Eastern Time Zone
| Eastern Time Zone | |
|---|---|
| Time zone | |
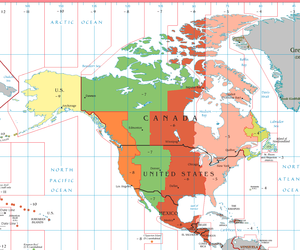 Eastern Time Zone | |
| UTC offset | |
| EST | UTC−05:00 |
| EDT | UTC−04:00 |
| Current time | |
| 17:34, 31 October 2024 EST [refresh] 18:34, 31 October 2024 EDT [refresh] | |
| Observance of DST | |
| DST is observed in parts of this time zone. | |
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, and the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico.
Places that use:
- Eastern Standard Time (EST), when observing standard time (autumn/winter), are five hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−05:00).
- Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), when observing daylight saving time (spring/summer), are four hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−04:00).
On the second Sunday in March, at 2:00 a.m. EST, clocks are advanced to 3:00 a.m. EDT leaving a one-hour gap. On the first Sunday in November, at 2:00 a.m. EDT, clocks are moved back to 1:00 a.m. EST, which results in one hour being duplicated.
History
[edit]The boundaries of the Eastern Time Zone have moved westward since the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) took over time-zone management from railroads in 1938. The easternmost and northernmost counties in Kentucky were added to the zone in the 1940s, and in 1961 most of the state went Eastern. In 2000, Wayne County, on the Tennessee border, switched from Central to Eastern Time.[1] Within the United States, the Eastern Time Zone is the most populous region, with nearly half of the country's population.
In March 2019, the Florida Legislature passed a bill requesting authorization from Congress for year-round daylight saving time, which would effectively put Florida on Atlantic Standard Time year-round (except for west of the Apalachicola River, which would be on Eastern Standard Time year-round).[2] A similar bill was proposed for the Canadian province of Ontario by its legislative assembly in late 2020, which would have a similar effect on the province if passed.[3]
Daylight saving time
[edit]For those in the United States, daylight saving time for the Eastern Time Zone was introduced by the Uniform Time Act of 1966, which specified that daylight saving time would run from the last Sunday of April until the last Sunday in October.[4] The act was amended to make the first Sunday in April the beginning of daylight saving time beginning in 1987.[4]
Later, the Energy Policy Act of 2005 extended daylight saving time in the United States, beginning in 2007. Since then, local times change at 2:00 a.m. EST to 3:00 a.m. EDT on the second Sunday in March, and return from 2:00 a.m. EDT to 1:00 a.m. EST on the first Sunday in November.[4]
In Canada, daylight saving time begins and ends on the same days and at the same times as it does in the United States.[5][6]
Canada
[edit]In Canada, the following provinces and territories are part of the Eastern Time Zone:[7] Within Canada, as with the United States, the Eastern Time Zone is the most populous time zone.
Most of Canada observes daylight saving time synchronously with the United States, with the exception of Saskatchewan, Yukon,[8] and several other very localized areas. None of those areas are in the Eastern Time Zone.
United States
[edit]The boundary between time zones is set forth in the Code of Federal Regulations, with the boundary between the Eastern and Central Time Zones being specifically detailed in 49 C.F.R. part 71.[9]
Washington, D.C., and 17 states are located entirely within the Eastern Time Zone. They are:
Five states are divided between the Eastern Time Zone and the Central Time Zone. The following locations observe Eastern Time:
- Florida: The majority of the state, including Big Bend regions east of the Apalachicola River and portions of Gulf County south of the Intracoastal Waterway
- Indiana: The majority of the state, except Northwest Indiana and the Evansville metropolitan area.
- Kentucky: The eastern portion of the state, including its three largest metropolitan areas: Louisville, Lexington, and Northern Kentucky
- Michigan: The entire state except for the four Upper Peninsula counties that border Wisconsin: Gogebic, Iron, Dickinson, and Menominee
- Tennessee: All of East Tennessee including the major cities of Chattanooga, Knoxville and the Tri-Cities region, with the exception of Bledsoe, Cumberland, and Marion counties[10]
Additionally, Phenix City, Alabama, and several nearby communities in Russell County, Alabama, unofficially observe Eastern Time.[11] This is due to their close proximity to Columbus, Georgia, which is on Eastern Time. In addition Smiths Station in Lee County along with Valley and Lanett in Chambers county honor Eastern Time.[12]
Mexico
[edit]- Quintana Roo: This is the only Mexican state to observe EST. It moved from Central Time to Eastern Time after a successful lobbying effort by tourism interests.[13] Quintana Roo does not observe daylight saving time.
Caribbean islands
[edit]The Bahamas and Haiti officially observe both Eastern Standard Time during the winter months and Eastern Daylight Time during the summer months. Cuba generally follows the U.S. with Eastern Standard Time in the winter, and Eastern Daylight Time in the summer, but the exact day of change varies year to year. The Cayman Islands and Jamaica use Eastern Standard Time year-round.[citation needed]
Turks and Caicos Islands
[edit]The Turks and Caicos Islands followed Eastern Time with daylight saving until 2015, when the territory switched to the Atlantic Time Zone. The Turks and Caicos Islands switched back to the pre-2015 schedule in March 2018.[14] A 2017 consultation paper highlighted the advantage for business and tourism of being in the same time zone as the eastern United States as an important factor in the decision.[15]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Why Louisville?". Louisville magazine. Archived from the original on July 20, 2018. Retrieved February 10, 2018.
- ^ Klas, Mary Ellen (March 6, 2018). "Legislature approves year-round daylight saving time—but it's not a done deal yet". Miami Herald. Retrieved March 30, 2018.
- ^ Patton, Jessica (October 7, 2020). "Ontario MPP puts forward bill to make Daylight Saving Time standard time". Global News. Retrieved October 9, 2020.
- ^ a b c Prerau, David (2006). "Early adoption and U.S. Law". Daylight Saving Time. Web Exhibit. Retrieved April 23, 2007.
- ^ Law, Gwillim (September 21, 2007). "United States Time Zones".
- ^ "Daylight Saving Time Starts Sunday". Government of Ontario. March 7, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2010.
- ^ "Time zones and daylight saving time". nrc.canada.ca. National Research Council Canada. March 23, 2019. Retrieved March 7, 2020.
- ^ "Yukon to end seasonal time change". yukon.ca. March 4, 2020. Retrieved May 13, 2022.
- ^ The specification for the Eastern Time Zone is set forth at 49 C.F.R. § 71.4, and is listed in text Archived January 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine and PDF Archived January 14, 2012, at the Wayback Machine formats. The boundary between Eastern and Central is set forth at 49 C.F.R. § 71.5, and is listed in text and PDF Archived January 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine formats.
- ^ McDearman, Brian (August 13, 2006). "Parts of Eastern Alabama split between 2 time zones". Decatur Daily. AP. Archived from the original on March 10, 2016. Retrieved March 22, 2009.
- ^ Emily. "Our Community". Phenix City, Alabama. Retrieved January 10, 2022.
- ^ https://www.al.com/living/2017/02/do_you_know_which_alabama_town.html
- ^ "On Mexican Time: Changing Time Zones To Accommodate Tourism". Forbes. Retrieved January 29, 2015.
- ^ "DST Dates Confirmed". Timeanddate.com. July 25, 2017. Retrieved January 10, 2019.
- ^ "Consultation paper Daylight Saving" (PDF). April 2017. pp. 6–7. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 10, 2019. Retrieved January 10, 2019.
External links
[edit]- Official U.S. time in the Eastern time zone (archived April 24, 2007)
- North American Time Zone border data and images
- World time zone map Archived December 24, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- U.S. time zone map Archived February 15, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- History of U.S. time zones and UTC conversion Archived August 8, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- Canada time zone map
- Federal Regulations defining time zones (archived May 28, 2010)


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch