Cannabis (drug)
| Cannabis | |
|---|---|
 Close-up of flowering cannabis plant | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Source plant(s) | Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, Cannabis ruderalis[a] |
| Part(s) of plant | Flower and fruit |
| Geographic origin | Central or South Asia |
| Active ingredients | Tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol, cannabinol, tetrahydrocannabivarin |
| Main producers | Afghanistan, Canada, China, Colombia, India, Jamaica, Lebanon, Mexico, Morocco, Netherlands, Pakistan, Paraguay, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, United Kingdom, United States |
| Legal status |
|
| Part of a series on |
| Cannabis |
|---|
 |
Cannabis (/ˈkænəbɪs/),[2] commonly known as marijuana (/ˌmærəˈwɑːnə/),[3] weed, and pot, among other names, is a non-chemically uniform drug from the cannabis plant. Native to Central or South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various traditional medicines for centuries. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main psychoactive component of cannabis, which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD). Cannabis can be used by smoking, vaporizing, within food, or as an extract.
Cannabis has various mental and physical effects, which include euphoria, altered states of mind and sense of time, difficulty concentrating, impaired short-term memory, impaired body movement (balance and fine psychomotor control), relaxation, and an increase in appetite. Onset of effects is felt within minutes when smoked, but may take up to 90 minutes when eaten (as orally consumed drugs must be digested and absorbed). The effects last for two to six hours, depending on the amount used. At high doses, mental effects can include anxiety, delusions (including ideas of reference), hallucinations, panic, paranoia, and psychosis. There is a strong relation between cannabis use and the risk of psychosis, though the direction of causality is debated. Physical effects include increased heart rate, difficulty breathing, nausea, and behavioral problems in children whose mothers used cannabis during pregnancy; short-term side effects may also include dry mouth and red eyes. Long-term adverse effects may include addiction, decreased mental ability in those who started regular use as adolescents,[4] chronic coughing, susceptibility to respiratory infections, and cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome.
Cannabis is mostly used recreationally or as a medicinal drug, although it may also be used for spiritual purposes. In 2013, between 128 and 232 million people used cannabis (2.7% to 4.9% of the global population between the ages of 15 and 65). It is the most commonly used largely-illegal drug in the world, with the highest use among adults in Zambia, the United States, Canada, and Nigeria. Since the 1970s, the potency of illicit cannabis has increased, with THC levels rising and CBD levels dropping.
Cannabis plants have been grown since at least the 3rd millennium BCE and there is evidence of it being smoked for its psychoactive effects around 500 BCE in the Pamir Mountains, Central Asia. Since the 14th century, cannabis has been subject to legal restrictions. The possession, use, and cultivation of cannabis has been illegal in most countries since the 20th century. In 2013, Uruguay became the first country to legalize recreational use of cannabis. Other countries to do so are Canada, Georgia, Germany, Luxembourg, Malta, South Africa, and Thailand. In the U.S., the recreational use of cannabis is legalized in 24 states, 3 territories, and the District of Columbia, though the drug remains federally illegal. In Australia, it is legalized only in the Australian Capital Territory.
Etymology
Cannabis is a Scythian word.[5][6][7] The ancient Greeks learned of the use of cannabis by observing Scythian funerals, during which cannabis was consumed.[6] In Akkadian, cannabis was known as qunubu (𐎯𐎫𐎠𐎭𐏂).[6] The word was adopted in to the Hebrew as qaneh bosem (קָנֶה בֹּשׂם).[6]
Uses
Medical

Medical cannabis, or medical marijuana, refers to the use of cannabis to treat disease or improve symptoms; however, there is no single agreed-upon definition (e.g., cannabinoids derived from cannabis and synthetic cannabinoids are also used).[8][9][10] The rigorous scientific study of cannabis as a medicine has been hampered by production restrictions and by the fact that it is classified as an illegal drug by many governments.[11] There is some evidence suggesting cannabis can be used to reduce nausea and vomiting during chemotherapy, to improve appetite in people with HIV/AIDS, or to treat chronic pain and muscle spasms. Evidence for its use for other medical applications is insufficient for drawing conclusions about safety or efficacy.[12][13][14] There is evidence supporting the use of cannabis or its derivatives in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, neuropathic pain, and multiple sclerosis. Lower levels of evidence support its use for AIDS wasting syndrome, epilepsy, rheumatoid arthritis, and glaucoma.[15]
The medical use of cannabis is legal only in a limited number of territories, including Canada,[16] Belgium, Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand,[17][18] Spain, and many U.S. states. This usage generally requires a prescription, and distribution is usually done within a framework defined by local laws.[15]
Recreational
According to DEA Chief Administrative Law Judge, Francis Young, "cannabis is one of the safest therapeutically active substances known to man".[19] Being under the effects of cannabis is usually referred to as being "high".[20] Cannabis consumption has both psychoactive and physiological effects.[21] The "high" experience can vary widely, based (among other things) on the user's prior experience with cannabis, and the type of cannabis consumed.[22]: p647 When smoking cannabis, a euphoriant effect can occur within minutes of smoking.[23]: p104 Aside from a subjective change in perception and mood, the most common short-term physical and neurological effects include increased heart rate, increased appetite, impairment of short-term and working memory, and impairment of psychomotor coordination.[24][25]
Additional desired effects from consuming cannabis include relaxation, a general alteration of conscious perception, increased awareness of sensation, increased libido[26] and distortions in the perception of time and space. At higher doses, effects can include altered body image, auditory and/or visual illusions, pseudohallucinations and ataxia from selective impairment of polysynaptic reflexes.[citation needed] In some cases, cannabis can lead to dissociative states such as depersonalization[27][28] and derealization.[29]
Spiritual
Cannabis has held sacred status in several religions and has served as an entheogen – a chemical substance used in religious, shamanic, or spiritual contexts[30] – in the Indian subcontinent since the Vedic period. The earliest known reports regarding the sacred status of cannabis in the Indian subcontinent come from the Atharva Veda, estimated to have been composed sometime around 1400 BCE.[31] The Hindu god Shiva is described as a cannabis user, known as the "Lord of bhang".[32]: p19
In modern culture, the spiritual use of cannabis has been spread by the disciples of the Rastafari movement who use cannabis as a sacrament and as an aid to meditation.[31]
Consumption
Modes of consumption

Many different ways to consume cannabis involve heat to decarboxylate THCA into THC;[33][34] common modes include:
- Smoking, involves burning and inhaling cannabinoids ("smoke") from small pipes, bongs (portable versions of hookahs with a water chamber), paper-wrapped joints, tobacco-leaf-wrapped blunts, or the like.[35]
- Vaporizing, heating various forms of cannabis to 165–190 °C (329–374 °F),[36] causing the active ingredients to form vapor without combustion of the plant material (the boiling point of THC is 157 °C (315 °F) at atmospheric pressure).[37]
- Edibles, adding cannabis as an ingredient to a wide variety of foods, including butter and baked goods. In India it is commonly consumed as the beverage bhang.
- Cannabis tea, prepared with attention to the lipophilic quality of THC, which is only slightly water-soluble (2.8 mg per liter),[38] often involving cannabis in a saturated fat.[39]
- Tincture of cannabis, sometimes known as green dragon, is an alcoholic cannabis concentrate.
- Capsules, typically containing cannabis oil, and other dietary supplement products, for which some 220 were approved in Canada in 2018.[16]
Consumption by country
| Substance | Best estimate | Low estimate | High estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine- type stimulants | 34.16 | 13.42 | 55.24 |
| Cannabis | 192.15 | 165.76 | 234.06 |
| Cocaine | 18.20 | 13.87 | 22.85 |
| Ecstasy | 20.57 | 8.99 | 32.34 |
| Opiates | 19.38 | 13.80 | 26.15 |
| Opioids | 34.26 | 27.01 | 44.54 |
In 2013, between 128 and 232 million people used cannabis (2.7% to 4.9% of the global population between the ages of 15 and 65).[41] Cannabis is by far the most widely used illicit substance,[42] with the highest use among adults (as of 2018[update]) in Zambia, the United States, Canada, and Nigeria.[43]
United States
Between 1973 and 1978, eleven states decriminalized marijuana.[44] In 2001, Nevada reduced marijuana possession to a misdemeanor and since 2012, several other states have decriminalized and even legalized marijuana.[44]
In 2018, surveys indicated that almost half of the people in the United States had tried marijuana, 16% had used it in the past year, and 11% had used it in the past month.[45] In 2014, surveys said daily marijuana use amongst US college students had reached its highest level since records began in 1980, rising from 3.5% in 2007 to 5.9% in 2014 and had surpassed daily cigarette use.[46]
In the US, men are over twice as likely to use marijuana as women, and 18–29-year-olds are six times more likely to use as over-65-year-olds.[47] In 2015, a record 44% of the US population has tried marijuana in their lifetime, an increase from 38% in 2013 and 33% in 1985.[47]
Marijuana use in the United States is three times above the global average, but in line with other Western democracies. Forty-four percent of American 12th graders have tried the drug at least once, and the typical age of first-use is 16, similar to the typical age of first-use for alcohol but lower than the first-use age for other illicit drugs.[42]
A 2022 Gallup poll concluded Americans are smoking more marijuana than cigarettes for the first time.[48]
Adverse effects
Short-term
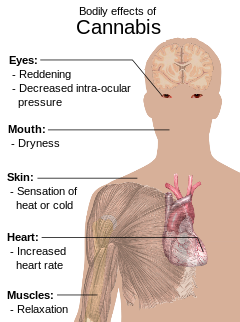
Acute negative effects may include anxiety and panic, impaired attention and memory, an increased risk of psychotic symptoms,[b] the inability to think clearly, and an increased risk of accidents.[51][52][53] Cannabis impairs a person's driving ability, and THC was the illicit drug most frequently found in the blood of drivers who have been involved in vehicle crashes. Those with THC in their system are from three to seven times more likely to be the cause of the accident than those who had not used either cannabis or alcohol, although its role is not necessarily causal because THC stays in the bloodstream for days to weeks after intoxication.[54][55][c]
Some immediate undesired side effects include a decrease in short-term memory, dry mouth, impaired motor skills, reddening of the eyes,[58] dizziness, feeling tired and vomiting.[13] Some users may experience an episode of acute psychosis, which usually abates after six hours, but in rare instances, heavy users may find the symptoms continuing for many days.[59]
Legalization has increased the rates at which children are exposed to cannabis, particularly from edibles. While the toxicity and lethality of THC in children is not known, they are at risk for encephalopathy, hypotension, respiratory depression severe enough to require ventilation, somnolence and coma.[60][61]
Fatality
There is no clear evidence for a link between cannabis use and deaths from cardiovascular disease, but a 2019 review noted that it may be an under-reported, contributory factor or direct cause in cases of sudden death, due to the strain it can place on the cardiovascular system. Some deaths have also been attributed to cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome.[62] There is an association between cannabis use and suicide, particularly in younger users.[63]
A 16-month survey of Oregon and Alaska emergency departments found a report of the death of an adult who had been admitted for acute cannabis toxicity.[64]
Long-term

Psychological effects
A 2015 meta-analysis found that, although a longer period of abstinence was associated with smaller magnitudes of impairment, both retrospective and prospective memory were impaired in cannabis users. The authors concluded that some, but not all, of the deficits associated with cannabis use were reversible.[66] A 2012 meta-analysis found that deficits in most domains of cognition persisted beyond the acute period of intoxication, but was not evident in studies where subjects were abstinent for more than 25 days.[67] Few high quality studies have been performed on the long-term effects of cannabis on cognition, and the results were generally inconsistent.[68] Furthermore, effect sizes of significant findings were generally small.[67] One review concluded that, although most cognitive faculties were unimpaired by cannabis use, residual deficits occurred in executive functions.[69] Impairments in executive functioning are most consistently found in older populations, which may reflect heavier cannabis exposure, or developmental effects associated with adolescent cannabis use.[70] One review found three prospective cohort studies that examined the relationship between self-reported cannabis use and intelligence quotient (IQ). The study following the largest number of heavy cannabis users reported that IQ declined between ages 7–13 and age 38. Poorer school performance and increased incidence of leaving school early were both associated with cannabis use, although a causal relationship was not established.[71] Cannabis users demonstrated increased activity in task-related brain regions, consistent with reduced processing efficiency.[72]
A reduced quality of life is associated with heavy cannabis use, although the relationship is inconsistent and weaker than for tobacco and other substances.[73] The direction of cause and effect, however, is unclear.[73]
The long-term effects of cannabis are not clear.[13] There are concerns surrounding memory and cognition problems, risk of addiction, and the risk of schizophrenia in young people.[12]
Neuroimaging
Although global abnormalities in white matter and grey matter are not consistently associated with cannabis use,[74] reduced hippocampal volume is consistently found.[75] Amygdala abnormalities are sometimes reported, although findings are inconsistent.[76][77][78]
Cannabis use is associated with increased recruitment of task-related areas, such as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which is thought to reflect compensatory activity due to reduced processing efficiency.[78][77][79] Cannabis use is also associated with downregulation of CB1 receptors. The magnitude of down regulation is associated with cumulative cannabis exposure, and is reversed after one month of abstinence.[71][80][81] There is limited evidence that chronic cannabis use can reduce levels of glutamate metabolites in the human brain.[82]
Cannabis dependence
About 9% of those who experiment with marijuana eventually become dependent according to DSM-IV (1994) criteria.[15] A 2013 review estimates daily use is associated with a 10–20% rate of dependence.[12] The highest risk of cannabis dependence is found in those with a history of poor academic achievement, deviant behavior in childhood and adolescence, rebelliousness, poor parental relationships, or a parental history of drug and alcohol problems.[83] Of daily users, about 50% experience withdrawal upon cessation of use (i.e. are dependent), characterized by sleep problems, irritability, dysphoria, and craving.[71] Cannabis withdrawal is less severe than withdrawal from alcohol.[84]
According to DSM-V criteria, 9% of those who are exposed to cannabis develop cannabis use disorder, compared to 20% for cocaine, 23% for alcohol and 68% for nicotine. Cannabis use disorder in the DSM-V involves a combination of DSM-IV criteria for cannabis abuse and dependence, plus the addition of craving, without the criterion related to legal troubles.[71]
Psychiatric
From a clinical perspective, two significant school of thought exists for psychiatric conditions associated with cannabis (or cannabinoids) use: transient, non-persistent psychotic reactions, and longer-lasting, persistent disorders that resemble schizophrenia. The former is formally known as acute cannabis-associated psychotic symptoms (CAPS).[85]
At an epidemiological level, a dose–response relationship exists between cannabis use and increased risk of psychosis and earlier onset of psychosis.[86][87][88][89][90] Although the epidemiological association is robust, evidence to prove a causal relationship is lacking.[91]
Cannabis may also increase the risk of depression, but insufficient research has been performed to draw a conclusion.[92][88] Cannabis use is associated with increased risk of anxiety disorders, although causality has not been established.[93]
A review in 2019 found that research was insufficient to determine the safety and efficacy of using cannabis to treat schizophrenia, psychosis, or other mental disorders.[94][95] Another found that cannabis during adolescence was associated with an increased risk of developing depression and suicidal behavior later in life, while finding no effect on anxiety.[96]
Physical
Heavy, long-term exposure to marijuana may have physical, mental, behavioral and social health consequences. It may be "associated with diseases of the liver (particularly with co-existing hepatitis C), lungs, heart, and vasculature".[97] A 2014 review found that while cannabis use may be less harmful than alcohol use, the recommendation to substitute it for problematic drinking was premature without further study.[98] Various surveys conducted between 2015 and 2019 found that many users of cannabis substitute it for prescription drugs (including opioids), alcohol, and tobacco; most of those who used it in place of alcohol or tobacco either reduced or stopped their intake of the latter substances.[99]
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) is a severe condition seen in some chronic cannabis users where they have repeated bouts of uncontrollable vomiting for 24–48 hours. Four cases of death have been reported as a result of CHS.[100][101]
A limited number of studies have examined the effects of cannabis smoking on the respiratory system.[102] Chronic heavy marijuana smoking is associated with respiratory infections,[103] coughing, production of sputum, wheezing, and other symptoms of chronic bronchitis.[51] The available evidence does not support a causal relationship between cannabis use and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[104] Short-term use of cannabis is associated with bronchodilation.[105] Other side effects of cannabis use include cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS), a condition which involves recurrent nausea, cramping abdominal pain, and vomiting.[106]
Cannabis smoke contains thousands of organic and inorganic chemical compounds. This tar is chemically similar to that found in tobacco smoke,[107] and over fifty known carcinogens have been identified in cannabis smoke,[108] including; nitrosamines, reactive aldehydes, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, including benz[a]pyrene.[109] Cannabis smoke is also inhaled more deeply than tobacco smoke.[110] As of 2015[update], there is no consensus regarding whether cannabis smoking is associated with an increased risk of cancer.[111] Light and moderate use of cannabis is not believed to increase risk of lung or upper airway cancer. Evidence for causing these cancers is mixed concerning heavy, long-term use. In general there are far lower risks of pulmonary complications for regular cannabis smokers when compared with those of tobacco.[112] A 2015 review found an association between cannabis use and the development of testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs), particularly non-seminoma TGCTs.[113] Another 2015 meta-analysis found no association between lifetime cannabis use and risk of head or neck cancer.[114] Combustion products are not present when using a vaporizer, consuming THC in pill form, or consuming cannabis foods.[115]
There is concern that cannabis may contribute to cardiovascular disease,[116] but as of 2018[update], evidence of this relationship was unclear.[117] Research in these events is complicated because cannabis is often used in conjunction with tobacco, and drugs such as alcohol and cocaine that are known to have cardiovascular risk factors.[118] Smoking cannabis has also been shown to increase the risk of myocardial infarction by 4.8 times for the 60 minutes after consumption.[119]
There is preliminary evidence that cannabis interferes with the anticoagulant properties of prescription drugs used for treating blood clots.[120] As of 2019[update], the mechanisms for the anti-inflammatory and possible pain relieving effects of cannabis were not defined, and there were no governmental regulatory approvals or clinical practices for use of cannabis as a drug.[95]
Emergency department visits
Emergency room (ER) admissions associated with cannabis use rose significantly from 2012 to 2016; adolescents from age 12–17 had the highest risk.[121] At one Colorado medical center following legalization, approximately two percent of ER admissions were classified as cannabis users. The symptoms of one quarter of these users were partially attributed to cannabis (a total of 2567 out of 449,031 patients); other drugs were sometimes involved. Of these cannabis admissions, one quarter were for acute psychiatric effects, primarily suicidal ideation, depression, and anxiety. An additional third of the cases were for gastrointestinal issues including cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome.[122]
According to the United States Department of Health and Human Services, there were 455,000 emergency room visits associated with cannabis use in 2011. These statistics include visits in which the patient was treated for a condition induced by or related to recent cannabis use. The drug use must be "implicated" in the emergency department visit, but does not need to be the direct cause of the visit. Most of the illicit drug emergency room visits involved multiple drugs.[123] In 129,000 cases, cannabis was the only implicated drug.[123][15]
Reproductive health
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
THC is a weak partial agonist at CB1 receptors, while CBD is a CB1 receptor antagonist.[125][126] The CB1 receptor is found primarily in the brain as well as in some peripheral tissues, and the CB2 receptor is found primarily in peripheral tissues, but is also expressed in neuroglial cells.[127] THC appears to alter mood and cognition through its agonist actions on the CB1 receptors, which inhibit a secondary messenger system (adenylate cyclase) in a dose-dependent manner.
Via CB1 receptor activation, THC indirectly increases dopamine release and produces psychotropic effects.[128] CBD also acts as an allosteric modulator of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors.[129] THC also potentiates the effects of the glycine receptors.[130] It is unknown if or how these actions contribute to the effects of cannabis.[131]
Pharmacokinetics
The high lipid-solubility of cannabinoids results in their persisting in the body for long periods of time.[132] Even after a single administration of THC, detectable levels of THC can be found in the body for weeks or longer (depending on the amount administered and the sensitivity of the assessment method).[132] Investigators have suggested that this is an important factor in marijuana's effects, perhaps because cannabinoids may accumulate in the body, particularly in the lipid membranes of neurons.[133]
Chemistry
Chemical composition
The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is formed via decarboxylation of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) from the application of heat. Raw leaf is not psychoactive because the cannabinoids are in the form of carboxylic acids.[citation needed] THC is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant,[134] including at least 65 other cannabinoids,[135] such as cannabidiol (CBD).[53]
Detection in body fluids
THC and its major (inactive) metabolite, THC-COOH, can be measured in blood, urine, hair, oral fluid or sweat using chromatographic techniques as part of a drug use testing program or a forensic investigation of a traffic or other criminal offense.[59] The concentrations obtained from such analyses can often be helpful in distinguishing active use from passive exposure, elapsed time since use, and extent or duration of use. These tests cannot, however, distinguish authorized cannabis smoking for medical purposes from unauthorized recreational smoking.[136] Commercial cannabinoid immunoassays, often employed as the initial screening method when testing physiological specimens for marijuana presence, have different degrees of cross-reactivity with THC and its metabolites.[137] Urine contains predominantly THC-COOH, while hair, oral fluid and sweat contain primarily THC.[59] Blood may contain both substances, with the relative amounts dependent on the recency and extent of usage.[59]
The Duquenois–Levine test is commonly used as a screening test in the field, but it cannot definitively confirm the presence of cannabis, as a large range of substances have been shown to give false positives.[138] Researchers at John Jay College of Criminal Justice reported that dietary zinc supplements can mask the presence of THC and other drugs in urine.[139] However, a 2013 study conducted by researchers at the University of Utah School of Medicine refute the possibility of self-administered zinc producing false-negative urine drug tests.[140]
Varieties and strains
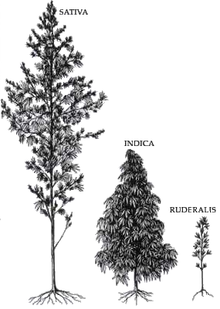

CBD is a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, which is under laboratory research to determine if it has an anxiolytic effect.[141] It is often claimed that sativa strains provide a more stimulating psychoactive high while indica strains are more sedating with a body high.[142] However, this is disputed by researchers.[143]
A 2015 review found that the use of high CBD-to-THC strains of cannabis showed significantly fewer positive symptoms, such as delusions and hallucinations, better cognitive function and both lower risk for developing psychosis, as well as a later age of onset of the illness, compared to cannabis with low CBD-to-THC ratios.[144]
Psychoactive ingredients
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), "the amount of THC present in a cannabis sample is generally used as a measure of cannabis potency."[145] The three main forms of cannabis products are the flower/fruit, resin (hashish), and oil (hash oil). The UNODC states that cannabis often contains 5% THC content, resin "can contain up to 20% THC content", and that "Cannabis oil may contain more than 60% THC content."[145]
Studies have found that the potency of illicit cannabis has greatly increased since the 1970s, with THC levels rising and CBD levels dropping.[146][147][148] It is unclear, however, whether the increase in THC content has caused people to consume more THC or if users adjust based on the potency of the cannabis. It is likely that the higher THC content allows people to ingest less tar. At the same time, CBD levels in seized samples have lowered, in part because of the desire to produce higher THC levels and because more illegal growers cultivate indoors using artificial lights. This helps avoid detection but reduces the CBD production of the plant.[149]
Australia's National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre (NCPIC) states that the buds (infructescences) of the female cannabis plant contain the highest concentration of THC, followed by the leaves. The stalks and seeds have "much lower THC levels".[150] The UN states that the leaves can contain ten times less THC than the buds, and the stalks 100 times less THC.[145]
After revisions to cannabis scheduling in the UK, the government moved cannabis back from a class C to a class B drug. A purported reason was the appearance of high potency cannabis. They believe skunk accounts for between 70% and 80% of samples seized by police[151] (despite the fact that skunk can sometimes be incorrectly mistaken for all types of herbal cannabis).[152][153] Extracts such as hashish and hash oil typically contain more THC than high potency cannabis infructescences.[154]
Laced cannabis and synthetic cannabinoids
Hemp buds (or low-potency cannabis buds) laced with synthetic cannabinoids started to be sold as cannabis street drug in 2020.[155][156][157][158]
The short-term effects of cannabis can be altered if it has been laced with opioid drugs such as heroin or fentanyl.[159] The added drugs are meant to enhance the psychoactive properties, add to its weight, and increase profitability, despite the increased danger of overdose.[160][d]
Preparations
- Dried flower buds (marijuana)
- A gram of kief
- Hashish
- Hash oil
- Infusion (dairy butter)
Marijuana
Marijuana or marihuana (herbal cannabis)[162] consists of the dried flowers and fruits and subtending leaves and stems of the female cannabis plant.[163][164][165][166] This is the most widely consumed form,[166] containing 3% to 20% THC,[167] with reports of up to 33% THC.[168] This is the stock material from which all other preparations are derived. Although herbal cannabis and industrial hemp derive from the same species and contain the psychoactive component (THC), they are distinct strains with unique biochemical compositions and uses. Hemp has lower concentrations of THC and higher concentrations of CBD, which gives lesser psychoactive effects.[169][170]
Kief
Kief is a powder, rich in trichomes,[171] which can be sifted from the leaves, flowers and fruits of cannabis plants and either consumed in powder form or compressed to produce cakes of hashish.[172] The word "kif" derives from colloquial Arabic كيف kēf/kīf, meaning pleasure.[173]
Hashish

Hashish (also spelled hasheesh, hashisha, or simply hash) is a concentrated resin cake or ball produced from pressed kief, the detached trichomes and fine material that falls off cannabis fruits, flowers and leaves,[174] or from scraping the resin from the surface of the plants and rolling it into balls. It varies in color from black to golden brown depending upon purity and variety of cultivar it was obtained from.[175] It can be consumed orally or smoked, and is also vaporized, or 'vaped'.[176] The term "rosin hash" refers to a high quality solventless product obtained through heat and pressure.[177]
Tincture
Cannabinoids can be extracted from cannabis plant matter using high-proof spirits (often grain alcohol) to create a tincture, often referred to as "green dragon".[32]: p17 Nabiximols is a branded product name from a tincture manufacturing pharmaceutical company.[178]
Hash oil
Hash oil is a resinous matrix of cannabinoids obtained from the cannabis plant by solvent extraction,[179] formed into a hardened or viscous mass.[180] Hash oil can be the most potent of the main cannabis products because of its high level of psychoactive compound per its volume, which can vary depending on the plant's mix of essential oils and psychoactive compounds.[181] Butane and supercritical carbon dioxide hash oil have become popular in recent years.[182]
Infusions
There are many varieties of cannabis infusions owing to the variety of non-volatile solvents used.[183] The plant material is mixed with the solvent and then pressed and filtered to express the oils of the plant into the solvent. Examples of solvents used in this process are cocoa butter, dairy butter, cooking oil, glycerine, and skin moisturizers. Depending on the solvent, these may be used in cannabis foods or applied topically.[184]
Marihuana prensada
Marihuana prensada ('pressed marijuana') is a cannabis-derived product widespread among the lower classes of South America,[185] especially from the 90s. Locally it is known as "paraguayo" or "paragua", since its main producer is Paraguay.[186] Marijuana is dried and mixed with binding agents that make it toxic and highly harmful to health.[187] It is cut into the shape of bricks (ladrillos) and sold for a low price in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Peru, Venezuela, and even the United States.[188]
History
Ancient history
Cannabis is indigenous to Central or South Asia[189] and its uses for fabric and rope dates back to the Neolithic age in China and Japan.[190][191] It is unclear when cannabis first became known for its psychoactive properties. The oldest archeological evidence for the burning of cannabis was found in Romanian kurgans dated 3,500 BC, and scholars suggest that the drug was first used in ritual ceremonies by Proto-Indo-European tribes living in the Pontic-Caspian steppe during the Chalcolithic period, a custom they eventually spread throughout Western Eurasia during the Indo-European migrations.[192][193] Some research suggests that the ancient Indo-Iranian drug soma, mentioned in the Vedas, sometimes contained cannabis. This is based on the discovery of a basin containing cannabis in a shrine of the second millennium BC in Turkmenistan.[194]
Cannabis was known to the ancient Assyrians, who discovered its psychoactive properties through the Iranians.[195] Using it in some religious ceremonies, they called it qunubu (meaning "way to produce smoke"), a probable origin of the modern word cannabis.[196] The Iranians also introduced cannabis to the Scythians, Thracians and Dacians, whose shamans (the kapnobatai – "those who walk on smoke/clouds") burned cannabis infructescences to induce trance.[197] The plant was used in China before 2800 BC, and found therapeutic use in India by 1000 BC, where it was used in food and drink, including bhang.[198][199]

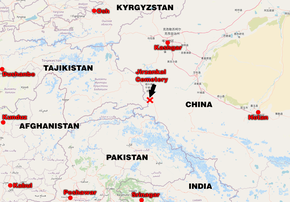
Cannabis has an ancient history of ritual use and has been used by religions around the world. It has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various traditional medicines for centuries.[200][201][162] The earliest evidence of cannabis smoking has been found in the 2,500-year-old tombs of Jirzankal Cemetery in the Pamir Mountains in Western China, where cannabis residue were found in burners with charred pebbles possibly used during funeral rituals.[202][203] Hemp seeds discovered by archaeologists at Pazyryk suggest early ceremonial practices like eating by the Scythians occurred during the 5th to 2nd century BC, confirming previous historical reports by Herodotus.[204] It was used by Muslims in various Sufi orders as early as the Mamluk period, for example by the Qalandars.[205] Smoking pipes uncovered in Ethiopia and carbon-dated to around c. AD 1320 were found to have traces of cannabis.[206]
Modern history
Cannabis was introduced to the New World by the Spaniards in 1530–1545.[207][208][209] Following an 1836–1840 travel in North Africa and the Middle East, French physician Jacques-Joseph Moreau wrote on the psychological effects of cannabis use; he founded the Paris' Club des Hashischins in 1844.[210] In 1842, Irish physician William Brooke O'Shaughnessy, who had studied the drug while working as a medical officer in Bengal with the East India Company, brought a quantity of cannabis with him on his return to Britain, provoking renewed interest in the West.[211] Examples of classic literature of the period featuring cannabis include Les paradis artificiels (1860) by Charles Baudelaire and The Hasheesh Eater (1857) by Fitz Hugh Ludlow.

Cannabis was criminalized in some countries beginning in the 14th century and was illegal in most countries by the middle of the 20th century. The colonial government of Mauritius banned cannabis in 1840 over concerns on its effect on Indian indentured workers;[212] the same occurred in Singapore in 1870.[213] In the United States, the first restrictions on sale of cannabis came in 1906 (in the District of Columbia).[214] Canada criminalized cannabis in The Opium and Narcotic Drug Act, 1923,[215] before any reports of the use of the drug in Canada, but eventually legalized its consumption for recreational and medicinal purposes in 2018.[16]
In 1925, a compromise was made at an international conference in The Hague about the International Opium Convention that banned exportation of "Indian hemp" to countries that had prohibited its use, and requiring importing countries to issue certificates approving the importation and stating that the shipment was required "exclusively for medical or scientific purposes". It also required parties to "exercise an effective control of such a nature as to prevent the illicit international traffic in Indian hemp and especially in the resin".[216][217] In the United States in 1937, the Marihuana Tax Act was passed,[218] and prohibited the production of hemp in addition to cannabis.

In 1972, the Dutch government divided drugs into more- and less-dangerous categories, with cannabis being in the lesser category. Accordingly, possession of 30 grams (1.1 oz) or less was made a misdemeanor.[219] Cannabis has been available for recreational use in coffee shops since 1976.[220] Cannabis products are only sold openly in certain local "coffeeshops" and possession of up to 5 grams (0.18 oz) for personal use is decriminalized, however: the police may still confiscate it, which often happens in car checks near the border. Other types of sales and transportation are not permitted, although the general approach toward cannabis was lenient even before official decriminalization.[221][222][223]
In Uruguay, President Jose Mujica signed legislation to legalize recreational cannabis in December 2013, making Uruguay the first country in the modern era to legalize cannabis. In August 2014, Uruguay legalized growing up to six plants at home, as well as the formation of growing clubs (Cannabis social club), and a state-controlled marijuana dispensary regime.
As of 17 October 2018[update], when recreational use of cannabis was legalized in Canada, dietary supplements for human use and veterinary health products containing not more than 10 parts per million of THC extract were approved for marketing; Nabiximols (as Sativex) is used as a prescription drug in Canada.[16]
The United Nations' World Drug Report stated that cannabis "was the world's most widely produced, trafficked, and consumed drug in the world in 2010", and estimated between 128 million and 238 million users globally in 2015.[224][225]
Culture, legality and economics
Culture

Cannabis has been one of the most used psychoactive drugs in the world since the late 20th century, following only tobacco and alcohol in popularity.[227] According to Vera Rubin, the use of cannabis has been encompassed by two major cultural complexes over time: a continuous, traditional folk stream, and a more circumscribed, contemporary configuration.[228] The former involves both sacred and secular use, and is usually based on small-scale cultivation: the use of the plant for cordage, clothing, medicine, food, and a "general use as an euphoriant and symbol of fellowship."[228][229] The second stream of expansion of cannabis use encompasses "the use of hemp for commercial manufacturers utilizing large-scale cultivation primarily as a fiber for mercantile purposes"; but it is also linked to the search for psychedelic experiences (which can be traced back to the formation of the Parisian Club des Hashischins).[229]
Legality

See also countries that have legalized medical use of cannabis.
Since the beginning of the 20th century, most countries have enacted laws against the cultivation, possession or transfer of cannabis.[230] These laws have had an adverse effect on cannabis cultivation for non-recreational purposes, but there are many regions where handling of cannabis is legal or licensed. Many jurisdictions have lessened the penalties for possession of small quantities of cannabis so that it is punished by confiscation and sometimes a fine, rather than imprisonment, focusing more on those who traffic the drug on the black market.
In some areas where cannabis use had been historically tolerated, new restrictions were instituted, such as the closing of cannabis coffee shops near the borders of the Netherlands,[231] and closing of coffee shops near secondary schools in the Netherlands.[232] In Copenhagen, Denmark in 2014, mayor Frank Jensen discussed possibilities for the city to legalize cannabis production and commerce.[233]
Some jurisdictions use free voluntary treatment programs and/or mandatory treatment programs for frequent known users. Simple possession can carry long prison terms in some countries, particularly in East Asia, where the sale of cannabis may lead to a sentence of life in prison or even execution. Political parties, non-profit organizations, and causes based on the legalization of medical cannabis and/or legalizing the plant entirely (with some restrictions) have emerged in such countries as China and Thailand.[234][235]
In December 2012, the U.S. state of Washington became the first state to officially legalize cannabis in a state law (Washington Initiative 502) (but still illegal by federal law),[236] with the state of Colorado following close behind (Colorado Amendment 64).[237] On 1 January 2013, the first cannabis "club" for private marijuana smoking (no buying or selling, however) was allowed for the first time in Colorado.[238] The California Supreme Court decided in May 2013 that local governments can ban medical cannabis dispensaries despite a state law in California that permits the use of cannabis for medical purposes. At least 180 cities across California have enacted bans in recent years.[239]
On 30 April 2024, the United States Department of Justice announced it would move to reclassify cannabis from a Schedule I to a Schedule III controlled substance.[240][241]
In December 2013, Uruguay became the first country to legalize growing, sale and use of cannabis.[242] After a long delay in implementing the retail component of the law, in 2017 sixteen pharmacies were authorized to sell cannabis commercially.[243] On 19 June 2018, the Canadian Senate passed a bill and the Prime Minister announced the effective legalization date as 17 October 2018.[16][244] Canada is the second country to legalize the drug.[245]
In November 2015, Uttarakhand became the first state of India to legalize the cultivation of hemp for industrial purposes.[246] Usage within the Hindu and Buddhist cultures of the Indian subcontinent is common, with many street vendors in India openly selling products infused with cannabis, and traditional medical practitioners in Sri Lanka selling products infused with cannabis for recreational purposes and well as for religious celebrations.[247] Indian laws criminalizing cannabis date back to the colonial period. India and Sri Lanka have allowed cannabis to be taken in the context of traditional culture for recreational/celebratory purposes and also for medicinal purposes.[247]
On 17 October 2015, Australian health minister Sussan Ley presented a new law that will allow the cultivation of cannabis for scientific research and medical trials on patients.[248]
On 17 October 2018, Canada legalized cannabis for recreational adult use[249] making it the second country in the world to do so after Uruguay and the first G7 nation.[250] This legalization comes with regulation similar to that of alcohol in Canada, age restrictions, limiting home production, distribution, consumption areas and sale times.[251] Laws around use vary from province to province including age limits, retail structure, and growing at home.[249] The Canadian Licensed Producer system aims to become the Gold Standard in the world for safe and secure cannabis production,[252] including provisions for a robust craft cannabis industry where many expect opportunities for experimenting with different strains.[253]
As the drug has increasingly been seen as a health issue instead of criminal behavior, cannabis has also been legalized or decriminalized in: Czech Republic,[254] Colombia,[255][256] Ecuador,[257][258][259] Portugal,[260] South Africa[261] and Canada.[16] Medical marijuana was legalized in Mexico in mid-2017 and legalized for recreational use in June 2021.[262][263][264]
Germany legalized cannabis for recreational use in April 2024.[265]
Legal status by country
As of 2022, Uruguay and Canada are the only countries that have fully legalized the cultivation, consumption and bartering of recreational cannabis nationwide.[266][267] In the United States, 24 states, 3 territories, and the District of Columbia have legalized the recreational use of cannabis – though the drug remains illegal at the federal level.[268] Laws vary from state to state when it comes to the commercial sale. Court rulings in Georgia and South Africa have led to the legalization of cannabis consumption, but not legal sales. A policy of limited enforcement has also been adopted in many countries, in particular Spain and the Netherlands where the sale of cannabis is tolerated at licensed establishments.[269][270] Contrary to popular belief, cannabis is not legal in the Netherlands,[271] but it has been decriminalized since the 1970s. In 2021, Malta was the first European Union member to legalize the use of cannabis for recreational purposes.[272] In Estonia, it is only legal to sell cannabis products with a THC content of less than 0.2%, although products may contain more cannabidiol.[273] Lebanon has recently become the first Arab country to legalize the plantation of cannabis for medical use.[274]
Penalties for illegal recreational use ranges from confiscation or small fines to jail time and even death.[275] In some countries citizens can be punished if they have used the drug in another country, including Singapore and South Korea.[276][277]
Economics
Production

Sinsemilla (Spanish for "without seed") is the dried, seedless (i.e. parthenocarpic) infructescences of female cannabis plants. Because THC production drops off once pollination occurs, the male plants (which produce little THC themselves) are eliminated before they shed pollen to prevent pollination, thus inducing the development of parthenocarpic fruits gathered in dense infructescences. Advanced cultivation techniques such as hydroponics, cloning, high-intensity artificial lighting, and the sea of green method are frequently employed as a response (in part) to prohibition enforcement efforts that make outdoor cultivation more risky.
"Skunk" refers to several named strains of potent cannabis, grown through selective breeding and sometimes hydroponics. It is a cross-breed of Cannabis sativa and C. indica (although other strains of this mix exist in abundance). Skunk cannabis potency ranges usually from 6% to 15% and rarely as high as 20%. The average THC level in coffee shops in the Netherlands is about 18–19%.[278]
The average levels of THC in cannabis sold in the United States rose dramatically between the 1970s and 2000.[279] This is disputed for various reasons, and there is little consensus as to whether this is a fact or an artifact of poor testing methodologies.[279] According to Daniel Forbes writing for slate.com, the relative strength of modern strains are likely skewed because undue weight is given to much more expensive and potent, but less prevalent, samples.[280] Some suggest that results are skewed by older testing methods that included low-THC-content plant material such as leaves in the samples, which are excluded in contemporary tests. Others believe that modern strains actually are significantly more potent than older ones.[279]
The main producing countries of cannabis are Afghanistan,[281] Canada,[282] China, Colombia,[283] India,[281] Jamaica,[281] Lebanon,[284] Mexico,[285] Morocco,[281] the Netherlands, Pakistan, Paraguay,[285] Spain,[281] Thailand, Turkey, the United Kingdom,[286] and the United States.[281]
Price
The price or street value of cannabis varies widely depending on geographic area and potency.[287] Prices and overall markets have also varied considerably over time.
- In 1997, cannabis was estimated to be overall the number four value crop in the US, and number one or two in many states, including California, New York, and Florida. This estimate is based on a value to growers of ~60% of retail value, or $3,000 per pound ($6,600/kg).[288]
- In 2006, cannabis was estimated to have been a $36 billion market.[289] This estimate has been challenged as exaggerated.[42] The UN World Drug Report (2008) estimated that 2006 street prices in the US and Canada ranged from about US$8.8 to $25 per gram (approximately $250 to $700 per ounce), depending on quality.[290] Typical U.S. retail prices were $10–15 per gram (approximately $280–420 per ounce).
- In 2017, the U.S. was estimated to constitute 90% of the worldwide $9.5 billion legal trade in cannabis.[291]
After some U.S. states legalized cannabis, street prices began to drop. In Colorado, the price of smokable buds (infructescences) dropped 40 percent between 2014 and 2019, from $200 per ounce to $120 per ounce ($7 per gram to $4.19 per gram).[292]
The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction reports that typical retail prices in Europe for cannabis varied from €2 to €20 per gram in 2008, with a majority of European countries reporting prices in the range €4–10.[293]
Cannabis as a gateway drug
The gateway hypothesis states that cannabis use increases the probability of trying "harder" drugs. The hypothesis has been hotly debated as it is regarded by some as the primary rationale for the United States prohibition on cannabis use.[294][295] A Pew Research Center poll found that political opposition to marijuana use was significantly associated with concerns about the health effects and whether legalization would increase cannabis use by children.[296]
Some studies state that while there is no proof for the gateway hypothesis,[297] young cannabis users should still be considered as a risk group for intervention programs.[298] Other findings indicate that hard drug users are likely to be poly-drug users, and that interventions must address the use of multiple drugs instead of a single hard drug.[299] Almost two-thirds of the poly drug users in the 2009–2010 Scottish Crime and Justice Survey used cannabis.[300]
The gateway effect may appear due to social factors involved in using any illegal drug. Because of the illegal status of cannabis, its consumers are likely to find themselves in situations allowing them to acquaint with individuals using or selling other illegal drugs.[301][302] Studies have shown that alcohol and tobacco may additionally be regarded as gateway drugs;[303] however, a more parsimonious explanation could be that cannabis is simply more readily available (and at an earlier age) than illegal hard drugs.[citation needed] In turn, alcohol and tobacco are typically easier to obtain at an earlier age than is cannabis (though the reverse may be true in some areas), thus leading to the "gateway sequence" in those individuals, since they are most likely to experiment with any drug offered.[294]
A related alternative to the gateway hypothesis is the common liability to addiction (CLA) theory. It states that some individuals are, for various reasons, willing to try multiple recreational substances. The "gateway" drugs are merely those that are (usually) available at an earlier age than the harder drugs. Researchers have noted in an extensive review that it is dangerous to present the sequence of events described in gateway "theory" in causative terms as this hinders both research and intervention.[304]
In 2020, the National Institute on Drug Abuse released a study backing allegations that marijuana is a gateway to harder drugs, though not for the majority of marijuana users.[305] The National Institute on Drug Abuse determined that marijuana use is "likely to precede use of other licit and illicit substances" and that "adults who reported marijuana use during the first wave of the survey were more likely than adults who did not use marijuana to develop an alcohol use disorder within 3 years; people who used marijuana and already had an alcohol use disorder at the outset were at greater risk of their alcohol use disorder worsening. Marijuana use is also linked to other substance use disorders including nicotine addiction."[305] It also reported that "These findings are consistent with the idea of marijuana as a "gateway drug". However, the majority of people who use marijuana do not go on to use other, "harder" substances. Also, cross-sensitization is not unique to marijuana. Alcohol and nicotine also prime the brain for a heightened response to other drugs and are, like marijuana, also typically used before a person progresses to other, more harmful substances."[305]
Research
Research on cannabis is challenging since the plant is illegal in most countries.[306][307][308][309][310] Research-grade samples of the drug are difficult to obtain for research purposes, unless granted under authority of national regulatory agencies, such as the US Food and Drug Administration.[311]
There are also other difficulties in researching the effects of cannabis. Many people who smoke cannabis also smoke tobacco.[312] This causes confounding factors, where questions arise as to whether the tobacco, the cannabis, or both that have caused a cancer. Another difficulty researchers have is in recruiting people who smoke cannabis into studies. Because cannabis is an illegal drug in many countries, people may be reluctant to take part in research, and if they do agree to take part, they may not say how much cannabis they actually smoke.[313]
See also
- Cannabis rights
- Glossary of cannabis terms
- List of books about cannabis
- List of celebrities who own cannabis businesses
References
Footnotes
- ^ Pure varieties of C. ruderalis are rarely used for recreational purposes.[1]
- ^ Psychotic episodes are well-documented and typically resolve within minutes or hours, while symptoms may last longer.[49] The use of a single joint can temporarily induce some psychiatric symptoms.[50]
- ^ A 2016 review also found a statistically significant increase in crash risk associated with marijuana use, but noted that this risk was "of low to medium magnitude."[56] The increase in risk of motor vehicle crash for cannabis use is between 2 and 3 times relative to baseline, whereas that for comparable doses of alcohol is between 6 and 15 times.[57]
- ^ Advocates of legalizing marijuana for recreational use, such as former Illinois state Senator Heather Steans, say that legalizing it would help reduce such hazardous added drugs: "Over 95 percent are buying it on the black market. You don't know what you're buying. It's not a safe product. We've seen it laced with rat poison, fentanyl, all sorts of things. It's funding the cartels and other criminal activity."[161]
Citations
- ^ Cervantes, Jorge (2006). Marijuana Horticulture: The Indoor/Outdoor Medical Grower's Bible (5th ed.). Van Patten Publishing. pp. 12. ISBN 9781878823236.
- ^ "cannabis noun – Definition, pictures, pronunciation and usage notes | Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary at OxfordLearnersDictionaries.com". www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com. Retrieved 10 November 2022.
- ^ "marijuana noun – Definition, pictures, pronunciation and usage notes | Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary at OxfordLearnersDictionaries.com". www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ^ Shrivastava, Amresh; Johnston, Megan; Tsuang, Ming (2011). "Cannabis use and cognitive dysfunction". Indian Journal of Psychiatry. 53 (3): 187–191. doi:10.4103/0019-5545.86796. ISSN 0019-5545. PMC 3221171. PMID 22135433.
- ^ Gray, Stephen (9 December 2016). Cannabis and Spirituality: An Explorer's Guide to an Ancient Plant Spirit Ally. Simon and Schuster. p. 69. ISBN 978-1-62055-584-2.
Cannabis is called kaneh bosem in Hebrew, which is now recognized as the Scythian word that Herodotus wrote as kánnabis (or cannabis).
- ^ a b c d Riegel, A.; Ellens, J.H. (2014). Seeking the Sacred with Psychoactive Substances: Chemical Paths to Spirituality and to God [2 volumes]. Psychology, Religion, and Spirituality. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 80. ISBN 979-8-216-14310-9. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- ^ Duncan, Perry M. (17 September 2020). Substance Use Disorders: A Biopsychosocial Perspective. Cambridge University Press. p. 441. ISBN 978-0-521-87777-0.
Cannabis is a Scythian word (Benet 1975).
- ^ Murnion B (December 2015). "Medicinal cannabis". Australian Prescriber. 38 (6): 212–15. doi:10.18773/austprescr.2015.072. ISSN 0312-8008. PMC 4674028. PMID 26843715.
- ^ "What is medical marijuana?". National Institute of Drug Abuse. July 2015. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
The term medical marijuana refers to using the whole unprocessed marijuana plant or its basic extracts to treat a disease or symptom.
- ^ Backes M (2014). Cannabis Pharmacy: The Practical Guide to Medical Marijuana. Hachette Books. p. 46. ISBN 978-1-60376-334-9.
- ^ "Release the strains". Nature Medicine. 21 (9): 963. September 2015. doi:10.1038/nm.3946. PMID 26340110.
- ^ a b c Borgelt LM, Franson KL, Nussbaum AM, Wang GS (February 2013). "The pharmacologic and clinical effects of medical cannabis". Pharmacotherapy. 33 (2): 195–209. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1017.1935. doi:10.1002/phar.1187. PMID 23386598. S2CID 8503107.
- ^ a b c Whiting PF, Wolff RF, Deshpande S, Di Nisio M, Duffy S, Hernandez AV, Keurentjes JC, Lang S, Misso K, Ryder S, Schmidlkofer S, Westwood M, Kleijnen J (23 June 2015). "Cannabinoids for Medical Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA. 313 (24): 2456–73. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.6358. hdl:10757/558499. PMID 26103030.
- ^ Jensen B, Chen J, Furnish T, Wallace M (October 2015). "Medical Marijuana and Chronic Pain: a Review of Basic Science and Clinical Evidence". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 19 (10): 50. doi:10.1007/s11916-015-0524-x. PMID 26325482. S2CID 9110606.
- ^ a b c d Volkow ND, Baler RD, Compton WM, Weiss SR (June 2014). "Adverse health effects of marijuana use". The New England Journal of Medicine. 370 (23): 2219–27. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1402309. PMC 4827335. PMID 24897085.
- ^ a b c d e f "Health products containing cannabis or for use with cannabis: Guidance for the Cannabis Act, the Food and Drugs Act, and related regulations". Government of Canada. 11 July 2018. Retrieved 19 October 2018.
- ^ Ainge Roy, Eleanor (11 December 2018). "New Zealand passes laws to make medical marijuana widely available". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
- ^ Schulz, Chris (30 June 2022). "You can get actual weed from the doctor now". The Spinoff.
- ^ "Information on Cannabis Safety". Americans for Safe Access.
- ^ Ernest Small (2016). Cannabis: A Complete Guide. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-315-35059-2.
- ^ Onaivi ES, Sugiura T, Di Marzo V (2005). Endocannabinoids: The Brain and Body's Marijuana and Beyond. Taylor & Francis. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-415-30008-7.
- ^ Curran, H. Valerie; Morgan, Celia J.A. (2014). "Desired and Undesired Effects of Cannabis on the Human Mind and Psychological Well-Being". In Pertwee, Roger G. (ed.). Handbook of Cannabis. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Ashton, C.Heather (2001). "Pharmacology and Effects of Cannabis: A Brief Review". British Journal of Psychiatry. 178 (2): 101–06. doi:10.1192/bjp.178.2.101. PMID 11157422. S2CID 15918781.
- ^ Mathre ML, ed. (1997). Cannabis in Medical Practice: A Legal, Historical, and Pharmacological Overview of the Therapeutic Use of Marijuana. University of Virginia Medical Center. pp. 144–. ISBN 978-0-7864-8390-7.
- ^ Riedel G, Davies SN (2005). "Cannabinoid function in learning, memory and plasticity". Cannabinoids. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Vol. 168. pp. 445–77. doi:10.1007/3-540-26573-2_15. ISBN 978-3-540-22565-2. PMID 16596784.
- ^ Osborne GB, Fogel C (2008). "Understanding the motivations for recreational marijuana use among adult Canadians" (PDF). Substance Use & Misuse. 43 (3–4): 539–72, discussion 573–79, 585–87. doi:10.1080/10826080701884911. PMID 18365950. S2CID 31053594.
- ^ "Medication-Associated Depersonalization Symptoms". Medscape.
- ^ Shufman E, Lerner A, Witztum E (April 2005). "[Depersonalization after withdrawal from cannabis usage]" (PDF). Harefuah (in Hebrew). 144 (4): 249–51, 303. PMID 15889607. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 April 2005.
- ^ Johnson BA (February 1990). "Psychopharmacological effects of cannabis". British Journal of Hospital Medicine. 43 (2): 114–16, 118–20, 122. PMID 2178712.
- ^ Souza RS, Albuquerque UP, Monteiro JM, de Amorim EL (2008). "Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology – Jurema-Preta (Mimosa tenuiflora [Willd.] Poir.): a review of its traditional use, phytochemistry and pharmacology". Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology. 51 (5): 937–47. doi:10.1590/S1516-89132008000500010.
- ^ a b Courtwright D (2001). Forces of Habit: Drugs and the Making of the Modern World. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-00458-0.
- ^ a b Iversen LL (2000). The Science of Marijuana. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-515110-7.
- ^ Golub A (2012). The Cultural/Subcultural Contexts of Marijuana Use at the Turn of the Twenty-First Century. Routledge. p. 82. ISBN 978-1-136-44627-6.
- ^ "Why Does Cannabis Have to be Heated?". patriotcare.org.
- ^ Tasman A, Kay J, Lieberman JA, First MB, Maj M (2011). Psychiatry. John Wiley & Sons. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-119-96540-4.
- ^ Rosenthal E (2002). Ask Ed: Marijuana Gold: Trash to Stash. Perseus Books Group. p. 15. ISBN 978-1-936807-02-4.
- ^ "Cannabis and Cannabis Extracts: Greater Than the Sum of Their Parts?" (PDF). Cannabis-med.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 June 2017. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- ^ Dronabinol from PubChem
- ^ Gieringer D, Rosenthal E (2008). Marijuana medical handbook: practical guide to therapeutic uses of marijuana. QUICK AMER Publishing Company. p. 182. ISBN 978-0-932551-86-3.
- ^ "Annual prevalence of use of drugs, by region and globally, 2016". World Drug Report 2018. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 2018. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ^ "Status and Trend Analysis of Illict [sic] Drug Markets" (PDF). World Drug Report 2015. p. 23. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Caulkins JP, Hawken A, Kilmer B, Kleiman MA (2012). Marijuana Legalization: What Everyone Needs to Know. Oxford University Press. p. 16. ISBN 978-0199913732.
- ^ "UNODC Statistics Online". data.unodc.org. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ a b Joshua CD (2015). "The business of getting high: head shops, countercultural capitalism, and the marijuana legalization movement". The Sixties. 8: 27–49. doi:10.1080/17541328.2015.1058480. hdl:11603/7422. S2CID 142795620.
- ^ "6 facts about marijuana". 22 November 2018. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ "Daily marijuana use among college students highest since 1980". The University Record.
- ^ a b McCarthy, Justin (22 July 2015). "More Than Four in 10 Americans Say They Have Tried Marijuana". Gallup.
- ^ "For the first time, Americans are smoking more marijuana than cigarettes, poll finds". cbsnews.com.
- ^ "Sativex Oral Mucosal Spray Public Assessment Report. Decentralized Procedure" (PDF). United Kingdom Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. p. 93. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
There is clear evidence that recreational cannabis can produce a transient toxic psychosis in larger doses or in susceptible individuals, which is said to characteristically resolve within a week or so of absence (Johns 2001). Transient psychotic episodes as a component of acute intoxication are well-documented (Hall et al 1994)
- ^ Hunt, Katie (17 March 2020). "Single cannabis joint linked with temporary psychiatric symptoms, review finds". CNN. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ a b Hall W, Solowij N (November 1998). "Adverse effects of cannabis". Lancet. 352 (9140): 1611–16. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)05021-1. PMID 9843121. S2CID 16313727.
- ^ Oltmanns T, Emery R (2015). Abnormal Psychology. New Jersey: Pearson. p. 294. ISBN 978-0205970742.
- ^ a b D'Souza DC, Sewell RA, Ranganathan M (October 2009). "Cannabis and psychosis/schizophrenia: human studies". European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 259 (7): 413–31. doi:10.1007/s00406-009-0024-2. PMC 2864503. PMID 19609589.
- ^ Abuse, National Institute on Drug. "Does marijuana use affect driving?". www.drugabuse.gov. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
- ^ Li MC, Brady JE, DiMaggio CJ, Lusardi AR, Tzong KY, Li G (4 October 2011). "Marijuana use and motor vehicle crashes". Epidemiologic Reviews. 34 (1): 65–72. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxr017. PMC 3276316. PMID 21976636.
- ^ Rogeberg O, Elvik R (August 2016). "The effects of cannabis intoxication on motor vehicle collision revisited and revised". Addiction. 111 (8): 1348–59. doi:10.1111/add.13347. PMID 26878835.
- ^ Hall W (January 2015). "What has research over the past two decades revealed about the adverse health effects of recreational cannabis use?" (PDF). Addiction. 110 (1): 19–35. doi:10.1111/add.12703. PMID 25287883.
- ^ Hall W, Pacula RL (2003). Cannabis Use and Dependence: Public Health and Public Policy. Cambridge University Press. p. 38. ISBN 978-0-521-80024-2.
- ^ a b c d Barceloux DG (2012). "Chapter 60: Marijuana (Cannabis sativa L.) and synthetic cannabinoids". Medical Toxicology of Drug Abuse: Synthesized Chemicals and Psychoactive Plants. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 910–. ISBN 978-1-118-10605-1. Retrieved 14 July 2013.
- ^ Wong, Kei U.; Baum, Carl R. (November 2019). "Acute Cannabis Toxicity". Pediatric Emergency Care. 35 (11): 799–804. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001970. ISSN 0749-5161. PMID 31688799. S2CID 207897219.
- ^ Claudet, Isabelle; Le Breton, Mathilde; Bréhin, Camille; Franchitto, Nicolas (April 2017). "A 10-year review of cannabis exposure in children under 3-years of age: do we need a more global approach?". European Journal of Pediatrics. 176 (4): 553–56. doi:10.1007/s00431-017-2872-5. ISSN 1432-1076. PMID 28210835. S2CID 11639790.
- ^ Drummer OH, Gerostamoulos D, Woodford NW (May 2019). "Cannabis as a cause of death: A review". Forensic Sci Int. 298: 298–306. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2019.03.007. PMID 30925348. S2CID 87511682.
- ^ Shamabadi A, Ahmadzade A, Pirahesh K, Hasanzadeh A, Asadigandomani H (December 2023). "Suicidality risk after using cannabis and cannabinoids: An umbrella review". Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 25 (1): 50–63. doi:10.1080/19585969.2023.2231466. PMC 10334849. PMID 37427882.
- ^ Takakuwa KM, Schears RM (February 2021). "The emergency department care of the cannabis and synthetic cannabinoid patient: a narrative review". Int J Emerg Med (Review). 14 (1): 10. doi:10.1186/s12245-021-00330-3. PMC 7874647. PMID 33568074.
- ^ Nutt D, King LA, Saulsbury W, Blakemore C (March 2007). "Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse". Lancet. 369 (9566): 1047–53. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60464-4. PMID 17382831. S2CID 5903121.
- ^ Schoeler T, Kambeitz J, Behlke I, Murray R, Bhattacharyya S (January 2016). "The effects of cannabis on memory function in users with and without psychotic disorder: findings from a combined meta-analysis". Psychological Medicine. 46 (1): 177–88. doi:10.1017/S0033291715001646. PMID 26353818. S2CID 23749219.
- ^ a b Schreiner AM, Dunn ME (October 2012). "Residual effects of cannabis use on neurocognitive performance after prolonged abstinence: a meta-analysis". Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 20 (5): 420–29. doi:10.1037/a0029117. PMID 22731735. S2CID 207618350.
Therefore, results indicate evidence for small neurocognitive effects that persist after the period of acute intoxication...As hypothesized, the meta-analysis conducted on studies eval- uating users after at least 25 days of abstention found no residual effects on cognitive performance...These results fail to support the idea that heavy cannabis use may result in long-term, persistent effects on neuropsychological functioning.
- ^ Gonzalez R, Carey C, Grant I (November 2002). "Nonacute (residual) neuropsychological effects of cannabis use: a qualitative analysis and systematic review". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 42 (S1): 48S–57S. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.2002.tb06003.x. PMID 12412836. S2CID 37826919.
- ^ Crean RD, Crane NA, Mason BJ (March 2011). "An evidence based review of acute and long-term effects of cannabis use on executive cognitive functions". Journal of Addiction Medicine. 5 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1097/ADM.0b013e31820c23fa. PMC 3037578. PMID 21321675.
Cannabis appears to continue to exert impairing effects in executive functions even after 3 weeks of abstinence and beyond. While basic attentional and working memory abilities are largely restored, the most enduring and detectable deficits are seen in decision-making, concept formation and planning.
- ^ Broyd SJ, van Hell HH, Beale C, Yücel M, Solowij N (April 2016). "Acute and Chronic Effects of Cannabinoids on Human Cognition-A Systematic Review". Biological Psychiatry. 79 (7): 557–67. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.12.002. PMID 26858214. S2CID 9858298.
- ^ a b c d Curran HV, Freeman TP, Mokrysz C, Lewis DA, Morgan CJ, Parsons LH (May 2016). "Keep off the grass? Cannabis, cognition and addiction" (PDF). Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 17 (5): 293–306. doi:10.1038/nrn.2016.28. hdl:10871/24746. PMID 27052382. S2CID 1685727. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 September 2017. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- ^ Ganzer F, Bröning S, Kraft S, Sack PM, Thomasius R (June 2016). "Weighing the Evidence: A Systematic Review on Long-Term Neurocognitive Effects of Cannabis Use in Abstinent Adolescents and Adults". Neuropsychology Review. 26 (2): 186–222. doi:10.1007/s11065-016-9316-2. PMID 27125202. S2CID 4335379.
- ^ a b Goldenberg M, IsHak WW, Danovitch I (January 2017). "Quality of life and recreational cannabis use". The American Journal on Addictions. 26 (1): 8–25. doi:10.1111/ajad.12486. PMID 28000973. S2CID 40707053.
- ^ Hampton WH, Hanik I, Olson IR (2019). "[Substance Abuse and White Matter: Findings, Limitations, and Future of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Research]". Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 197 (4): 288–298. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.02.005. PMC 6440853. PMID 30875650.
Given that [the human] central nervous system is an intricately balanced, complex network of billions of neurons and supporting cells, some might imagine that extrinsic substances could cause irreversible brain damage. Our review paints a less gloomy picture of the substances reviewed, however. Following prolonged abstinence, abusers of alcohol (Pfefferbaum et al., 2014) or opiates (Wang et al., 2011) have white matter microstructure that is not significantly different from nonusers. There was also no evidence that the white matter microstructural changes observed in longitudinal studies of cannabis, nicotine, or cocaine were completely irreparable. It is therefore possible that, at least to some degree, abstinence can reverse effects of substance abuse on white matter. The ability of white matter to "bounce back" very likely depends on the level and duration of abuse, as well as the substance being abused.
- ^ Yücel, M; Lorenzetti, V; Suo, C; Zalesky, A; Fornito, A; Takagi, M J; Lubman, D I; Solowij, N (January 2016). "Hippocampal harms, protection and recovery following regular cannabis use". Translational Psychiatry. 6 (1): e710–. doi:10.1038/tp.2015.201. PMC 5068875. PMID 26756903.
- ^ Rocchetti M, Crescini A, Borgwardt S, Caverzasi E, Politi P, Atakan Z, Fusar-Poli P (November 2013). "Is cannabis neurotoxic for the healthy brain? A meta-analytical review of structural brain alterations in non-psychotic users". Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 67 (7): 483–92. doi:10.1111/pcn.12085. PMID 24118193. S2CID 8245635.
- ^ a b Batalla A, Bhattacharyya S, Yücel M, Fusar-Poli P, Crippa JA, Nogué S, Torrens M, Pujol J, Farré M, Martin-Santos R (2013). "Structural and functional imaging studies in chronic cannabis users: a systematic review of adolescent and adult findings". PLOS ONE. 8 (2): e55821. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...855821B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055821. PMC 3563634. PMID 23390554.
The most consistently reported brain alteration was reduced hippocampal volume which was shown to persist even after several months of abstinence in one study and also to be related to the amount of cannabis use Other frequently reported morphological brain alterations related to chronic cannabis use were reported in the amygdala the cerebellum and the frontal cortex...These findings may be interpreted as reflecting neuroadaptation, perhaps indicating the recruitment of additional regions as a compensatory mechanism to maintain normal cognitive performance in response to chronic cannabis exposure, particularly within the prefrontal cortex area.
- ^ a b Weinstein A, Livny A, Weizman A (2016). "Brain Imaging Studies on the Cognitive, Pharmacological and Neurobiological Effects of Cannabis in Humans: Evidence from Studies of Adult Users". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 22 (42): 6366–79. doi:10.2174/1381612822666160822151323. PMID 27549374.
1) The studies reviewed so far demonstrated that chronic cannabis use has been associated with a volume reduction of the hippocampus...3) The overall conclusion arising from these studies is that recent cannabis users may experience subtle neurophysiological deficits while performing on working memory tasks, and that they compensate for these deficits by "working harder" by using additional brain regions to meet the demands of the task.
- ^ Blest-Hopley G, Giampietro V, Bhattacharyya S (May 2018). "Residual effects of cannabis use in adolescent and adult brains – A meta-analysis of fMRI studies" (PDF). Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 88: 26–41. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.03.008. PMID 29535069. S2CID 4402954.
This may reflect the multitude of cognitive tasks employed by the various studies included in these meta-analyses, all of which involved performing a task thereby requiring the participant to reorient their attention and attempt to solve the problem at hand and suggest that greater engagement of this region indicates less efficient cognitive performance in cannabis users in general, irrespective of their age.
- ^ Parsons LH, Hurd YL (October 2015). "Endocannabinoid signalling in reward and addiction". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 16 (10): 579–94. doi:10.1038/nrn4004. PMC 4652927. PMID 26373473.
- ^ Zehra A, Burns J, Liu CK, Manza P, Wiers CE, Volkow ND, Wang GJ (March 2018). "Cannabis Addiction and the Brain: a Review". Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology. 13 (4): 438–52. doi:10.1007/s11481-018-9782-9. PMC 6223748. PMID 29556883.
- ^ Colizzi M, McGuire P, Pertwee RG, Bhattacharyya S (May 2016). "Effect of cannabis on glutamate signalling in the brain: A systematic review of human and animal evidence". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 64: 359–81. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.010. PMID 26987641. S2CID 24043856.
- ^ Hall W, Degenhardt L (October 2009). "Adverse health effects of non-medical cannabis use". Lancet. 374 (9698): 1383–91. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(09)61037-0. PMID 19837255. S2CID 31616272.
- ^ Subbaraman MS (2014). "Can cannabis be considered a substitute medication for alcohol?". Alcohol and Alcoholism. 49 (3): 292–98. doi:10.1093/alcalc/agt182. PMC 3992908. PMID 24402247.
- ^ Schoeler, Tabea; Baldwin, Jessie R.; Martin, Ellen; Barkhuizen, Wikus; Pingault, Jean-Baptiste (3 June 2024). "Assessing rates and predictors of cannabis-associated psychotic symptoms across observational, experimental and medical research". Nature Mental Health. 2 (7): 865–876. doi:10.1038/s44220-024-00261-x. ISSN 2731-6076. PMC 11236708. PMID 39005547.
- ^ Leweke FM, Mueller JK, Lange B, Rohleder C (April 2016). "Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoids in Psychosis". Biological Psychiatry. 79 (7): 604–12. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.11.018. PMID 26852073. S2CID 24160677.
Epidemiological data indicate a strong relationship between cannabis use and psychosis and schizophrenia beyond transient intoxication with an increased risk of any psychotic outcome in individuals who had ever used cannabis
- ^ Marconi A, Di Forti M, Lewis CM, Murray RM, Vassos E (September 2016). "Meta-analysis of the Association Between the Level of Cannabis Use and Risk of Psychosis". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 42 (5): 1262–69. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbw003. PMC 4988731. PMID 26884547.
- ^ a b Moore TH, Zammit S, Lingford-Hughes A, Barnes TR, Jones PB, Burke M, Lewis G (July 2007). "Cannabis use and risk of psychotic or affective mental health outcomes: a systematic review" (PDF). Lancet. 370 (9584): 319–28. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61162-3. PMID 17662880. S2CID 41595474.
- ^ Semple DM, McIntosh AM, Lawrie SM (March 2005). "Cannabis as a risk factor for psychosis: systematic review". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 19 (2): 187–94. doi:10.1177/0269881105049040. PMID 15871146. S2CID 44651274.
- ^ Large M, Sharma S, Compton MT, Slade T, Nielssen O (June 2011). "Cannabis use and earlier onset of psychosis: a systematic meta-analysis". Archives of General Psychiatry. 68 (6): 555–61. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.5. PMID 21300939.
- ^ McLaren JA, Silins E, Hutchinson D, Mattick RP, Hall W (January 2010). "Assessing evidence for a causal link between cannabis and psychosis: a review of cohort studies". The International Journal on Drug Policy. 21 (1): 10–19. doi:10.1016/j.drugpo.2009.09.001. PMID 19783132.
The contentious issue of whether cannabis use can cause serious psychotic disorders that would not otherwise have occurred cannot be answered based on the existing data
- ^ Lev-Ran S, Roerecke M, Le Foll B, George TP, McKenzie K, Rehm J (March 2014). "The association between cannabis use and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies". Psychological Medicine. 44 (4): 797–810. doi:10.1017/S0033291713001438. PMID 23795762. S2CID 36763290.
- ^ Kedzior KK, Laeber LT (May 2014). "A positive association between anxiety disorders and cannabis use or cannabis use disorders in the general population – a meta-analysis of 31 studies". BMC Psychiatry. 14: 136. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-14-136. PMC 4032500. PMID 24884989.
- ^ Black, Nicola; Stockings, Emily; Campbell, Gabrielle; Tran, Lucy T.; Zagic, Dino; Hall, Wayne D.; Farrell, Michael; Degenhardt, Louisa (December 2019). "Cannabinoids for the treatment of mental disorders and symptoms of mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Lancet. Psychiatry. 6 (12): 995–1010. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30401-8. PMC 6949116. PMID 31672337.
- ^ a b VanDolah, Harrison J.; Bauer, Brent A.; Mauck, Karen F. (September 2019). "Clinicians' Guide to Cannabidiol and Hemp Oils". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 94 (9): 1840–51. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.01.003. PMID 31447137.
- ^ Gobbi, Gabriella; Atkin, Tobias; Zytynski, Tomasz; Wang, Shouao; Askari, Sorayya; Boruff, Jill; Ware, Mark; Marmorstein, Naomi; Cipriani, Andrea; Dendukuri, Nandini; Mayo, Nancy (13 February 2019). "Cannabis Use in Adolescence and Risk of Depression, Anxiety, and Suicidality in Young Adulthood". JAMA Psychiatry. 76 (4): 426–34. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.4500. PMC 6450286. PMID 30758486.
- ^ Gordon AJ, Conley JW, Gordon JM (December 2013). "Medical consequences of marijuana use: a review of current literature". Current Psychiatry Reports. 15 (12): 419. doi:10.1007/s11920-013-0419-7. PMID 24234874. S2CID 29063282.
- ^ Subbaraman MS (8 January 2014). "Can cannabis be considered a substitute medication for alcohol?". Alcohol and Alcoholism. 49 (3): 292–98. doi:10.1093/alcalc/agt182. PMC 3992908. PMID 24402247.
- ^ Armentano, Paul (5 February 2019). "Marijuana access is associated with decreased use of alcohol, tobacco and other prescription drugs". The Hill.
- ^ Nourbakhsh, Mahra; Miller, Angela; Gofton, Jeff; Jones, Graham; Adeagbo, Bamidele (2019). "Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome: Reports of Fatal Cases". Journal of Forensic Sciences. 64 (1): 270–74. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.13819. ISSN 1556-4029. PMID 29768651. S2CID 21718690.
- ^ Rudavsky, Shari. "He loved weed. Then the vomiting began. Months later, he died". USA Today. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ Maisto S, Galizio M, Connors G (2014). Drug Use and Abuse. Cengage Learning. p. 278. ISBN 978-1-305-17759-8.
- ^ "Commonly Abused Drugs Charts: Marijuana (Cannabis)". National Institute on Drug Abuse, US National Institutes of Health. 22 July 2019. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- ^ Owen KP, Sutter ME, Albertson TE (February 2014). "Marijuana: respiratory tract effects". Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology. 46 (1): 65–81. doi:10.1007/s12016-013-8374-y. PMID 23715638. S2CID 23823391.
- ^ Tetrault JM, Crothers K, Moore BA, Mehra R, Concato J, Fiellin DA (February 2007). "Effects of marijuana smoking on pulmonary function and respiratory complications: a systematic review". Archives of Internal Medicine. 167 (3): 221–28. doi:10.1001/archinte.167.3.221. PMC 2720277. PMID 17296876.
- ^ Sorensen CJ, DeSanto K, Borgelt L, Phillips KT, Monte AA (March 2017). "Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome: Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment-a Systematic Review". Journal of Medical Toxicology. 13 (1): 71–87. doi:10.1007/s13181-016-0595-z. PMC 5330965. PMID 28000146.
- ^ Hashibe M, Straif K, Tashkin DP, Morgenstern H, Greenland S, Zhang ZF (April 2005). "Epidemiologic review of marijuana use and cancer risk". Alcohol. 35 (3): 265–75. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2005.04.008. PMID 16054989.
- ^ "Does smoking cannabis cause cancer?". Cancer Research UK. 20 September 2010. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
- ^ Tashkin, Donald (March 1997). "Effects of marijuana on the lung and its immune defenses". UCLA School of Medicine. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- ^ Gates P, Jaffe A, Copeland J (July 2014). "Cannabis smoking and respiratory health: consideration of the literature". Respirology. 19 (5): 655–62. doi:10.1111/resp.12298. PMID 24831571. S2CID 29423964.
- ^ Huang YH, Zhang ZF, Tashkin DP, Feng B, Straif K, Hashibe M (January 2015). "An epidemiologic review of marijuana and cancer: an update". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 24 (1): 15–31. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-1026. PMC 4302404. PMID 25587109.
- ^ Tashkin DP (June 2013). "Effects of marijuana smoking on the lung". Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 10 (3): 239–47. doi:10.1513/annalsats.201212-127fr. PMID 23802821. S2CID 20615545.
- ^ Gurney J, Shaw C, Stanley J, Signal V, Sarfati D (November 2015). "Cannabis exposure and risk of testicular cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis". BMC Cancer. 15 (1): 897. doi:10.1186/s12885-015-1905-6. PMC 4642772. PMID 26560314.
- ^ de Carvalho MF, Dourado MR, Fernandes IB, Araújo CT, Mesquita AT, Ramos-Jorge ML (December 2015). "Head and neck cancer among marijuana users: a meta-analysis of matched case-control studies". Archives of Oral Biology. 60 (12): 1750–55. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.09.009. PMID 26433192.
- ^ Loflin M, Earleywine M (2015). "No smoke, no fire: What the initial literature suggests regarding vapourized cannabis and respiratory risk". Canadian Journal of Respiratory Therapy. 51 (1): 7–9. PMC 4456813. PMID 26078621.
- ^ Riecher-Rössler A (2014). Comorbidity of Mental and Physical Disorders. Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. p. 88. ISBN 978-3-318-02604-7.
- ^ Ravi D, Ghasemiesfe M, Korenstein D, Cascino T, Keyhani S (February 2018). "Associations Between Marijuana Use and Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Outcomes: A Systematic Review". Annals of Internal Medicine. 168 (3): 187–94. doi:10.7326/M17-1548. PMC 6157910. PMID 29357394.
- ^ Thomas G, Kloner RA, Rezkalla S (January 2014). "Adverse cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and peripheral vascular effects of marijuana inhalation: what cardiologists need to know". The American Journal of Cardiology. 113 (1): 187–90. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.09.042. PMID 24176069.
- ^ Franz CA, Frishman WH (9 February 2016). "Marijuana Use and Cardiovascular Disease". Cardiology in Review. 24 (4): 158–62. doi:10.1097/CRD.0000000000000103. PMID 26886465. S2CID 205566342.
- ^ Greger, Jessica; Bates, Vernice; Mechtler, Laszlo; Gengo, Fran (2020). "A review of cannabis and interactions with anticoagulant and antiplatelet agents". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 60 (4): 432–38. doi:10.1002/jcph.1557. PMID 31724188. S2CID 208019237.
- ^ Shen, Jay J.; Shan, Guogen; Kim, Pearl C.; Yoo, Ji Won; Dodge-Francis, Carolee; Lee, Yong-Jae (2019). "Trends and Related Factors of Cannabis-Associated Emergency Department Visits in the United States: 2006–2014". Journal of Addiction Medicine. 13 (3): 193–200. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000479. ISSN 1932-0620. PMID 30418337. S2CID 53286585.
- ^ Shelton, Shelby K.; Mills, Eleanor; Saben, Jessica L.; Devivo, Michael; Williamson, Kayla; Abbott, Diana; Hall, Katelyn E.; Monte, Andrew A. (2020). "Why do patients come to the emergency department after using cannabis?". Clinical Toxicology. 58 (6): 453–59. doi:10.1080/15563650.2019.1657582. ISSN 1556-9519. PMC 7073292. PMID 31526057.
- ^ a b "National Estimates of Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits" (PDF). Drug Abuse Warning Network. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ Hayer S, Mandelbaum AD, Watch L, Ryan KS, Hedges MA, Manuzak JA, Easley CA, Schust DJ, Lo JO (July 2023). "Cannabis and Pregnancy: A Review". Obstet Gynecol Surv. 78 (7): 411–428. doi:10.1097/OGX.0000000000001159. PMC 10372687. PMID 37480292.
- ^ Bow, Eric (2016). "The Structure–Function Relationships of Classical Cannabinoids: CB1/CB2 Modulation". Perspectives in Medicinal Chemistry. 8: 17–39. doi:10.4137/PMC.S32171. PMC 4927043. PMID 27398024.
- ^ Thomas, A (2007). "Cannabidiol displays unexpectedly high potency as an antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists in vitro". Br J Pharmacol. 150 (5): 613–623. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707133. PMC 2189767. PMID 17245363.
- ^ Wilson RI, Nicoll RA (April 2002). "Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain". Science. 296 (5568): 678–82. Bibcode:2002Sci...296..678W. doi:10.1126/science.1063545. PMID 11976437. S2CID 21573145.
- ^ Oleson EB, Cheer JF (August 2012). "A brain on cannabinoids: the role of dopamine release in reward seeking". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine. 2 (8): a012229. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a012229. PMC 3405830. PMID 22908200.
- ^ Kathmann M, Flau K, Redmer A, Tränkle C, Schlicker E (February 2006). "Cannabidiol is an allosteric modulator at mu- and delta-opioid receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 372 (5): 354–61. doi:10.1007/s00210-006-0033-x. PMID 16489449. S2CID 4877869.
- ^ Hejazi N, Zhou C, Oz M, Sun H, Ye JH, Zhang L (March 2006). "Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and endogenous cannabinoid anandamide directly potentiate the function of glycine receptors". Molecular Pharmacology. 69 (3): 991–97. doi:10.1124/mol.105.019174. PMID 16332990. S2CID 21801428.
- ^ Xiong W, Cheng K, Cui T, Godlewski G, Rice KC, Xu Y, Zhang L (May 2011). "Cannabinoid potentiation of glycine receptors contributes to cannabis-induced analgesia". Nature Chemical Biology. 7 (5): 296–303. doi:10.1038/nchembio.552. PMC 3388539. PMID 21460829.
- ^ a b Hall W, Pacula RL (2003). Cannabis Use and Dependence: Public Health and Public Policy. Cambridge University Press. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-521-80024-2.
- ^ Hollister LE, et al. (March 1986). "Health aspects of cannabis". Pharma Review. 38 (38): 1–20. PMID 3520605. Archived from the original on 15 April 2013. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ Russo EB (2013). Cannabis and Cannabinoids: Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Potential. Routledge. p. 28. ISBN 978-1-136-61493-4.
- ^ Newton DE (2013). Marijuana: a reference handbook. Santa Barbara, Calif.: ABC-CLIO. p. 7. ISBN 9781610691499.
- ^ Baselt RC (2008). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man. Biomedical Publications. pp. 1513–18. ISBN 978-0-9626523-7-0.
- ^ Shaw LM, Kwong TC (2001). The Clinical Toxicology Laboratory: Contemporary Practice of Poisoning Evaluation. Amer. Assoc. for Clinical Chemistry. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-890883-53-9.
- ^ "The Non-Specificity of the Duquenois-Levine Field Test for Marijuana". ResearchGate.
- ^ Venkatratnam A, Lents NH (July 2011). "Zinc reduces the detection of cocaine, methamphetamine, and THC by ELISA urine testing". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 35 (6): 333–40. doi:10.1093/anatox/35.6.333. PMID 21740689.
- ^ Lin CN, Strathmann FG (10 July 2013). "Elevated urine zinc concentration reduces the detection of methamphetamine, cocaine, THC and opiates in urine by EMIT". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 37 (9): 665–69. doi:10.1093/jat/bkt056. PMID 23843421.
- ^ Joy JE, Watson SJ, Benson JA (1999). Marijuana and Medicine: Assessing The Science Base. Washington, D.C.: National Academy of Sciences Press. doi:10.17226/6376. ISBN 978-0-585-05800-9. PMID 25101425.
- ^ Elliott S. "The Ultimate Guide on Indicas vs. Sativas". Herb. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ Piomelli D, Russo EB (2016). "The Cannabis sativa Versus Cannabis indica Debate: An Interview with Ethan Russo, MD". Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. 1 (1): 44–46. doi:10.1089/can.2015.29003.ebr. PMC 5576603. PMID 28861479.
- ^ Iseger TA, Bossong MG (March 2015). "A systematic review of the antipsychotic properties of cannabidiol in humans". Schizophrenia Research. 162 (1–3): 153–61. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2015.01.033. PMID 25667194. S2CID 3745655.
- ^ a b c "Why Does Cannabis Potency Matter?". United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 29 June 2009.
- ^ "Cannabis strength soars over past half century". ScienceDaily. 16 November 2020.
- ^ ElSohly MA, Mehmedic Z, Foster S, Gon C, Chandra S, Church JC (2016). "Changes in Cannabis Potency Over the Last 2 Decades (1995–2014): Analysis of Current Data in the United States". Biological Psychiatry. 79 (7): 613–619. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.01.004. PMC 4987131. PMID 26903403.
- ^ Cascini F, Aiello C, Di Tanna G (March 2012). "Increasing delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ-9-THC) content in herbal cannabis over time: systematic review and meta-analysis". Current Drug Abuse Reviews. 5 (1): 32–40. doi:10.2174/1874473711205010032. PMID 22150622. S2CID 24350419.
- ^ Smith D (17 January 2014). "Cannabis and memory loss: dude, where's my CBD?". The Guardian.
- ^ "Cannabis Potency". National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre. Archived from the original on 6 December 2011. Retrieved 13 December 2011.
- ^ "BBC: Cannabis laws to be strengthened. May 2008 20:55 UK". BBC News. 7 May 2008. Retrieved 20 September 2010.
- ^ Di Forti M, Morgan C, Dazzan P, Pariante C, Mondelli V, Marques TR, Handley R, Luzi S, et al. (December 2009). "High-potency cannabis and the risk of psychosis". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 195 (6): 488–91. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.109.064220. PMC 2801827. PMID 19949195.
- ^ Hope, Christopher (6 February 2008). "Use of extra strong 'skunk' cannabis soars". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022.
- ^ Doweiko H (2011). Concepts of Chemical Dependency. Cengage Learning. p. 124. ISBN 978-1-133-17081-5.
- ^ "Fake Hanf: Ein Drogentrend schwappt in die Schweiz – was du darüber wissen musst". Watson (in German).
- ^ "Fake Hanf: Tödliches Marihuana hat bereits 61 Menschen getötet". Watson (in German).
- ^ "Fake Hanf mit synthetischen Cannabinoiden besprüht". drugcom (in German).
- ^ "Tödlicher Fake Hanf – Chemisch behandelte Hanfblüten – niemand kann sie erkennen". Schweizer Radio und Fernsehen (SRF) (in German). 14 August 2020.
- ^ "Growing Array of Street Drugs Now Laced with Fentanyl", MedPageToday, 17 July 2018
- ^ "Is the opioid epidemic now the fentanyl epidemic?" Archived 18 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine, The Baltimore Sun, 7 December 2018
- ^ "Medical officials oppose effort to legalize recreational use of marijuana", State Journal-Register, (Springfield, IL), 15 December 2018
- ^ a b Spanish Word Histories and Mysteries: English Words That Come From Spanish. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 2007. p. 142. ISBN 978-0-547-35021-9.
- ^ Potter G, Bouchard M, Decorte T (2013). World Wide Weed: Global Trends in Cannabis Cultivation and its Control (revised ed.). Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 17. ISBN 978-1-4094-9438-6.
- ^ Hall W, Pacula RL (2003). Cannabis Use and Dependence: Public Health and Public Policy. Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-521-80024-2.
- ^ United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (2009). Recommended Methods for the Identification and Analysis of Cannabis and Cannabis Products. United Nations Publications. p. 15. ISBN 978-92-1-148242-3.
- ^ a b Houck MM (2015). Forensic Chemistry. Elsevier Science. p. 131. ISBN 978-0-12-800624-5.
- ^ Adler PA, Adler P, O'Brien PK (2012). Drugs and the American Dream: An Anthology. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 330–. ISBN 978-0-470-67027-9.
- ^ Mosher CJ, Akins SM (2013). Drugs and Drug Policy: The Control of Consciousness Alteration. Sage Publications. p. 17. ISBN 978-1-4833-2188-2.
- ^ "Hemp Facts". Naihc.org. Archived from the original on 27 November 2012. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
- ^ Earleywine, Mitch (2002). Understanding Marijuana: A New Look at the Scientific Evidence. Oxford University Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-19-988143-7.
- ^ Rosenthal E (2002). Ask Ed: Marijuana Gold: Trash to Stash. QUICK AMER Publishing Company. p. 116. ISBN 978-0-932551-52-8.
- ^ "Kief". Cannabisculture.com. 9 March 2005. Archived from the original on 5 June 2009. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- ^ Bukszpan D (2012). Is That a Word?: From AA to ZZZ, the Weird and Wonderful Language of SCRABBLE. Chronicle Books. p. 94. ISBN 978-1-4521-0824-7.
- ^ "Hashish". dictionary.reference.com.
- ^


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch



