailand. 8 March 2023. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1931. p. 44.
- ^ "Rapport de Politique Extérieure 2007" (in French). p. 44. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Italy". Republic of Serbia Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Storia delle relazioni diplomatiche fra Italia e Bulgaria". Ambasciata d'Italia Sofia (in Italian). Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ "Diplomatic Relations of Romania". Ministerul Afacerilor Externe. Retrieved 28 December 2023.
- ^ a b Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1931. p. 53.
- ^ a b P. Ruppert (1892). Le grand-duché de Luxembourg dans ses relations internationales (in French). la cour V. Bück, L. Bück successeur. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ a b I trattati di commercio, dogana e navigazione fra l'Italia e gli altri stati in vigore al ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero delle Finanze. 1911. p. 360.
- ^ "I Documenti Diplomatici Italiani Terza Serie: 1896-1907 Volume II (1 maggio 1897 - 23 giugno 1898)". farnesina.ipzs.it (in Italian). p. 369. Retrieved 14 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Cuba e Italia: la certeza de que se puede hacer más juntos". misiones.cubaminrex.cu (in Spanish). 19 June 2023. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ "Relaciones diplomaticas de la Reublica de Panama" (PDF). Memoria 2011-2012 (in Spanish). p. 197. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 August 2020. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ "Norges opprettelse af diplomatiske forbindelser med fremmede stater" (PDF). regjeringen.no (in Norwegian). April 27, 1999. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1931. p. 31.
- ^ "Přehled velvyslanců Československa a ČR v Itálii - od roku 1918 do současnosti" (in Czech). Retrieved 27 September 2023.
- ^ a b "Polonia in Italia". gov.pl (in Italian). Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Finland and Italy". Finland in Italy. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d Annuario diplomatico del Regno d'Italia ... (in Italian). Italia : Ministero degli affari esteri. 1931. p. 63.
- ^ a b "Centenario relazioni diplomatiche Italia – Afghanistan". Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale Italia (in Italian). June 3, 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2023.
- ^ "Rappresentanti Diplomatici in Egitto" (PDF). Personalita Istituzionali Italiane (in Italian). p. 286. Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ "Britain's position of the Italian Treaty of Yemen 1926-1936 AD". Iraqi Academic Scientific Journals (in Arabic). 2009. Retrieved 2 January 2024.
- ^ "Diplomatic relations of the Holy See". Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- ^ a b "Italia-Arabia Saudita: guardando al futuro dopo 80 anni di relazioni". formiche (in Italian). 4 October 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ "I Documenti Diplomatici Italiani Ottava Serie: 1935-1939 Volume VII (1 luglio- 31 dicembre 1937)". farnesina.ipzs.it (in Italian). p. 887. Retrieved 29 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Iceland - Establishment of Diplomatic Relations". Government of Iceland. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ "I Documenti Diplomatici Italiani Decima Serie: 1943-1948 Volume IV (13 luglio 1946 - l o febbraio 1947)". farnesina.ipzs.it (in Italian). p. 855. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ "I DOCUMENTI DIPLOMATICI ITALIANI DECIMA SERIE: 1943-1948 VOLUME IV (13 luglio 1946 - l o febbraio 1947)". farnesina.ipzs.it (in Italian). p. 857. Retrieved 28 October 2023.
- ^ Linwood, DeLong (January 2020). "A Guide to Canadian Diplomatic Relations 1925-2019". Retrieved 26 June 2023.
- ^ "I Documenti Diplomatici Italiani Decima Serie: 1943-1948 Volume VI (31 maggio - 14 dicembre 1947)" (in Italian). p. 1021. Retrieved 1 October 2023.
- ^ a b Lorenzo Angeloni, Maria Elettra Verrone (2018). There's Something in the Air Life Stories from Italy and India. Juggernaut Books. p. xiii.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch