3D symmetry group
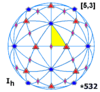
Selected point groups in three dimensions Involutional symmetry s , (*)Cyclic symmetry nv , (*nn)Dihedral symmetry nh , (*n22) Polyhedral group , [n,3], (*n32) Tetrahedral symmetry d , (*332)Octahedral symmetry h , (*432)Icosahedral symmetry h , (*532)
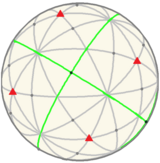
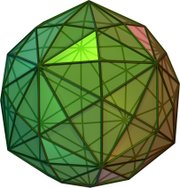
Icosahedral symmetry fundamental domains A soccer ball , a common example of a spherical truncated icosahedron , has full icosahedral symmetry. Rotations and reflections form the symmetry group of a great icosahedron . In mathematics, and especially in geometry, an object has icosahedral symmetry if it has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron . Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual of the icosahedron) and the rhombic triacontahedron .
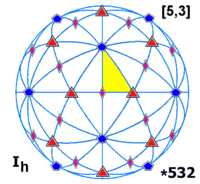
Every polyhedron with icosahedral symmetry has 60 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries and 60 orientation-reversing symmetries (that combine a rotation and a reflection ), for a total symmetry order of 120. The full symmetry group is the Coxeter group of type H3 . It may be represented by Coxeter notation [5,3] and Coxeter diagram alternating group A5 on 5 letters.
Icosahedral symmetry is a mathematical property of objects indicating that an object has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron .
Apart from the two infinite series of prismatic and antiprismatic symmetry, rotational icosahedral symmetry or chiral icosahedral symmetry of chiral objects and full icosahedral symmetry or achiral icosahedral symmetry are the discrete point symmetries (or equivalently, symmetries on the sphere ) with the largest symmetry groups .
Icosahedral symmetry is not compatible with translational symmetry , so there are no associated crystallographic point groups or space groups .
Presentations corresponding to the above are:
I : ⟨ s , t ∣ s 2 , t 3 , ( s t ) 5 ⟩ {\displaystyle I:\langle s,t\mid s^{2},t^{3},(st)^{5}\rangle \ } I h : ⟨ s , t ∣ s 3 ( s t ) − 2 , t 5 ( s t ) − 2 ⟩ . {\displaystyle I_{h}:\langle s,t\mid s^{3}(st)^{-2},t^{5}(st)^{-2}\rangle .\ } These correspond to the icosahedral groups (rotational and full) being the (2,3,5) triangle groups .
The first presentation was given by William Rowan Hamilton in 1856, in his paper on icosian calculus .[ 1]
Note that other presentations are possible, for instance as an alternating group (for I ).
The full symmetry group is the Coxeter group of type H3 . It may be represented by Coxeter notation [5,3] and Coxeter diagram alternating group A5 on 5 letters.
Every polyhedron with icosahedral symmetry has 60 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries and 60 orientation-reversing symmetries (that combine a rotation and a reflection ), for a total symmetry order of 120.
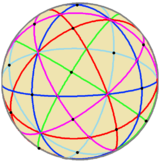
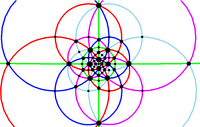
The edges of a spherical compound of five octahedra represent the 15 mirror planes as colored great circles. Each octahedron can represent 3 orthogonal mirror planes by its edges. The pyritohedral symmetry is an index 5 subgroup of icosahedral symmetry, with 3 orthogonal green reflection lines and 8 red order-3 gyration points. There are 5 different orientations of pyritohedral symmetry.
The icosahedral rotation group I I is isomorphic to A 5 , the alternating group of even permutations of five objects. This isomorphism can be realized by I acting on various compounds, notably the compound of five cubes (which inscribe in the dodecahedron ), the compound of five octahedra , or either of the two compounds of five tetrahedra (which are enantiomorphs , and inscribe in the dodecahedron). The group contains 5 versions of T h with 20 versions of D3 (10 axes, 2 per axis), and 6 versions of D5 .
The full icosahedral group Ih I as normal subgroup of index 2. The group Ih is isomorphic to I × Z 2 , or A 5 × Z 2 , with the inversion in the center corresponding to element (identity,-1), where Z 2 is written multiplicatively.
Ih acts on the compound of five cubes and the compound of five octahedra , but −1 acts as the identity (as cubes and octahedra are centrally symmetric). It acts on the compound of ten tetrahedra : I acts on the two chiral halves (compounds of five tetrahedra ), and −1 interchanges the two halves. Notably, it does not act as S5 , and these groups are not isomorphic; see below for details.
The group contains 10 versions of D3d and 6 versions of D5d (symmetries like antiprisms).
I is also isomorphic to PSL2 (5), but Ih is not isomorphic to SL2 (5).
Isomorphism of I with A5 [ edit ] It is useful to describe explicitly what the isomorphism between I and A5 looks like. In the following table, permutations Pi and Qi act on 5 and 12 elements respectively, while the rotation matrices Mi are the elements of I . If Pk is the product of taking the permutation Pi and applying Pj to it, then for the same values of i , j and k , it is also true that Qk is the product of taking Qi and applying Qj , and also that premultiplying a vector by Mk is the same as premultiplying that vector by Mi and then premultiplying that result with Mj , that is Mk = Mj × Mi . Since the permutations Pi are all the 60 even permutations of 12345, the one-to-one correspondence is made explicit, therefore the isomorphism too.
Rotation matrix Permutation of 5 Permutation of 12 M 1 = [ 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle M_{1}={\begin{bmatrix}1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} P 1 {\displaystyle P_{1}} Q 1 {\displaystyle Q_{1}} M 2 = [ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{2}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 2 {\displaystyle P_{2}} Q 2 {\displaystyle Q_{2}} M 3 = [ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{3}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 3 {\displaystyle P_{3}} Q 3 {\displaystyle Q_{3}} M 4 = [ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{4}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 4 {\displaystyle P_{4}} Q 4 {\displaystyle Q_{4}} M 5 = [ ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{5}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 5 {\displaystyle P_{5}} Q 5 {\displaystyle Q_{5}} M 6 = [ − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{6}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 6 {\displaystyle P_{6}} Q 6 {\displaystyle Q_{6}} M 7 = [ ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{7}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 7 {\displaystyle P_{7}} Q 7 {\displaystyle Q_{7}} M 8 = [ 0 − 1 0 0 0 1 − 1 0 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{8}={\begin{bmatrix}0&-1&0\\0&0&1\\-1&0&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 8 {\displaystyle P_{8}} Q 8 {\displaystyle Q_{8}} M 9 = [ − ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{9}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 9 {\displaystyle P_{9}} Q 9 {\displaystyle Q_{9}} M 10 = [ − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{10}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 10 {\displaystyle P_{10}} Q 10 {\displaystyle Q_{10}} M 11 = [ 0 0 − 1 − 1 0 0 0 1 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{11}={\begin{bmatrix}0&0&-1\\-1&0&0\\0&1&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 11 {\displaystyle P_{11}} Q 11 {\displaystyle Q_{11}} M 12 = [ 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{12}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 12 {\displaystyle P_{12}} Q 12 {\displaystyle Q_{12}} M 13 = [ 1 0 0 0 − 1 0 0 0 − 1 ] {\displaystyle M_{13}={\begin{bmatrix}1&0&0\\0&-1&0\\0&0&-1\end{bmatrix}}} P 13 {\displaystyle P_{13}} Q 13 {\displaystyle Q_{13}} M 14 = [ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{14}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 14 {\displaystyle P_{14}} Q 14 {\displaystyle Q_{14}} M 15 = [ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{15}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 15 {\displaystyle P_{15}} Q 15 {\displaystyle Q_{15}} M 16 = [ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{16}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 16 {\displaystyle P_{16}} Q 16 {\displaystyle Q_{16}} M 17 = [ − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{17}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 17 {\displaystyle P_{17}} Q 17 {\displaystyle Q_{17}} M 18 = [ ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{18}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 18 {\displaystyle P_{18}} Q 18 {\displaystyle Q_{18}} M 19 = [ − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{19}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 19 {\displaystyle P_{19}} Q 19 {\displaystyle Q_{19}} M 20 = [ 0 0 1 − 1 0 0 0 − 1 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{20}={\begin{bmatrix}0&0&1\\-1&0&0\\0&-1&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 20 {\displaystyle P_{20}} Q 20 {\displaystyle Q_{20}} M 21 = [ 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{21}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 21 {\displaystyle P_{21}} Q 21 {\displaystyle Q_{21}} M 22 = [ ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{22}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 22 {\displaystyle P_{22}} Q 22 {\displaystyle Q_{22}} M 23 = [ 0 1 0 0 0 − 1 − 1 0 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{23}={\begin{bmatrix}0&1&0\\0&0&-1\\-1&0&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 23 {\displaystyle P_{23}} Q 23 {\displaystyle Q_{23}} M 24 = [ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{24}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 24 {\displaystyle P_{24}} Q 24 {\displaystyle Q_{24}} M 25 = [ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{25}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 25 {\displaystyle P_{25}} Q 25 {\displaystyle Q_{25}} M 26 = [ ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{26}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 26 {\displaystyle P_{26}} Q 26 {\displaystyle Q_{26}} M 27 = [ − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{27}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 27 {\displaystyle P_{27}} Q 27 {\displaystyle Q_{27}} M 28 = [ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{28}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 28 {\displaystyle P_{28}} Q 28 {\displaystyle Q_{28}} M 29 = [ − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{29}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 29 {\displaystyle P_{29}} Q 29 {\displaystyle Q_{29}} M 30 = [ ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{30}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 30 {\displaystyle P_{30}} Q 30 {\displaystyle Q_{30}} M 31 = [ − ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{31}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 31 {\displaystyle P_{31}} Q 31 {\displaystyle Q_{31}} M 32 = [ 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{32}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 32 {\displaystyle P_{32}} Q 32 {\displaystyle Q_{32}} M 33 = [ 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{33}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 33 {\displaystyle P_{33}} Q 33 {\displaystyle Q_{33}} M 34 = [ 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{34}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 34 {\displaystyle P_{34}} Q 34 {\displaystyle Q_{34}} M 35 = [ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{35}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 35 {\displaystyle P_{35}} Q 35 {\displaystyle Q_{35}} M 36 = [ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{36}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 36 {\displaystyle P_{36}} Q 36 {\displaystyle Q_{36}} M 37 = [ ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{37}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 37 {\displaystyle P_{37}} Q 37 {\displaystyle Q_{37}} M 38 = [ 0 − 1 0 0 0 − 1 1 0 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{38}={\begin{bmatrix}0&-1&0\\0&0&-1\\1&0&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 38 {\displaystyle P_{38}} Q 38 {\displaystyle Q_{38}} M 39 = [ − ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{39}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 39 {\displaystyle P_{39}} Q 39 {\displaystyle Q_{39}} M 40 = [ − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{40}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 40 {\displaystyle P_{40}} Q 40 {\displaystyle Q_{40}} M 41 = [ 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{41}={\begin{bmatrix}0&0&1\\1&0&0\\0&1&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 41 {\displaystyle P_{41}} Q 41 {\displaystyle Q_{41}} M 42 = [ 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{42}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 42 {\displaystyle P_{42}} Q 42 {\displaystyle Q_{42}} M 43 = [ − ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{43}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 43 {\displaystyle P_{43}} Q 43 {\displaystyle Q_{43}} M 44 = [ 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{44}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 44 {\displaystyle P_{44}} Q 44 {\displaystyle Q_{44}} M 45 = [ 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{45}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 45 {\displaystyle P_{45}} Q 45 {\displaystyle Q_{45}} M 46 = [ 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{46}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 46 {\displaystyle P_{46}} Q 46 {\displaystyle Q_{46}} M 47 = [ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{47}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 47 {\displaystyle P_{47}} Q 47 {\displaystyle Q_{47}} M 48 = [ − 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 − 1 ] {\displaystyle M_{48}={\begin{bmatrix}-1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&-1\end{bmatrix}}} P 48 {\displaystyle P_{48}} Q 48 {\displaystyle Q_{48}} M 49 = [ − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{49}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 49 {\displaystyle P_{49}} Q 49 {\displaystyle Q_{49}} M 50 = [ 0 0 − 1 1 0 0 0 − 1 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{50}={\begin{bmatrix}0&0&-1\\1&0&0\\0&-1&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 50 {\displaystyle P_{50}} Q 50 {\displaystyle Q_{50}} M 51 = [ 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{51}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 51 {\displaystyle P_{51}} Q 51 {\displaystyle Q_{51}} M 52 = [ ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{52}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 52 {\displaystyle P_{52}} Q 52 {\displaystyle Q_{52}} M 53 = [ 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 ] {\displaystyle M_{53}={\begin{bmatrix}0&1&0\\0&0&1\\1&0&0\end{bmatrix}}} P 53 {\displaystyle P_{53}} Q 53 {\displaystyle Q_{53}} M 54 = [ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{54}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 54 {\displaystyle P_{54}} Q 54 {\displaystyle Q_{54}} M 55 = [ 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{55}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 55 {\displaystyle P_{55}} Q 55 {\displaystyle Q_{55}} M 56 = [ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ] {\displaystyle M_{56}={\begin{bmatrix}-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\end{bmatrix}}} P 56 {\displaystyle P_{56}} Q 56 {\displaystyle Q_{56}} M 57 = [ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{57}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 57 {\displaystyle P_{57}} Q 57 {\displaystyle Q_{57}} M 58 = [ 1 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{58}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 58 {\displaystyle P_{58}} Q 58 {\displaystyle Q_{58}} M 59 = [ 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ϕ 2 1 2 ϕ − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 − 1 2 ϕ ] {\displaystyle M_{59}={\begin{bmatrix}{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2\phi }}&-{\frac {\phi }{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2\phi }}\end{bmatrix}}} P 59 {\displaystyle P_{59}} Q 59 {\displaystyle Q_{59}} M 60 = [ − 1 0 0 0 − 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle M_{60}={\begin{bmatrix}-1&0&0\\0&-1&0\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}}} P 60 {\displaystyle P_{60}} Q 60 {\displaystyle Q_{60}}
Commonly confused groups [ edit ] The following groups all have order 120, but are not isomorphic:
They correspond to the following short exact sequences (the latter of which does not split) and product
1 → A 5 → S 5 → Z 2 → 1 {\displaystyle 1\to A_{5}\to S_{5}\to Z_{2}\to 1} I h = A 5 × Z 2 {\displaystyle I_{h}=A_{5}\times Z_{2}} 1 → Z 2 → 2 I → A 5 → 1 {\displaystyle 1\to Z_{2}\to 2I\to A_{5}\to 1} In words,
A 5 {\displaystyle A_{5}} normal subgroup S 5 {\displaystyle S_{5}} A 5 {\displaystyle A_{5}} factor of I h {\displaystyle I_{h}} direct product A 5 {\displaystyle A_{5}} quotient group 2 I {\displaystyle 2I} Note that A 5 {\displaystyle A_{5}} exceptional irreducible 3-dimensional representation (as the icosahedral rotation group), but S 5 {\displaystyle S_{5}}
These can also be related to linear groups over the finite field with five elements, which exhibit the subgroups and covering groups directly; none of these are the full icosahedral group:
A 5 ≅ PSL ( 2 , 5 ) , {\displaystyle A_{5}\cong \operatorname {PSL} (2,5),} projective special linear group , see here for a proof; S 5 ≅ PGL ( 2 , 5 ) , {\displaystyle S_{5}\cong \operatorname {PGL} (2,5),} projective general linear group ; 2 I ≅ SL ( 2 , 5 ) , {\displaystyle 2I\cong \operatorname {SL} (2,5),} special linear group .The 120 symmetries fall into 10 conjugacy classes.
conjugacy classes I additional classes of Ih identity, order 1 12 × rotation by ±72°, order 5, around the 6 axes through the face centers of the dodecahedron 12 × rotation by ±144°, order 5, around the 6 axes through the face centers of the dodecahedron 20 × rotation by ±120°, order 3, around the 10 axes through vertices of the dodecahedron 15 × rotation by 180°, order 2, around the 15 axes through midpoints of edges of the dodecahedron central inversion, order 2 12 × rotoreflection by ±36°, order 10, around the 6 axes through the face centers of the dodecahedron 12 × rotoreflection by ±108°, order 10, around the 6 axes through the face centers of the dodecahedron 20 × rotoreflection by ±60°, order 6, around the 10 axes through the vertices of the dodecahedron 15 × reflection, order 2, at 15 planes through edges of the dodecahedron
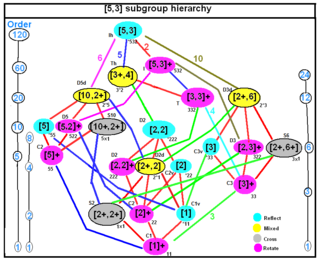
Subgroups of the full icosahedral symmetry group [ edit ] Subgroup relations Chiral subgroup relations Each line in the following table represents one class of conjugate (i.e., geometrically equivalent) subgroups. The column "Mult." (multiplicity) gives the number of different subgroups in the conjugacy class.
Explanation of colors: green = the groups that are generated by reflections, red = the chiral (orientation-preserving) groups, which contain only rotations.
The groups are described geometrically in terms of the dodecahedron.
The abbreviation "h.t.s.(edge)" means "halfturn swapping this edge with its opposite edge", and similarly for "face" and "vertex".
Schön. Coxeter Orb. H-M Structure Cyc. Order Index Mult. Description Ih [5,3] *532 53 2/mA5 ×Z2 120 1 1 full group D2h [2,2] *222 mmm D4 ×D2 =D2 3 8 15 5 fixing two opposite edges, possibly swapping them C5v [5] *55 5m D10 10 12 6 fixing a face C3v [3] *33 3m D6 =S3 6 20 10 fixing a vertex C2v [2] *22 2mm D4 =D2 2 4 30 15 fixing an edge Cs [ ] * 2 or mD2 2 60 15 reflection swapping two endpoints of an edge Th [3+ ,4] 3*2 m3 A4 ×Z2 24 5 5 pyritohedral group D5d [2+ ,10] 2*5 10 m2D20 =Z2 ×D10 20 6 6 fixing two opposite faces, possibly swapping them D3d [2+ ,6] 2*3 3 mD12 =Z2 ×D6 12 10 10 fixing two opposite vertices, possibly swapping them D1d = C2h [2+ ,2] 2* 2/m D4 =Z2 ×D2 4 30 15 halfturn around edge midpoint, plus central inversion S10 [2+ ,10+ ] 5× 5 Z10 =Z2 ×Z5 10 12 6 rotations of a face, plus central inversion S6 [2+ ,6+ ] 3× 3 Z6 =Z2 ×Z3 6 20 10 rotations about a vertex, plus central inversion S2 [2+ ,2+ ] × 1 Z2 2 60 1 central inversion I [5,3]+ 532 532 A5 60 2 1 all rotations T [3,3]+ 332 332 A4 12 10 5 rotations of a contained tetrahedron D5 [2,5]+ 522 522 D10 10 12 6 rotations around the center of a face, and h.t.s.(face) D3 [2,3]+ 322 322 D6 =S3 6 20 10 rotations around a vertex, and h.t.s.(vertex) D2 [2,2]+ 222 222 D4 =Z2 2 4 30 5 halfturn around edge midpoint, and h.t.s.(edge) C5 [5]+ 55 5 Z5 5 24 6 rotations around a face center C3 [3]+ 33 3 Z3 =A3 3 40 10 rotations around a vertex C2 [2]+ 22 2 Z2 2 60 15 half-turn around edge midpoint C1 [ ]+ 11 1 Z1 1 120 1 trivial group
Stabilizers of an opposite pair of vertices can be interpreted as stabilizers of the axis they generate.
vertex stabilizers in I give cyclic groups C 3 vertex stabilizers in Ih give dihedral groups D 3 stabilizers of an opposite pair of vertices in I give dihedral groups D 3 stabilizers of an opposite pair of vertices in Ih give D 3 × ± 1 {\displaystyle D_{3}\times \pm 1} Stabilizers of an opposite pair of edges can be interpreted as stabilizers of the rectangle they generate.
edges stabilizers in I give cyclic groups Z 2 edges stabilizers in Ih give Klein four-groups Z 2 × Z 2 {\displaystyle Z_{2}\times Z_{2}} stabilizers of a pair of edges in I give Klein four-groups Z 2 × Z 2 {\displaystyle Z_{2}\times Z_{2}} stabilizers of a pair of edges in Ih give Z 2 × Z 2 × Z 2 {\displaystyle Z_{2}\times Z_{2}\times Z_{2}} Stabilizers of an opposite pair of faces can be interpreted as stabilizers of the antiprism they generate.
face stabilizers in I give cyclic groups C 5 face stabilizers in Ih give dihedral groups D 5 stabilizers of an opposite pair of faces in I give dihedral groups D 5 stabilizers of an opposite pair of faces in Ih give D 5 × ± 1 {\displaystyle D_{5}\times \pm 1} Polyhedron stabilizers [ edit ] For each of these, there are 5 conjugate copies, and the conjugation action gives a map, indeed an isomorphism, I → ∼ A 5 < S 5 {\displaystyle I{\stackrel {\sim }{\to }}A_{5}<S_{5}}
stabilizers of the inscribed tetrahedra in I are a copy of T stabilizers of the inscribed tetrahedra in Ih are a copy of T stabilizers of the inscribed cubes (or opposite pair of tetrahedra, or octahedra) in I are a copy of T stabilizers of the inscribed cubes (or opposite pair of tetrahedra, or octahedra) in Ih are a copy of Th Coxeter group generators [ edit ] The full icosahedral symmetry group [5,3] (0 , R1 , R2 below, with relations R0 2 = R1 2 = R2 2 = (R0 ×R1 )5 = (R1 ×R2 )3 = (R0 ×R2 )2 = Identity. The group [5,3]+ (0,1 , S1,2 , S0,2 . A rotoreflection of order 10 is generated by V0,1,2 , the product of all 3 reflections. Here ϕ = 5 + 1 2 {\displaystyle \phi ={\tfrac {{\sqrt {5}}+1}{2}}} golden ratio .
[5,3], Reflections Rotations Rotoreflection Name R0 R1 R2 S0,1 S1,2 S0,2 V0,1,2 Group Order 2 2 2 5 3 2 10 Matrix [ − 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]} [ 1 − ϕ 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 1 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 − ϕ 2 ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]} [ 1 0 0 0 − 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0\\0&-1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]} [ ϕ − 1 2 ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 1 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 − ϕ 2 ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]} [ 1 − ϕ 2 ϕ 2 − 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]} [ − 1 0 0 0 − 1 0 0 0 1 ] {\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&0&0\\0&-1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]} [ ϕ − 1 2 − ϕ 2 1 2 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 1 − ϕ 2 − 1 2 ϕ − 1 2 ϕ 2 ] {\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]} (1,0,0)n ( ϕ 2 , 1 2 , ϕ − 1 2 ) {\displaystyle ({\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {\phi }{2}},{\frac {1}{2}},{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}\end{smallmatrix}})} n (0,1,0)n ( 0 , − 1 , ϕ ) {\displaystyle (0,-1,\phi )} axis ( 1 − ϕ , 0 , ϕ ) {\displaystyle (1-\phi ,0,\phi )} axis ( 0 , 0 , 1 ) {\displaystyle (0,0,1)} axis
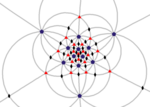
Fundamental domains for the icosahedral rotation group and the full icosahedral group are given by:
In the disdyakis triacontahedron one full face is a fundamental domain; other solids with the same symmetry can be obtained by adjusting the orientation of the faces, e.g. flattening selected subsets of faces to combine each subset into one face, or replacing each face by multiple faces, or a curved surface.
Polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry [ edit ] Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual of the icosahedron) and the rhombic triacontahedron .
Full icosahedral symmetry [ edit ] 







![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . The set of rotational symmetries forms a subgroup that is isomorphic to the alternating group A5 on 5 letters.
. The set of rotational symmetries forms a subgroup that is isomorphic to the alternating group A5 on 5 letters. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . The set of rotational symmetries forms a subgroup that is isomorphic to the alternating group A5 on 5 letters.
. The set of rotational symmetries forms a subgroup that is isomorphic to the alternating group A5 on 5 letters. 








![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ) of order 120 has generators represented by the reflection matrices R0, R1, R2 below, with relations R02 = R12 = R22 = (R0×R1)5 = (R1×R2)3 = (R0×R2)2 = Identity. The group [5,3]+ (
) of order 120 has generators represented by the reflection matrices R0, R1, R2 below, with relations R02 = R12 = R22 = (R0×R1)5 = (R1×R2)3 = (R0×R2)2 = Identity. The group [5,3]+ (![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ) of order 60 is generated by any two of the rotations S0,1, S1,2, S0,2. A rotoreflection of order 10 is generated by V0,1,2, the product of all 3 reflections. Here denotes the golden ratio.
) of order 60 is generated by any two of the rotations S0,1, S1,2, S0,2. A rotoreflection of order 10 is generated by V0,1,2, the product of all 3 reflections. Here denotes the golden ratio. 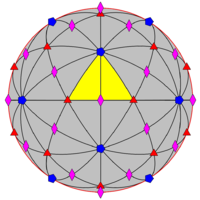






 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch





































































































































































































![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b81bf2648cef2b0f3cb2f82f0f0bcba89c595af1)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/94a2f124af793abcdec2a757fa54eacd8e12183f)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0\\0&-1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0d98311a57b2d6575867fb3100199be36b656299)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bef78ac2c56b1aeecf4b2ee91fa450dd1b0bbc29)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8c62a981424dfb7bce1a413d58b0ee62a9322924)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&0&0\\0&-1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/29ecfba65b611468342e533ba54ae7b9f240f3bb)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {-\phi }{2}}&{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {1-\phi }{2}}\\{\frac {-1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi -1}{2}}&{\frac {\phi }{2}}\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4f358516e6f6d9c29e3ca1c9f6bac53e18019636)



