Proxima Centauri c
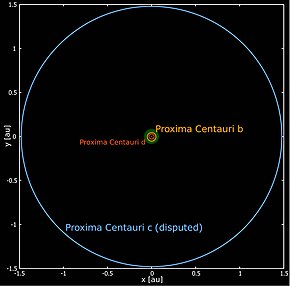 Schematic: Orbits of Proxima Centauri d, Proxima Centauri b and Proxima Centauri c around Proxima Centauri | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Damasso et al. |
| Discovery site | HARPS |
| Discovery date | January 2020 |
| Radial velocity | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 1.489±0.049 AU[2] | |
| Eccentricity | 0.04±0.01[3] |
| 1928±20 d[3] | |
| Inclination | 133±1[3] |
| 331±1[3] | |
| −4±4[3] | |
| 2456202±21[3] | |
| Semi-amplitude | 1.1±0.2[3] |
| Star | Proxima Centauri |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mass | 7±1 ME[3] |
| Temperature | 39 K (−234.2 °C; −389.5 °F)[1] |
Proxima Centauri c (also called Proxima c[2] or Alpha Centauri Cc) is a controversial[why?][4] exoplanet candidate claimed to be orbiting the red dwarf star Proxima Centauri, which is the closest star to the Sun and part of a triple star system.
Characteristics
[edit]It is located approximately 4.2 light-years (1.3 parsecs; 40 trillion kilometres; 25 trillion miles) from Earth in the constellation of Centaurus, making it, Proxima b, and Proxima d the closest known exoplanets to the Solar System.
Proxima Centauri c is a super-Earth or mini-Neptune about 7 times as massive as Earth, orbiting at roughly 1.49 AU (223 million km; 139 million mi) every 1,928 days (5.28 yr).[3] Due to its large mass and its distance from Proxima Centauri, the exoplanet is uninhabitable and too cold for liquid water to exist on the surface, with an equilibrium temperature of approximately 39 K (−234.2 °C; −389.5 °F).[1][5] The planet is not transiting its parent star from the point of view of an Earth-based observer.[6]
Discovery
[edit]The planet was first reported by Italian astrophysicist Mario Damasso and his colleagues in April 2019. Damasso's team had noticed minor movements of Proxima Centauri in the radial velocity data from the ESO's HARPS instrument, analyzed earlier by Ukrainian astrophysicist Yakiv Pavlenko and his colleages at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias[7][8][9], indicating a possible second planet orbiting Proxima Centauri.[10] The discovery was published on 15 January 2020.[1]
Red dwarfs has wide developed convection zones, where magnetic fields are forming. So, for them stellar flares are tipical (by analogy to the flares on Sun). [...] From another side, red dwarfs are low mass objects, thats why their movement is a more sensitive to existience of exoplanets.
— Yakiv Pavlenko, Proxima Centauri could be a home for the second planet [updated], 16 January 2020, https://scienceukraine.com/cosmos/proxima-c-candidate/
In June 2020, the planet's existence was initially confirmed using Hubble astrometry data from c. 1995, allowing its inclination and true mass to be determined.[3][11] Also in June 2020, a possible directly imaged counterpart of Proxima c was detected in the infrared with SPHERE, but the authors admit that they "did not obtain a clear detection".[12] If their candidate source is in fact Proxima Centauri c, it is too bright for a planet of its mass and age, implying that the planet may have a ring system with a radius of around 5 RJ.[12]
However, a 2022 study questioned the planetary nature of the observed radial velocity signal corresponding to Proxima c, attributing it to systematic effects.[4] If this is the case, it is unclear why astrometric observations detected what appeared to be a similar planetary signature.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Damasso, Mario; et al. (January 2020). "A low-mass planet candidate orbiting Proxima Centauri at a distance of 1.5 AU". Science Advances. 6 (3): eaax7467. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.7467D. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aax7467. PMC 6962037. PMID 31998838.
- ^ a b Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Schneider, Jean (March 2020). "Orbital inclination and mass of the exoplanet candidate Proxima c". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 635: L14. arXiv:2003.13106. Bibcode:2020A&A...635L..14K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202037551. S2CID 214713486.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Benedict, G. Fritz; McArthur, Barbara E. (June 2020). "A Moving Target—Revising the Mass of Proxima Centauri c". Research Notes of the AAS. 4 (6): 86. Bibcode:2020RNAAS...4...86B. doi:10.3847/2515-5172/ab9ca9. S2CID 225798015.
- ^ a b Artigau, Étienne; Cadieux, Charles; Cook, Neil J.; Doyon, René; Vandal, Thomas; et al. (June 23, 2022). "Line-by-line velocity measurements, an outlier-resistant method for precision velocimetry". The Astronomical Journal. 164:84 (3) (published August 8, 2022): 18pp. arXiv:2207.13524. Bibcode:2022AJ....164...84A. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ac7ce6.
- ^ "A new super-Earth may orbit the star next door". Science. 2020-01-15. Retrieved 2024-10-16.
- ^ Gilbert, Emily A.; Barclay, Thomas; Kruse, Ethan; Quintana, Elisa V.; Walkowicz, Lucianne M. (2021), "No Transits of Proxima Centauri Planets in High-Cadence TESS Data", Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 8: 190, arXiv:2110.10702, Bibcode:2021FrASS...8..190G, doi:10.3389/fspas.2021.769371
- ^ Pavlenko, Ya. V.; Suárez Mascareño, A.; Zapatero Osorio, M. R.; Rebolo, R.; Lodieu, N.; Béjar, V. J. S.; González Hernández, J. I.; Mohorian, M. (June 2019). "Temporal changes of the flare activity of Proxima Centauri". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 626: A111. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834258. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ "Проксима Центавра може бути домом для другої планети [оновлено]". scienceukraine.com (in Ukrainian). 16 January 2020. Archived from the original on 2020-09-23.
Автори використали наші результати, отримані у співпраці з групою вчених з Інституту астрофізики на Канарських о-вах, для того, щоб відкинути можливість пояснення довгоперіодичної варіації параметрів спектру Проксими явищами зоряної активності.
- ^ "Проксима Центавра може бути домівкою для ще однієї землеподібної планети". www.old.nas.gov.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 2024-10-29.
- ^ Billings, Lee (April 12, 2019). "A Second Planet May Orbit Earth's Nearest Neighboring Star". Scientific American. Retrieved April 12, 2019.
- ^ Benedict, Fritz (June 2, 2020). "Texas astronomer uses 25 year-old Hubble data to confirm planet Proxima Centauri c". McDonald Observatory. University of Texas.
- ^ a b Gratton, R.; et al. (June 2020). "Searching for the near-infrared counterpart of Proxima c using multi-epoch high-contrast SPHERE data at VLT". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 638: A120. arXiv:2004.06685. Bibcode:2020A&A...638A.120G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202037594. S2CID 215754278.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch