2021 Czech parliamentary election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 200 seats in the Chamber of Deputies 101 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 65.39% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parliamentary elections were held in the Czech Republic on 8 and 9 October 2021. All 200 members of the Chamber of Deputies were elected, with the leader of the resulting government to become the Prime Minister of the Czech Republic. Following the 2017 parliamentary elections, the country had been ruled by a minority government consisting of ANO 2011 (ANO), led by prime minister Andrej Babiš, and the Czech Social Democratic Party (ČSSD), led by interior minister Jan Hamáček, with confidence and supply support from the Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia (KSČM) until April 2021. The largest opposition party was the Civic Democratic Party (ODS), followed by the Czech Pirate Party. Other parties in the Chamber of Deputies included SPD, TOP 09, STAN, and KDU-ČSL.
Babiš ran again as leader of ANO, and the main opposition parliamentary parties formed two electoral alliances, SPOLU and Pirates and Mayors (abbreviated to PirStan or PaS). ANO was front runner of the election, as it was polling first ahead of SPOLU and PirStan prior to the election.[1][2][3] The result was a surprise victory for the liberal conservative alliance SPOLU, which received the highest number of votes, while the populist ANO received the highest number of seats.[4] No opinion poll placed Spolu in the first place prior to the vote.[5] It was the closest parliamentary election in the history of Czech Republic.[6]
The opposition parties won a majority in the Chamber of Deputies and agreed to form a coalition government with SPOLU leader Petr Fiala as the new prime minister.[7][8][9] Traditional left-wing parties ČSSD and KSČM failed to reach the 5% threshold to win any seats in the Chamber of Deputies for the first time since the dissolution of Czechoslovakia in 1993.[10] The Pirates, which were one of the leading opposition parties, were heavily defeated due to preferential votes and won just 4 seats in the Chamber of Deputies.[11] Petr Fiala was appointed as the new prime minister on 28 November 2021 while rest of the new cabinet was appointed on 17 December 2021.
Background
[edit]According to the Constitution of the Czech Republic, an election to the Chamber of Deputies, the lower house of the Czech parliament, must be held every four years. The government is answerable to the Chamber of Deputies and remains in power only with the confidence of the majority of members of parliament. Article 19(1) of the constitution states that any citizen of the Czech Republic who has right to vote and is 21 years old is eligible to serve as an MP.[12]
ANO 2011 (ANO) emerged as the largest party in the 2017 parliamentary election and formed a minority government, which then lost a vote of confidence on 16 January 2018. The party formed a coalition government with the Czech Social Democratic Party (ČSSD), supported by the Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia (KSČM), which lasted until April 2021. Andrej Babiš became the new prime minister. The Civic Democratic Party (ODS) emerged as the second largest party and main opposition party, narrowly ahead of the Czech Pirate Party.[13]
2018 Senate and municipal elections
[edit]In 2018, voters elected 27 of 81 members of the Senate and approximately 61,900 members of local councils. ODS won the Senate election with 10 senators elected.[14] ANO won the municipal elections in most regional cities, with ODS finishing first in Prague and STAN in Liberec.[15] ČSSD and KSČM lost over half of their votes and seats in municipal councils.[16][17]
2019 European Parliament election
[edit]In May 2019, voters elected 21 members of the European Parliament. ANO came first, with ODS and the Pirates close behind in number of seats. As ČSSD failed to achieve more than 5 percent of votes in national elections for the first time since the mid-1990s, it did not get any seat.[18][19][20]
2020 Senate and regional elections
[edit]In October 2020, voters elected 675 members of regional assemblies in 13 regions of the nation, except Prague, which then formed regional governments. ANO won the election with 21.8% of votes but opposition parties, especially the Pirates, made gains, while allies of ANO were heavily defeated.[21][22][23] The governing parties were also heavily defeated in the Senate elections, which were won by Mayors and Independents ahead of ODS.[24]
Coalitions of political parties
[edit]Following these elections, opposition parties began negotiations about potential electoral alliances. It was speculated that two electoral blocs would be formed: a conservative bloc led by ODS, which would also include KDU-ČSL and TOP 09, with Petr Fiala as leader, and a liberal bloc composed of the Pirates and Mayors and Independents, with Ivan Bartoš as the leader.[25]
The ODS leadership agreed to form an alliance on 25 October 2020, with a memorandum to be signed two days later.[26] On 27 October 2020, Fiala, Marian Jurečka, and Markéta Pekarová Adamová announced that ODS, KDU-ČSL, and TOP 09 would form an electoral alliance for the next parliamentary election, with ODS leader Fiala as the alliance's candidate for prime minister.[27] On 11 November 2020, the parties agreed that ODS would nominate the leaders of the election lists in nine regions, KDU-ČSL in three regions, and TOP 09 in two regions.[28] The name of the alliance was announced as SPOLU, meaning "Together" in English.[29] Fiala was confirmed as the alliance's candidate for prime minister on 16 December 2020.[30]

The leadership of Mayors and Independents agreed to start negotiations on 8 October 2020.[31] The Pirates are required to ratify any alliance in a members' referendum. In a poll on 20 October 2020, 51% of Pirate members were opposed to the alliance while 43% supported it. The referendum to starting negotiations for an alliance was originally scheduled for 13 to 16 November 2020[32] but was rescheduled for 20 to 23 November 2020.[33] Among Pirate members, 695 out of 858 voted in favour of negotiations, with a turnout of 80%.[34] Ivan Bartoš was nominated to be the Pirate's election leader on 25 November 2020,[35] and was confirmed on 2 December 2020. The Pirates also offered the Green Party the possibility to join its electoral list.[36] Bartoš was confirmed as the alliance's electoral leader on 14 December 2020.[37] Pirate members voted to approve the alliance on 13 January 2021.[38]
ČSSD started to negotiate the formation of a third electoral bloc in January 2021, negotiating with the Green Party and some regional parties about the formation of a left-wing electoral alliance.[39] The Green Party stated as a condition for joining an alliance that the parties would not form a government coalition with ANO after the election.[40]
In early 2021, the Tricolour Citizens' Movement, Svobodní, the Freeholder Party of the Czech Republic, and other minor parties began negotiations about a potential alliance.[41] On 5 March 2021, these three parties confirmed the formation of a coalition, stating that they would run either in a formal electoral alliance or as a single party, depending on the new electoral law.[42] The Independence Party of the Czech Republic declared support for this coalition soon after.[43] On 23 March 2021, Tricolour leader Václav Klaus Jr. resigned from all political functions for personal reasons.[44] Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková became acting leader of the party.[45]
On 23 March 2021, a group of minor parties including the Alliance for the Future, Agrarian Democratic Party, Order of the Nation, and Democratic Green Party formed an electoral alliance, the Alliance for the Future, with Pavel Sehnal as leader.[46] The Party of Common Sense also subsequently joined the alliance.[47]
Some commentators have described the election as a "hidden referendum" on membership of the European Union (EU).[48][49][50]
Electoral system
[edit]
During the 2017 parliamentary election, the 200 members of the Chamber of Deputies were elected from 14 multi-member constituencies by open list proportional representation with an electoral threshold of 5%. It was raised to 10% for two-party political alliances, 15% for three-party alliances, and 20% for alliances of four or more parties. Seats were allocated using the D'Hondt method. Voters can give preference votes to up to four candidates on a list. Candidates who receive preferential votes from more than 5% of voters are moved to the top of their list; in cases where more than one candidate receives over 5% of the preferential votes, they are ranked in order of votes received.[51]
Although it was expected that the 2021 parliamentary election would take place using the same electoral system, the Constitutional Court ruled on a complaint submitted by a group of senators from Mayors and Independents, KDU-ČSL, and TOP 09 that the electoral system was unproportional and favoured larger parties. It focused on the D'Hondt method, the division of the country into 14 constituencies, and the increased electoral threshold for alliances.[52] The Constitutional Court's decision, published on 3 February 2021, set the threshold for alliances at 5% and removed some provisions relating to seat allocation.[53] New provisions were put into law before the election, establishing a threshold of 5% for single parties, 8% for coalitions of two parties, and 11% for coalitions of three or more parties.[54]
Registration process
[edit]The deadline to submit candidate lists for election was 4 August 2021. As of 2 August 2021, 29 subjects had made an application to the registration bureau.[55] All of them were approved by the bureau and permitted to run.[56]
Observers
[edit]Czech Republic invited experts from Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) and Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights (ODIHR) to observe election.[57] OSCE provided four observers.[58]
Covid-19 pandemic
[edit]
As with the regional elections in 2020, the pandemic emergency, covered by the pandemic law,[59] allowed for the establishment of special polling stations for people in isolation or quarantine, as well as drive-in voting locations. Disinfection and respiratory protection were provided to ensure hygienic conditions in traditional polling stations. Special election dates were announced on 6 and 7 October 2021.[60]
Local referendums
[edit]Simultaneously with the election, there were local referendums held in 20 cities and towns: Blšany u Loun, Blučina, Bzenec, Dačice, Drnholec, Jáchymov, Jezeřany-Maršovice, Katovice, Losiná, Pardubice, Podolí, Příkosice, Řevnice, Slavonice, Sušice, Ševětín, Temelín, Třemošnice, Velký Beranov, Zduchovice and Stará Bělá (part of Ostrava).[61][62]
Political parties
[edit]The table below lists political parties represented in the Chamber of Deputies after the 2017 parliamentary election.
| Name | Ideology | Position | Leader | 2017 result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes (%) | Seats | |||||
| ANO | Populism | Centre to centre-right | Andrej Babiš | 29.6% | 78 / 200 | |
| ODS | Liberal conservatism | Centre-right to right-wing | Petr Fiala | 11.3% | 25 / 200 | |
| Pirates | Pirate politics | Centre to centre-left | Ivan Bartoš | 10.8% | 22 / 200 | |
| SPD | Right-wing populism | Right-wing to far-right | Tomio Okamura | 10.6% | 22 / 200 | |
| KSČM | Communism | Left-wing to far-left | Vojtěch Filip | 7.8% | 15 / 200 | |
| ČSSD | Social democracy | Centre-left | Jan Hamáček | 7.3% | 15 / 200 | |
| KDU-ČSL | Christian democracy | Centre to centre-right | Marian Jurečka | 5.8% | 10 / 200 | |
| TOP 09 | Liberal conservatism | Centre-right | Markéta Adamová | 5.3% | 7 / 200 | |
| STAN | Liberalism, localism | Centre to centre-right | Vít Rakušan | 5.2% | 6 / 200 | |
Pre-election composition
[edit]Competing parties
[edit]| List | Name | Ideology | Position | Leader | 2017 result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Green Party | Green politics | Centre-left | Magdalena Davis | 1.56% (0 Seats) | |
| 2 | Swiss Democracy | Swiss system | Centre-right | Tomáš Raždík | new | |
| 3 | Free Bloc | Nationalism | Far-right | Lubomír Volný | didn't stand | |
| 4 | Freedom and Direct Democracy | Right-wing populism | Far-right | Tomio Okamura | 10.64% (22 Seats) | |
| 5 | Czech Social Democratic Party | Social democracy | Centre-left | Jan Hamáček | 7.27% (15 Seats) | |
| 6 | Right Bloc | Anti-communism | Right-wing | Petr Cibulka | 0% (0 Seats) | |
| 7 | Alliance of National Forces | Nationalism | Far-right | Vladimíra Vítová | 0% (0 Seats) | |
| 8 | Tricolour–Svobodní–Soukromníci | National conservatism | Right-wing to far-right | Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková | 1.56% (0 Seats) | |
| 9 | Alliance for the Future | Liberalism | Centre-right | Pavel Sehnal | 0.15% (0 Seats) | |
| 10 | Sources Movement | Decentralization[63] | none[64] | no leader | new | |
| 11 | The Left | Democratic socialism | Left-wing | Markéta Juřicová | new | |
| 12 | Přísaha | Populism | Centre to centre-right | Robert Šlachta | new | |
| 13 | SPOLU | Liberal conservatism | Centre-right | Petr Fiala | 22.4% (42 Seats) | |
| 14 | Pensioners 21 | Pensioners' interests | none | Jaromír Fojtík | new | |
| 15 | Urza.cz | Anarcho-capitalism | none | Martin Urza | new | |
| 16 | Czech Crown | Monarchism | Right-wing | Radim Špaček | supported TOP 09 | |
| 17 | Pirates and Mayors | Liberalism | Centre | Ivan Bartoš | 15.97% (28 Seats) | |
| 18 | Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia | Communism | Left-wing to far-left | Vojtěch Filip | 7.76% (15 Seats) | |
| 19 | Moravian Land Movement | Regionalism | Centre | Ondřej Hýsek | new | |
| 20 | ANO 2011 | Populism | Centre to centre-right | Andrej Babiš | 29.64% (78 Seats) | |
| 21 | We Will Open Czechia | Opposition to COVID-19 restrictions | Far-right | Jakub Olbert | new | |
| 22 | Moravané | Regionalism | Centre | Pavel Dohnal | didn't stand | |
MPs not standing for reelection
[edit]| MP | Seat | First elected | Party | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiří Bláha | Liberec | 2017 | ANO | [65] | |
| Alexander Černý | Olomouc | 2002 | KSČM | [65] | |
| Monika Červíčková | Prague | 2018 (surrogate) | ANO | [66][better source needed] | |
| Jan Čižinský | Prague | 2017 | KDU-ČSL | [65] | |
| Petr Dolínek | Prague | 2017 | ČSSD | [65] | |
| Miroslav Grebeníček | South Moravia | 1993 | KSČM | [67] | |
| Stanislav Juránek | South Moravia | 2017 | KDU-ČSL | [65] | |
| Pavel Juříček | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | ANO | [68] | |
| Iva Kalátová | Karlovy Vary | 2019 (surrogate) | ANO | [69] | |
| Václav Klaus Jr. | Prague | 2017 | Tricolour | Elected for ODS originally.[70] | |
| Jiří Kohoutek | Pardubice | 2017 | SPD | [71] | |
| Josef Kott | Vysočina | 2013 | ANO | [65] | |
| Pavel Kováčik | South Moravia | 1996 | KSČM | [72] | |
| Lenka Kozlová | Central Bohemia | 2017 | Piráti | The only Pirate MP to not seek reelection.[65] | |
| Jana Levová | Plzeň | 2017 | SPD | [73] | |
| Přemysl Mališ | Central Bohemia | 2017 | ANO | [74] | |
| Eva Matyášová | Hradec Králové | 2017 | ANO | [75] | |
| Marcela Melková | Central Bohemia | 2017 | ANO | [74] | |
| Jiří Mihola | South Moravia | 2013 | KDU-ČSL | [65] | |
| Ivana Nevludová | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | Jednotní | Originally elected for SPD.[67] | |
| Monika Oborná | Vysočina | 2017 | ANO | [65] | |
| Petr Pávek | Liberec | 2017 | STAN | The only STAN MP to not seek reelection.[67] | |
| Pavel Pustějovský | Zlín | 2017 | ANO | [65] | |
| Jaroslava Puntová | Ústí nad Labem | 2020 (surrogate) | ANO | [65] | |
| Miloslava Rutová | Plzeň | 2016 (surrogate) | ANO | [76] | |
| Karel Schwarzenberg | Prague | 2010 | TOP 09 | [65] | |
| Roman Sklenák | South Moravia | 2010 | ČSSD | [65] | |
| Olga Sommerová | Prague | 2021 (surrogate) | LES | Elected on TOP 09 list.[65] | |
| Pavel Staněk | South Moravia | 2017 | ANO | [65] | |
| Pavel Šindelář | Plzeň | 2021 (surrogate) | ODS | [65] | |
| Karla Šlechtová | Plzeň | 2017 | ANO | [65] | |
| František Vácha | South Bohemia | 2013 | TOP 09 | [65] | |
| Adam Vojtěch | South Bohemia | 2017 | ANO | [65] | |
| Václav Votava | Plzeň | 2002 | ČSSD | [65] | |
| Jaroslav Vymazal | Vysočina | 2020 (surrogate) | ODS | [65] | |
| Rostislav Vyzula | South Moravia | 2013 | ANO | [65] | |
| Jan Zahradník | South Bohemia | 2013 | ODS | [65] | |
| Radek Zlesák | Vysočina | 2017 | ANO | [65] | |
Campaign
[edit]
Issues
[edit]The campaign was significantly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, with opposition parties criticizing the government for its handling of the pandemic and emphasising the country's high death rate. Some parties also focused their campaigns around opposition to the COVID-19 restrictions. Meanwhile, the government parties defended their handling of the crisis, and some government ministers argued that the situation would have been worse if the opposition had been in government. This issue later lost prominence, with economic issues receiving more attention. Several political scientists, including Daniel Prokop, characterised the election as a referendum on Prime Minister Andrej Babiš.[77][78] During the final phase of the campaign, inflation and the increasing prices of groceries became the main issue, reflected in Spolu's campaign slogan: "The cost of Babiš".[79]
ANO 2011 and the far-right parties also focused on immigration during their campaigns, criticising multiculturalism and pledging to prevent "Muslim Europe".[80]
Party campaigns
[edit]Alliance for the Future
[edit]In March 2021, the Civic Democratic Alliance (ODA) formed an electoral alliance with other minor parties called Alliance for the Future (APB), led by Pavel Sehnal. Parties in the alliance included the Agrarian Democratic Party, Order of the Nation and the Democratic Party of Greens.[81] The same year in July, the Party of Common Sense joined the alliance.[82] ODA formally changed its name to Alliance for the Future to avoid the higher electoral threshold.[83]
The alliance's campaign was launched at a press conference on 16 June 2021, where Sehnal introduced APB's priorities, including support for Czech businesses and lower taxes. He also declared support for transatlantic cooperation and EU membership.[84]
ANO 2011
[edit]
After opinion polls in early 2021 showed ANO 2011 (ANO) falling behind the Czech Pirate Party, prime minister Andrej Babiš reacted by attacking the Pirates for their progressive stances, such as their supposed support for immigration and legalisation of drug use.[85] The party's campaign thus focused on criticism of the Pirates in early 2021.[86] On 27 June 2021 President Miloš Zeman endorsed ANO 2011, stating that he would vote for the party.[87]
In July 2021, ANO 2011 published a book, Share it, before they ban it, allegedly written by Babiš, who began promoting the book during the campaign with book signings. The book primarily boasted about Babiš record in government.[88][89] Ice cream was also given out at these sessions, in response to the campaign of Pirates and Mayors.[90][91][92]
The party officially launched its campaign on 2 September 2021. Babiš promised higher pensions and measures against illegal immigration. He also attacked the opposition alliances, stating that they wanted to destroy the Visegrád Group. Babiš also talked about the defence of Czech national interests.[93] In September 2021, ANO released an election advert for Czech television which attacked the Pirates over alleged support for immigration and links to "antifa".[94][95] His campaign used the slogan "I will fight for you until my body falls apart!"[96] The launch of the campaign was impacted by the arrival of Babiš' son Andrej Babiš Jr., who was allegedly kidnapped on his father orders leading to the 2018 Czech political crisis. Babiš Jr. confronted his father during the meeting and accused him of deceiving the nation. Babiš later stated that he would not wish any parent to go through such an experience.[97][98]
On 29 September 2021 Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán visited the Czech Republic and formally endorsed ANO 2011 at a rally in Ústí nad Labem.[99][100] Orbán praised Babiš, saying that Hungarians would be glad for a prime minister like Babiš. He also warned about immigration and the European Union during the rally, which was compared to a talkshow of two prime ministers.[101]
Babiš was named in the Pandora Papers leak around a month later.[102] According to the leak, Babiš used offshore companies to buy French Mansion in 2009.[103]
Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia
[edit]
The Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia (KSČM) launched its campaign on 4 June 2021. Leader Vojtěch Filip said that a vote for KSČM meant certainty for the future. KSČM named its five priorities as help for children in need, better conditions for life and safety, the right to a dignified life and better environment, a higher minimum wage, and shorter working periods. Filip also stated his party's wish to leave NATO and establish better relationships with China and Russia.[104]
Czech Crown
[edit]The monarchist party Koruna Česká launched its campaign on 9 August 2021. The party supported TOP 09 in the 2017 elections. Chairman Radim Špaček described the program goals, to reform the Czech state from a republic to a parliamentary monarchy, to restore the historical lands of Bohemia, Moravia and Silesia, and revise the legal order. Deputy Chairman Petr Krátký cited a public opinion polling indicating that almost 10% of Czech citizens, especially younger voters, are in favor of a monarchy. The party's list also includes members of other small parties, such as the Conservative Party and Morava 1918.[105]
Czech Pirate Party and Mayors and Independents
[edit]
The Czech Pirate Party and Mayors and Independents (STAN) formed the liberal electoral alliance Pirates and Mayors led by Ivan Bartoš, presenting their cooperation agreement in December 2020. Priorities in the agreement included lower taxes, better availability of health care in the regions, protection of the climate, and transparent governance. The parties also agreed to support adoption of the euro.[106] Bartoš said on 11 January that the alliance's priorities during the campaign would include reform of the debt collection system, digitalisation, environmental issues, and education.[107]
Pirates and STAN launched their campaign on 18 May 2021, with the slogan "Let's give the country back its future" (Czech: Vraťme zemi budoucnost). Bartoš and Rakušan promised to regulate debt collection, raise taxes on commercial buildings, and begin preparations to adopt the euro.[108] A major focus of the alliance's platform is digitalisation of the country.[109] In response to the 2021 South Moravia tornado, Pirates and STAN interrupted their campaign.[110]

At a press conference on 24 June 2021, Pirates and STAN launched an anti-corruption campaign, publishing a list of the 10 biggest corruption cases since 1989, primarily involving ODS. The campaign also listed the 10 biggest corruption cases involving the ruling ANO.[111] In July 2021, the alliance released a poster featuring Jakub Michálek, its candidate for Minister of Justice, trying to catch a man in a suit with a lasso, accompanied with anti-corruption slogans. The campaign attracted significant media attention but was also criticised as amateurish and populist.[112][113]
The alliance relaunched its campaign in August 2021 as a reaction to declining opinion polls. The campaign began to focus more on STAN and its leader Vít Rakušan, though Bartoš remained the alliance's electoral leader and candidate for prime minister.[114] The campaign also focused more on budgetary spending and education.[115]
The final phase of the campaign was launched on 9 September 2021. The alliance introduced an electoral bus in an attempt to replicate the success of the 2017 elections. Pirates and Mayors focused on criticism of the government for its handling of the COVID-19 pandemic and budget spending. Messages written on the bus also recalled various controversies of the government.[116]

Czech Social Democratic Party
[edit]The Czech Social Democratic Party (ČSSD) launched its campaign on 29 March 2021 with the slogan "We know what to do after Covid." The campaign focused on the solution of the COVID-19 crisis, opposition to privatization of hospitals, support for Kurzarbeit, and shorter working hours. The party also promised to increase taxes for banks and large companies.[117]
The final phase of campaign was launched on 22 August 2021. Party leader Jan Hamáček said that ČSSD was not dead, despite low opinion polling. Major topics of the party's campaign were higher salaries, pension reform, and just redistribution of COVID-19 expenditures. Slogans included "For a just Czech Republic" and "So that no one endangers your life security." ČSSD also expressed their intention to implement progressive taxation and a lower tax on groceries, rejected privatisation of health care, and promised more achievable housing.[118][119]
ČSSD used Minister of Labour and Social Affairs Jana Maláčová prominently in its campaign. In September, Maláčová and Matěj Stropnický, a candidate for the party in Prague, made a video called "Cool pair", in which they attacked opposition parties, accusing them of corruption and intending to privatize public companies.[120][121] Maláčová also campaigned at Metro stations giving out leaflets for the party.[122][123]
Free Bloc
[edit]
The Free Bloc launched it campaign on 28 August 2021 with a meeting on Letná. Led by MP Lubomír Volný, it focused mainly on opposition to COVID-19 restrictions. Other prominent figures in their campaign were Jana Bobošíková and Hana Lipovská.[124] The Free Bloc held electoral meetings at markets, with Volný travelling around the Czech Republic in a bus called "Volňásek".[125] The campaign concluded with a meeting in Krupka on 6 October 2021.[126]

Freedom and Direct Democracy
[edit]Freedom and Direct Democracy (SPD) launched its campaign on 15 July 2021 with a meeting on Letná.[127] SPD stated that the price for their participation in post-election coalition discussions would be a referendum law, and to hold a referendum on membership of the EU and NATO.[128][129] Other issues in the party's campaign included opposition to COVID-19 restrictions and mandatory vaccination. SPD used an election truck called "espéďák" to travel around the country, and attempted to attract potential voters to meetings by holding fairs with cheap food.[130][131]
Green Party
[edit]The Green Party launched its campaign on 29 June 2021, with the slogan "Lets Give Green to Women", focused on feminist issues and environmentalism. Besides green, the party used pink in its campaign.[132] Magdalena Davis was announced as the party's electoral leader,[133] and a large number of their candidates were women. Davis described the predominance of men in politics as a medieval custom.[134]
The final phase of the party's campaign was launched on 31 August 2021 in Brno, at the Brno astronomical clock. The Greens described it as a phallic, masculine symbol, and covered it with various images of female potential. Participants in the meeting held signs with slogans such as "We love modern schools" and "We love fathers on parental leave". Another key issue was the climate crisis, with the party proposing higher penalties for environmental crimes.[135]
People FOR
[edit]The People FOR political movement, led by political activist Mikuláš Minář, was launched on 3 December 2020, and started gathering the 500,000 signatures required for participation in the elections. Minář said that the movement does not want to be another 5% party.[136] On 24 March 2021, Minář announced the end of the movement due to low interest from voters, having collected only 39,251 signatures.[137]
Přísaha
[edit]
Robert Šlachta, the former Director of the police unit against organized crime, formed the anti-corruption party Přísaha before the election. He launched the campaign at a meeting on 28 January 2021. Šlachta stated that he did not believe it was the right time to adopt the euro and was opposed to migrant quotas.[138]
The final phase of the campaign was launched on 25 August 2021. Přísaha introduced its regional leaders and program, under the slogan "Let's go to them!" The main campaign topic was fighting corruption and clientelism. Šlachta also stated that he wanted to make courts faster and fight for Czech identity, rejecting the euro and migration quotas. He also pledged to investigate all state contracts concluded under the state of emergency.[139] Šlachta stated that Přísaha had crowdfunded 13.8 million CZK for the campaign, and calculated that the campaign would cost around 15 million CZK.[140]
The party hovered around the 5% electoral threshold in polling between May and the election.[141][142] In September 2021, Přísaha's support in opinion polls gradually declined, which was blamed on the launch of the ANO campaign.[143] Šlachta stated before voting that he believed the party would reach his goal of surpassing the 5% threshold.[144]
SPOLU
[edit]
Three centre-right parties, the Civic Democratic Party, KDU-ČSL, and TOP 09, formed an electoral alliance called SPOLU. Led by Petr Fiala, the alliance launched its campaign on 9 December 2020, promising to reform tax, the social and pension system, and healthcare. Its proposals included a minimum pension, a simplification of social benefits, support for education, and better use of EU funds as well as a focus on climate change. It opposes leaving the EU and supports membership of NATO. TOP 09 leader Markéta Pekarová Adamová described the alliance as a centre-right liberal conservative political force.[145]

SPOLU launched its campaign on 19 May 2021 in Brno.[146] The campaign's slogan was "We will bring the Czech Republic together." Fiala said that SPOLU wants an "economically capable and educated Czechia".[147][146] Spolu planned to use Dominik Feri as the face of an Instagram campaign targeting young voters entitled "I have a voice". In May 2021, Feri resigned from his political posts after being accused of sexual assault and rape by eight women, and the campaign was withdrawn.[148][149] In response to the 2021 South Moravia tornado, Spolu interrupted its campaign in South Moravia and donated 1.5 million CZK to help people in the affected areas.[150]

From August, Spolu's campaign featured a bus, known as the "positive bus", to be used for its candidates' personal campaigns. Spolu also screened the film Women on the Run at its campaign meetings, and featured stand-up comedians including Petr Čtvrtníček in electoral adverts.[151][152] Fiala became more active on social media and travelled around the Czech Republic as part of a personal campaign.[153] In late August 2021, Spolu used billboards featuring the leaders of ANO, KSČM, and SPD with the word "Threat", which was often juxtaposed with a billboard featuring the leaders of Spolu with the words "Change you can trust."[154] On 4 September 2021, SPOLU reacted to the launch of ANO's campaign by launching a parody meme generator inspired by the ANO campaign and its slogan "Until my body falls apart!".[155] On 3 September 2021, SPOLU were endorsed by Austrian Chancellor Sebastian Kurz, who sent a letter to Fiala wishing the alliance electoral success.[156]
SPOLU launched the final phase of their campaign on 20 September 2021 with a meeting inspired by the United States presidential campaigns.[157] In a speech, Fiala criticised Andrej Babiš' Cabinet for populism and warned against extremists. Fiala pledged that SPOLU would reduce the public debt without increasing taxes, guarantee the pro-Western orientation of the country, and digitalise public administration. He also said he wanted to solve the housing crisis. The meeting was held under the slogans "It is about everything now" and "Let's start change."[158] Around this time, prominent representatives of Spolu visited the regions to meet with citizens.[159]
Following the television debates, SPOLU used the line "The cost of Babiš" to attack the government over inflation and the rising prices of energy and groceries. The term was first used by Fiala during a debate on Prima CNN News, before becoming a part of the alliance's billboard campaign and spreading among ODS supporters.[160][161] Fiala himself used the term repeatedly during debates.[162]
In the last polls before the election, Spolu were polling second behind ANO. Commentators noted that the gap between ANO and Spolu was narrowing, but none predicted that Spolu would pull ahead.[163][1]
Tricolour–Svobodní–Soukromníci
[edit]
The Tricolour Citizens' Movement, Svobodní, and Freeholder Party of the Czech Republic formed an electoral alliance called Tricolour–Svobodní–Soukromníci (TSS), led by Tricolour leader Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková.[164] Václav Klaus Jr. was originally meant to be the electoral leader, but he quit politics soon after formation of the alliance.[165][166]
TSS launched its campaign on 17 June 2021 with the slogan "We have a right to live". Their campaign focused on traditional values and opposition to COVID-19 restrictions. Majerová Zahradníková targeted right-wing Eurosceptic voters,[167] and also wanted to use former Czech President Václav Klaus during the campaign.[168] Majerová Zahradníková stated during the campaign that TSS rejected the lockdown, Green New Deal, and grocery quotas. During September 2021 she also campaigned on the issue of rising prices.[169] TSS aimed to win 7% of votes.[170]
During final phase of the campaign, TSS focused on Spolu voters, distributing leaflets warning of a new Opposition agreement.[171] TSS also attacked Spolu for being too Green and too pro-Europe. The party warned of "Covid totalitarianism" while attacking COVID-19 restrictions, rejecting a new lockdown, school closures, or "segregation of the non-vaccinated".[172] TSS argued that it was the only "true authentic right" on the Czech political scene. A few hours prior to the election it was endorsed by former Czech president Václav Klaus.[173]

Urza.cz
[edit]Urza.cz is an anarcho-capitalist party led by Martin Urza. Its campaign began gathering signatures in April 2021.[174] The party was registered in July 2021.[175] Urza was campaigning to promote his beliefs, rather than attract votes.[176] The party promised that its MPs would resign if elected, as it did not believe that anyone should govern by force.[177]
We Will Open Czechia
[edit]The Chcípl pes (English: The Dog Croaked) initiative was created in opposition to COVID-19 restrictions. Its members decided to form a political party called "We Will Open Czechia". Its campaign was focused against COVID-19 restrictions and included various protests. The party also called on pub owners to open their businesses despite government orders.[178][179] In April 2021 the party sent a mobile barber shop to Prague, where the public could get haircuts or buy beer. It was also used as a petition stand. The barber shop later moved from Prague to other locations around the country, finishing its journey in Ostrava.[180] In August 2021, the leaders of the party called for a new Prague defenestration, saying that "people should do anything required to overthrow criminal deputies."[181]
Independent initiatives
[edit]
Million Moments for Democracy
[edit]Million Moments for Democracy led a campaign against Andrej Babiš and ANO 2011, attempting to persuade voters to support the opposition alliances Spolu or Pirates and Mayors. Members of the movement talked to people in the streets and gave them leaflets in order to change their minds vote for one of major opposition alliances. The campaign also included a messenger app called "I vote change", which aimed to persuade people through gifs and various questions that they should vote for Spolu or Pirates and Mayors.[182] Leader Benjamin Roll denied that the organisation's activities were a real election campaign, insisting that it was aiming to inform people.[183] The group's activities attracted the attention of the Office for the Supervision of the Management of Political Parties and Political Movements, which launched an investigation into possible election law violations, as the organisation had not registered as an organisation participating in the campaign.[184]
Campaign finances
[edit]
| Party | Money raised (CZK) | Services cost (CZK) | Money Spent (CZK) | Debt (CZK) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPOLU | 18,859,722.00 | 3,446,676.00 | 89,773,505.08 | 0 | [185] |
| ANO 2011 | 1,065,000.00 | 60,000.00 | 87,618,996.62 | 0 | [186] |
| Pirates and Mayors | 20,396,221.00 | 1,857,516.66 | 81,337,980.42 | 0 | [187] |
| Freedom and Direct Democracy | 3,141,861.99 | 1,358,038.00 | 75,939,166.10 | 5,000,000 | [188] |
| Czech Social Democratic Party | 2,546,420.00 | 1,593,742.50 | 54,380,892.21 | 0 | [189] |
| Přísaha | 12,244,707.00 | 14,238,221.12 | 43,820,819.80 | 0 | [190] |
| Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia | 694,051.00 | 1,075,624.00 | 32,363,258.74 | 0 | [191] |
| Tricolour–Svobodní–Soukromníci | 20,705,726.88 | 5,564,966.00 | 31,172,191.62 | 0 | [192] |
| Alliance for the Future | 1,742,000.00 | 1,593,400.00 | 14,363,179.49 | 0 | [193] |
| Free Bloc | 245,383.99 | 1,130,051.00 | 4,457,980.03 | 0 | [194] |
| Czech Crown | 1,261,558.00 | 1,036,215.00 | 3,285,740.98 | 20,070 | [195] |
| Svobodní | 2,397,275.93 | 503,200.00 | 3,141,005.48 | 0 | [196] |
| Green Party | 2,629,918.54 | 58,723,55.00 | 2,327,904.13 | 0 | [197] |
| Swiss Democracy | 1,952,494.66 | 0 | 1,901,264.69 | 0 | [198] |
| We Will Open Czechia | 851,513.00 | 0 | 848,312.50 | 0 | [199] |
| Alliance of National Forces | 307,578.30 | 273,700.00 | 581,278.30 | 0 | [200] |
| Moravané | 509,457.80 | 13,000.00 | 513,001.89 | 0 | [201] |
| Party of Common Sense | 305,300.00 | 29,000.00 | 330,034.90 | 0 | [202] |
| The Left | 233,133.00 | 0 | 232,744.29 | 0 | [203] |
| Sources Movement | 98,000.00 | 4,000.00 | 161,054.65 | 0 | [204] |
| National Democracy | 141,461.07 | 25,400.00 | 25,400.00 | 0 | [205] |
Endorsements
[edit]ANO 2011
[edit]Individuals
[edit]Czech Social Democratic Party
[edit]Parties
[edit]- Patriots of Olomouc Region[208]
Individuals
[edit]Pirates and Mayors
[edit]Parties
[edit]- Clean Budějovice[211]
- Idealists.cz[212]
- Senator 21[213]
Individuals
[edit]SPOLU
[edit]Parties
[edit]Individuals
[edit]Tricolour–Svobodní–Soukromníci
[edit]Parties
[edit]Individuals
[edit]Debates
[edit]| 2021 Czech parliamentary election debates | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Organisers | |||||||||
| P Present S Surrogate NI Not invited A Absent N No debate NI Not invited | ||||||||||
| ANO | SPOLU | PirStan | SPD | KSČM | ČSSD | P | T–S–S | Z | ||
| 1 July 2021 | CNN Prima News[218] | NI | NI | NI | NI | S Stanislav Grospič | S Jana Maláčová | P Robert Šlachta | P Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková | NI |
| S Radek Vondráček | S Martin Kupka | S Jan Farský | P Tomio Okamura | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | ||
| 18 August - 29 September 2021 | Denik.cz[219] | P Andrej Babiš | P Petr Fiala | P Ivan Bartoš | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI |
| 19 August 2021 | CNN Prima News[220] | NI | NI | NI | NI | P Vojtěch Filip | P Jan Hamáček | P Robert Šlachta | P Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková | NI |
| S Karel Havlíček | S Marian Jurečka | S Vít Rakušan | P Tomio Okamura | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | ||
| 1 September 2021 | CNN Prima News[221] | P Andrej Babiš | S Marian Jurečka | P Ivan Bartoš | NI | NI | P Jan Hamáček | NI | NI | NI |
| 8 September 2021 | CNN Prima News[222] | NI | NI | NI | S Radim Fiala | S Jiří Dolejš | NI | P Robert Šlachta | S Petr Bajer | NI |
| 22 September 2021 | CNN Prima News[223] | S Radek Vondráček | NI | NI | P Tomio Okamura | S Zdeněk Ondráček | P Jan Hamáček | NI | NI | NI |
| 26 September 2021 | Prima[224] | P Andrej Babiš | P Petr Fiala | S Vít Rakušan | P Tomio Okamura | P Vojtěch Filip | P Jan Hamáček | P Robert Šlachta | P Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková | NI |
| 29 September 2021 | CNN Prima News[225] | NI | S Jana Černochová | S Jan Lipavský | NI | NI | NI | P Robert Šlachta | S Libor Vondráček | NI |
| 30 September 2021 | Televize Seznam[226] | S Alena Schillerová | S Marian Jurečka | P Ivan Bartoš | P Tomio Okamura | S Stanislav Grospič | P Jan Hamáček | P Robert Šlachta | S Libor Vondráček | P Magdalena Davis |
| 3 October 2021 | Prima[227] | P Andrej Babiš | P Petr Fiala | P Ivan Bartoš | P Tomio Okamura | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI |
| 4 October 2021 | iDnes[228] | P Andrej Babiš | P Petr Fiala | P Ivan Bartoš | P Tomio Okamura | P Vojtěch Filip | P Jan Hamáček | P Robert Šlachta | 'NI | 'NI |
| 6 October 2021 | CNN Prima News[229] | S Alena Schillerová | S Zbyněk Stanjura | S Věslav Michalík | S Jan Hrnčíř | S Miloslava Vostrá | S Jana Maláčová | S Pavel Žeřábek | S Libor Vondráček | NI |
| 6 October 2021 | Česká televize[230] | P Andrej Babiš | P Petr Fiala | S Vít Rakušan | P Tomio Okamura | P Vojtěch Filip | P Jan Hamáček | P Robert Šlachta | P Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková | NI |
| 8 October 2021 | Český Rozhlas[231] | P Andrej Babiš | P Petr Fiala | S Vít Rakušan | P Tomio Okamura | P Vojtěch Filip | P Jan Hamáček | P Robert Šlachta | P Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková | NI |
| 7 October 2021 | Nova[232] | NI | NI | NI | P Tomio Okamura | P Vojtěch Filip | P Jan Hamáček | P Robert Šlachta | NI | NI |
| P Andrej Babiš | P Petr Fiala | P Ivan Bartoš | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | ||
| Candidate viewed as "most convincing" in each debate | ||||||||||
| Debate | Poll/Survey | ANO | SPOLU | PirStan | SPD | KSČM | ČSSD | P | T–S–S | Z |
| 1 September 2021 CNN Prima News | Prima News[233] | Andrej Babiš 30.8 | Marian Jurečka 13.8 | Ivan Bartoš 45.0 | NI | NI | Jan Hamáček 10.4 | NI | NI | NI |
| 8 September 2021 CNN Prima News | Prima News[234] | NI | NI | NI | Radim Fiala 10.8 | Jiří Dolejš 14.2 | NI | Robert Šlachta 44.4 | Petr Bajer 30.6 | NI |
| 22 September 2021 CNN Prima News | Prima News[235] | Radek Vondráček 7.2 | NI | NI | Tomio Okamura 46.2 | Zdeněk Ondráček 2.8 | Jan Hamáček 43.9 | NI | NI | NI |
| 26 September 2021 CNN Prima News | Prima News[236] | Andrej Babiš 11.6 | Petr Fiala 31.8 | Vít Rakušan 33.1 | Tomio Okamura 5.9 | Vojtěch Filip 1.0 | Jan Hamáček 3.6 | Robert Šlachta 4.9 | Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková 8.1 | NI |
| 18 August - 29 September 2021 Denik.cz | Denik.cz[237] | Andrej Babiš 25 | Petr Fiala 39 | Ivan Bartoš 32 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI |
| 29 September 2021 CNN Prima News | Prima News[238] | NI | Jana Černochová 22.1 | Jan Lipavský 13.5 | NI | NI | NI | Robert Šlachta 19.0 | Libor Vondráček 45.4 | NI |
| 3 October 2021 CNN Prima News | Prima News[239] | Andrej Babiš 34.4 | Petr Fiala 35.4 | Ivan Bartoš 19.8 | Tomio Okamura 10.4 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI |
| 4 October 2021 iDnes | iDnes[228] | Andrej Babiš 15 | Petr Fiala 38 | Ivan Bartoš 26 | Tomio Okamura 7 | Vojtěch Filip 3 | Jan Hamáček 6 | Robert Šlachta 5 | 'NI | 'NI |
| 6 October 2021 CNN Prima News | Prima News[239] | NI | NI | NI | Jan Hrnčíř 8.3 | NI | Jana Maláčová 35.8 | Pavel Řežábek 5.0 | Libor Vondráček 51.0 | NI |
| Alena Schillerová 36.4 | Zbyněk Stanjura 58.0 | Věslav Michalik 3.5 | NI | Miloslava Vostrá 2.0 | NI | NI | NI | NI | ||
Opinion polls
[edit]Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Results
[edit]
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | +/– | Seats | +/– | |
| Spolu | 1,493,905 | 27.79 | +5.36 | 71 | +29 | |
| ANO 2011 | 1,458,140 | 27.13 | –2.51 | 72 | –6 | |
| Pirates and Mayors | 839,776 | 15.62 | –0.36 | 37 | +9 | |
| Freedom and Direct Democracy | 513,910 | 9.56 | –1.08 | 20 | –2 | |
| Přísaha | 251,562 | 4.68 | New | 0 | New | |
| Czech Social Democratic Party | 250,397 | 4.66 | –2.62 | 0 | –15 | |
| Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia | 193,817 | 3.61 | –4.16 | 0 | –15 | |
| Tricolour–Svobodní–Soukromníci | 148,463 | 2.76 | +1.20 | 0 | 0 | |
| Free Bloc | 71,587 | 1.33 | New | 0 | New | |
| Green Party | 53,343 | 0.99 | –0.47 | 0 | 0 | |
| We Will Open Czechia | 21,804 | 0.41 | New | 0 | New | |
| Swiss Democracy | 16,823 | 0.31 | New | 0 | New | |
| Moravané | 14,285 | 0.27 | New | 0 | New | |
| Alliance for the Future | 11,531 | 0.21 | –0.11 | 0 | 0 | |
| Koruna Česká | 8,635 | 0.16 | New | 0 | New | |
| Sources Movement | 8,599 | 0.16 | New | 0 | New | |
| Urza.cz | 6,775 | 0.13 | New | 0 | New | |
| Alliance of National Forces | 5,167 | 0.10 | +0.09 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pensioners 21 | 3,698 | 0.07 | New | 0 | New | |
| Moravian Land Movement | 1,648 | 0.03 | New | 0 | New | |
| The Left | 639 | 0.01 | New | 0 | New | |
| Right Bloc | 586 | 0.01 | +0.00 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 5,375,090 | 100.00 | – | 200 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 5,375,090 | 99.32 | ||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 36,794 | 0.68 | ||||
| Total votes | 5,411,884 | 100.00 | ||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 8,275,752 | 65.39 | ||||
| Source: Volby (results), E15 (seats) | ||||||
Distribution of seats for individual parties
[edit] | ||||||
| Party | Seats | +/– | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANO 2011 | 72 | –6 | ||||
| Civic Democratic Party | 34 | +9 | ||||
| Mayors and Independents | 33 | +27 | ||||
| KDU-ČSL | 23 | +13 | ||||
| Freedom and Direct Democracy | 20 | –2 | ||||
| TOP 09 | 14 | +7 | ||||
| Czech Pirate Party | 4 | –18 | ||||
MPs by party membership
[edit]| Party | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANO 2011 | 63 | 0 | |
| Civic Democratic Party | 33 | +10 | |
| Mayors and Independents | 31 | +25 | |
| Freedom and Direct Democracy | 20 | –2 | |
| KDU-ČSL | 19 | +9 | |
| Independents | 15 | -5 | |
| TOP 09 | 13 | +7 | |
| Czech Pirate Party | 4 | –18 | |
| Mayors for the Liberec Region | 1 | +1 | |
| Non-partisans | 1 | +1 | |
Results by region
[edit]
| Region | SPOLU | ANO | PirStan | SPD | Přísaha | ČSSD | KSČM | Others | Turnout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prague | 40.0 | 17.5 | 22.6 | 4.6 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 2.1 | 5.8 | 70.2 |
| Central Bohemia | 28.7 | 24.9 | 19.5 | 7.8 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 6.4 | 68.0 |
| South Bohemia | 29.1 | 26.7 | 13.5 | 9.0 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 7.2 | 66.3 |
| Plzeň | 26.6 | 29.0 | 13.9 | 10.0 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 4.1 | 6.7 | 64.7 |
| Karlovy Vary | 20.2 | 33.1 | 14.2 | 12.8 | 4.9 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 7.6 | 57.1 |
| Ústí nad Labem | 19.8 | 35.6 | 14.0 | 11.9 | 4.4 | 3.2 | 3.9 | 7.2 | 57.7 |
| Liberec | 22.8 | 26.9 | 21.4 | 11.0 | 4.3 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 7.1 | 64.6 |
| Hradec Králové | 28.6 | 27.0 | 15.1 | 9.1 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 3.4 | 7.2 | 67.9 |
| Pardubice | 28.5 | 26.8 | 14.1 | 9.4 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 67.9 |
| Vysočina | 28.0 | 26.7 | 13.5 | 8.9 | 5.2 | 6.7 | 4.7 | 6.3 | 68.9 |
| South Moravia | 30.0 | 25.4 | 14.2 | 9.4 | 6.0 | 4.4 | 3.7 | 6.9 | 66.4 |
| Olomouc | 24.5 | 29.8 | 12.4 | 12.2 | 4.7 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 7.9 | 64.7 |
| Zlín | 27.8 | 27.0 | 13.4 | 11.4 | 4.2 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 8.0 | 67.4 |
| Moravia-Silesia | 20.6 | 33.7 | 11.1 | 12.8 | 4.9 | 5.4 | 4.0 | 7.5 | 60.6 |
| Czech Republic | 27.8 | 27.1 | 15.6 | 9.6 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 3.6 | 6.9 | 65.4 |
| Source:[242] | |||||||||
| Region | ANO | SPOLU | PirStan | SPD | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prague | 5 | 11 | 6 | 1 | 23 |
| Central Bohemia | 8 | 10 | 6 | 2 | 26 |
| South Bohemia | 5 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 13 |
| Plzeň | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 11 |
| Karlovy Vary | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Ústí nad Labem | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 14 |
| Liberec | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| Hradec Králové | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 11 |
| Pardubice | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 10 |
| Vysočina | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 10 |
| South Moravia | 8 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 23 |
| Olomouc | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Zlín | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 12 |
| Moravia-Silesia | 10 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 22 |
| Czech Republic | 72 | 71 | 37 | 20 | 200 |
| Kraj | ANO | ODS | STAN | KDU-ČSL | SPD | TOP 09 | Piráti | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prague | 5 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 23 |
| Central Bohemia | 8 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 26 |
| South Bohemia | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | N/A | 13 |
| Plzeň | 4 | 2 | 2 | N/A | 1 | 2 | N/A | 11 |
| Karlovy Vary | 2 | 1 | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | N/A | 5 |
| Ústí nad Labem | 7 | 2 | 1 | N/A | 2 | 1 | 1 | 14 |
| Liberec | 3 | 2 | 2 | N/A | 1 | N/A | N/A | 8 |
| Hradec Králové | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | N/A | 11 |
| Pardubice | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | N/A | 10 |
| Vysočina | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | N/A | 10 |
| South Moravia | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | N/A | 23 |
| Olomouc | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | N/A | N/A | 12 |
| Zlín | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | N/A | N/A | 12 |
| Moravia-Silesia | 10 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | N/A | N/A | 22 |
| Czech Republic | 72 | 34 | 33 | 23 | 20 | 14 | 4 | 200 |
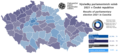
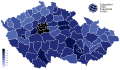
Results by district
[edit]- Results of the election by districts.
- SPOLU
- ANO
- PirStan
- SPD
- Přísaha
- ČSSD
- KSČM
- Turnout
- Turnout by district compared with national turnout.
Voters abroad
[edit]
| Party | Votes | % |
|---|---|---|
| Pirates and Mayors | 6,654 | 50.47% |
| SPOLU | 4,517 | 34.26% |
| ANO 2011 | 659 | 4.99% |
| Freedom and Direct Democracy | 289 | 2.19% |
| Green Party | 245 | 1.86% |
| Tricolour–Svobodní–Soukromníci | 212 | 1.61% |
| Přísaha | 211 | 1.60% |
| Czech Social Democratic Party | 201 | 1.53% |
| Free Bloc | 68 | 0.52% |
| Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia | 50 | 0.38% |
| Swiss Democracy | 19 | 0.14% |
| Czech Crown | 17 | 0.13% |
| We Will Open Czechia | 11 | 0.08% |
| Alliance of National Forces | 9 | 0.07% |
| Sources Movement | 9 | 0.07% |
| Alliance for the Future | 7 | 0.05% |
| Urza.cz | 6 | 0.05% |
| Source:[243] | ||
Voter demographics
[edit]| Social group | SPOLU | ANO | PirStan | SPD | Přísaha | ČSSD | KSČM | T–S–S | Free Bloc | Greens | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Vote | 27.8 | 27.1 | 15.6 | 9.6 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 3.6 | 2.8 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Age | |||||||||||
| 18-34 | 31 | 13 | 33 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 35-44 | 34 | 15 | 21 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 45-54 | 31 | 21 | 12 | 13 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 55-64 | 26 | 32 | 7 | 12 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 65+ | 18 | 47 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Education | |||||||||||
| Basic | 22 | 30 | 17 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| High without Matura | 17 | 38 | 7 | 16 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| High with Matura | 29 | 25 | 17 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| University | 40 | 16 | 22 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Education and Age | |||||||||||
| Without Matura 18-34 | 25 | 12 | 26 | 17 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Without Matura 35-54 | 22 | 24 | 12 | 21 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Without Matura 55+ | 14 | 49 | 4 | 12 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| With Matura 18-34 | 34 | 13 | 36 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| With Matura 35-54 | 38 | 15 | 19 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| With Matura 55+ | 27 | 35 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Gender and Age | |||||||||||
| Women 18-34 | 25 | 12 | 26 | 17 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Women 35-54 | 22 | 24 | 12 | 21 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Women 55+ | 14 | 49 | 4 | 12 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Men 18-34 | 34 | 13 | 36 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Men 35-54 | 38 | 15 | 19 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Men 55+ | 27 | 35 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Working Status | |||||||||||
| Employed | 31 | 19 | 18 | 11 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Self-employed | 39 | 14 | 19 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Students | 34 | 11 | 40 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Parental Leave | 29 | 14 | 26 | 13 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Pensioners | 17 | 47 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Unemployed | 21 | 29 | 20 | 11 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Others | 23 | 20 | 17 | 17 | 4 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 4 |
| Working Status and Income | |||||||||||
| Unemployed in Poverty | 24 | 22 | 18 | 14 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Employed with income below median | 30 | 16 | 20 | 13 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Employed with income over median | 36 | 20 | 18 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Pensioners | 17 | 47 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Others | 30 | 12 | 29 | 12 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Vaccination and Age | |||||||||||
| Vaccinated 18-34 | 36 | 13 | 36 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Vaccinated 35-54 | 38 | 20 | 16 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Vaccinated 55+ | 22 | 44 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Unvaccinated 18-34 | 22 | 7 | 32 | 17 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 2 |
| Unvaccinated 35-54 | 24 | 10 | 19 | 16 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Unvaccinated 55+ | 18 | 25 | 3 | 22 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 5 |
| Source:[244] | |||||||||||
| Social group | SPOLU | ANO | PirStan | SPD | Přísaha | ČSSD | KSČM | T–S–S | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Vote | 27.8 | 27.1 | 15.6 | 9.6 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 3.6 | 2.8 | 4.3 |
| Gender | |||||||||
| Men | 24 | 27 | 18 | 12 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Women | 25 | 29 | 18 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Age | |||||||||
| 18-29 | 34 | 10 | 34 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 30-44 | 25 | 17 | 25 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| 45-59 | 29 | 20 | 14 | 17 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| 60+ | 19 | 44 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 2 |
| Education | |||||||||
| Without Matura | 17 | 35 | 11 | 15 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| With Matura | 27 | 25 | 22 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| University | 34 | 17 | 22 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| By the size of village/town | |||||||||
| 999 and less | 18 | 31 | 17 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 6 |
| 1,000-4,999 | 23 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| 5,000-19,999 | 27 | 24 | 15 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| 20,000-99,999 | 23 | 27 | 19 | 11 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| 100,000 and more | 31 | 25 | 18 | 11 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Working Status | |||||||||
| Employed | 25 | 19 | 21 | 14 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| Self-employed | 47 | 17 | 19 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Students | 38 | 9 | 38 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Pensioners | 17 | 45 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 2 |
| Unemployed/House | 21 | 22 | 25 | 17 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source:[245] | |||||||||
| Social group | SPOLU | ANO | PirStan | SPD | Přísaha | ČSSD | KSČM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Vote | 27.8 | 27.1 | 15.6 | 9.6 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 3.6 |
| By the size of village/town | |||||||
| 1,000 and less | 24.5 | 29.3 | 13.3 | 10.8 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 4.9 |
| 1,000 - 1,999 | 26.4 | 28.3 | 14 | 10.4 | 5.1 | 4.6 | 4 |
| 2,000 - 4,999 | 26.4 | 28.5 | 13.9 | 10.5 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 3.9 |
| 5,000 - 19,999 | 26.3 | 28.5 | 14.7 | 10.1 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 3.7 |
| 20,000 - 49,999 | 24.3 | 30 | 14.1 | 11 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 3.8 |
| 50,000 - 89,999 | 21.7 | 33 | 12.7 | 11.7 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 3.8 |
| 90,000 and more | 29.4 | 25.9 | 17.8 | 8.4 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 3 |
| Source:[246] | |||||||
MPs with highest number of preferential votes
[edit]| Number | MP | Party | Region | Votes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Vít Rakušan | STAN | Central Bohemia | 59,792 (43.47%) |
| 2. | Markéta Pekarová Adamová | TOP 09 | Prague | 49,074 (19.54%) |
| 3. | Petr Fiala | ODS | South Moravia | 38,555 (20.56%) |
| 4. | Andrej Babiš | ANO 2011 | Ústí nad Labem | 38,277 (28.49%) |
| 5. | Jana Černochová | ODS | Prague | 35,583 (14.17%) |
| 6. | Olga Richterová | Piráti | Prague | 32,888 (23.14%) |
| 7. | Pavel Žáček | ODS | Prague | 31,347 (12.48%) |
| 8. | Martin Kupka | ODS | Central Bohemia | 30,286 (14.91%) |
| 9. | Bohuslav Svoboda | ODS | Prague | 29,033 (11.56%) |
| 10. | Ondřej Lochman | STAN | Central Bohemia | 27,656 (20.10%) |
| 11. | Ondřej Kolář | TOP 09 | Prague | 27,259 (10.85%) |
| 12. | Jan Lacina | STAN | Prague | 26,117 (18.37%) |
| 13. | Věra Kovářová | STAN | Central Bohemia | 25,367 (18.44%) |
| 14. | Hayato Okamura | KDU-ČSL | Prague | 24,426 (9.72%) |
| 15. | Marek Benda | ODS | Prague | 23,164 (9.22%) |
| 16. | Alena Schillerová | ANO 2011 | South Moravia | 22,968 (14.50%) |
| 17. | Jan Skopeček | ODS | Central Bohemia | 22,950 (11.30%) |
| 18. | Karel Havlíček | ANO 2011 | Central Bohemia | 22,592 (12.82%) |
| 19. | Vladimír Balaš | STAN | Prague | 21,241 (14.94%) |
| 20. | Barbora Urbanová | STAN | Central Bohemia | 19,969 (14.51%) |
| Source:[247] | ||||
MPs who lost their seats
[edit]164 incumbents stood in the election but only 98 of them were reelected.[248]
| Party | Name | Region | Year became MP | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANO 2011 | Margita Balaštíková | Zlín | 2013 | She later became MP once again when Radim Holiš resigned on his seat.[249] | |
| Irena Blažková | Olomouc | 2020 (surrogate) | [250] | ||
| Andrea Brzobohatá | Central Bohemia | [74] | |||
| Josef Hájek | Moravia-Silesia | 2013 | |||
| Adam Kalous | Olomouc | 2017 | |||
| Barbora Kořanová | Plzeň | [251] | |||
| Jaroslav Kytýr | Pardubice | 2017 | |||
| Milan Pour | Central Bohemia | [74] | |||
| Pavel Plzák | Hradec Králové | 2013 | [75] | ||
| Věra Procházková | Karlovy Vary | 2017 | |||
| Jan Řehounek | Pardubice | 2017 | |||
| Miroslav Samaš | Central Bohemia | [74] | |||
| Civic Democratic Party | Libor Hoppe | South Moravia | 2021 (surrogate) | [252] | |
| Jaroslav Martinů | Pardubice | 2010 | [253] | ||
| Piráti | Dana Balcarová | Prague | 2017 | [254] | |
| Lukáš Bartoň | Plzeň | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Lukáš Černohorský | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | [254] | ||
| František Elfmark | Zlín | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Mikuláš Ferjenčík | Pardubice | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Radek Holomčík | South Moravia | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Martin Jiránek | Hradec Králové | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Lukáš Kolářík | South Bohemia | 2017 | [254] | ||
| František Kopřiva | Central Bohemia | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Jan Lipavský | Central Bohemia | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Tomáš Martínek | Liberec | 2017 | [254] | ||
| František Navrkal | Ústí nad Labem | 2019 (surrogate) | [254] | ||
| Vojtěch Pikal | Olomouc | 2017 | Deputy Speaker of the Chamber of Deputies.[254] | ||
| Ondřej Polanský | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Jan Pošvář | Vysočina | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Ondřej Profant | Prague | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Petr Třešňák | Karlovy Vary | 2017 | [254] | ||
| Tomáš Vymazal | South Moravia | 2017 | [254] | ||
| SPD | Jaroslav Holík | Karlovy Vary | 2017 | [255] | |
| Zdeněk Podal | Hradec Králové | 2017 | [75] | ||
| Miloslav Rozner | South Bohemia | 2017 | [255] | ||
| Josef Nerušil | Prague | 2017 | [255] | ||
| KSČM | Hana Aulická Jírovcová | Ústí nad Labem | 2013 | ||
| Jiří Dolejš | Prague | 2002 | [256] | ||
| Vojtěch Filip | South Bohemia | 2002 | Leader of the party. | ||
| Stanislav Grospič | Central Bohemia | 2002 | |||
| Leo Luzar | Moravia-Silesia | 2014 | |||
| Květa Matušovská | Pardubice | 2010 | |||
| Zdeněk Ondráček | Hradec Králové | 2013 | |||
| Daniel Pawlas | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | |||
| Marie Pěnčíková | Zlín | 2018 (surrogate) | |||
| Ivo Pojezný | South Moravia | 2013 | |||
| Jiří Valenta | Plzeň | 2013 | |||
| Miloslava Vostrá | Central Bohemia | 2013 | |||
| ČSSD | Jiří Běhounek | Vysočina | 2013 | ||
| Jan Birke | Hradec Králové | 2013 | |||
| Jan Chvojka | Pardubice | 2010 | |||
| Jan Hamáček | Central Bohemia | 2006 | Leader of the party. | ||
| Tomáš Hanzel | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | |||
| Alena Gajdůšková | Zlín | 2017 | |||
| Roman Onderka | South Moravia | 2017 | |||
| Lukáš Vágner | South Moravia | 2021 (surrogate) | |||
| Kateřina Valachová | South Bohemia | 2017 | |||
| Ondřej Veselý | South Bohemia | 2010 | |||
| Lubomír Zaorálek | Moravia-Silesia | 1996 | |||
| Tricolour | Tereza Hyťhová | Ústí nad Labem | 2017 | Originally elected for the Freedom and Direct Democracy.[257] | |
| Zuzana Majerová Zahradníková | Olomouc | 2017 | Originally elected for the Civic Democratic Party.[258] | ||
| VB | Marian Bojko | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | Originally elected for the Freedom and Direct Democracy. | |
| Lubomír Volný | Moravia-Silesia | 2017 | Originally elected for the Freedom and Direct Democracy. | ||
Aftermath
[edit]Analysis
[edit]
The electoral coalition Spolu won the most votes but finished with one fewer seat (71) in the Chamber of Deputies than ANO 2011, which won 72 with a lower vote share. ANO had the largest number of deputies of any party, winning twice as many seats as the second place Civic Democratic Party (ODS). The Pirates and Mayors (PirStan) electoral coalition came third with 37 seats. Due to preference voting, Mayors and Independents won 33 seats and the Czech Pirate Party won just 4 seats. Freedom and Direct Democracy (SPD) came fourth, and were the only other political party or electoral coalition to be elected to the Chamber.[259] The election saw the highest ever number of discarded votes for parties not meeting the 5% threshold in the history of elections in the Czech Republic, with more than 1 million, or about 20%.[260] The Czech Social Democratic Party and the Communist Party of Bohemia and Moravia failed to win any seats in the lower chamber for the first time since 1990, and the respective party leaders Jan Hamáček and Vojtěch Filip resigned. For the first time since the Third Czechoslovak Republic, a Communist party would not be represented in the national parliament covering the Czech lands.[261]
Political analyst Jiří Pehe of the New York University in Prague hailed the results as a "triumph for liberal democracy" and said they "signalled the end of the post-Communist era".[262] Political analyst Michal Klima told Czech public television that the result meant "an absolute change of the politics in the Czech Republic. It stabilises the country's position in the West camp. It's a huge defeat for [Babiš]."[263]
The media considered the result a surprise and an upset, as polls had shown ANO 2011 as the clear front-runner.[264] Spolu were polling second but the last polls showed a surge in support, but it was still expected that they would lose. Martin Buchtík, Director of the STEM polling agency, said he thought it would be impossible that ANO 2011 would not receive the highest number of votes. Director of Median, Přemysl Čech, said it was unlikely that Spolu would be first. The Director of Kantar, Pavel Ranocha, also said he believed ANO 2011 would be first, but noted that the latest data showed that gap between ANO 2011 and Spolu narrowing. The directors of all three major polling agencies agreed that Pirates and Mayors had no chance of defeating ANO 2011, and also agreed that only ANO 2011, Spolu, Pirates and Mayors and SPD could be certain of winning seats in the Chamber of Deputies, as KSČM, ČSSD and Přísaha were all hovering around the 5% threshold.[1] Spolu's victory in the election, against polling evidence, was attributed to a "last minute swing". Sociologist Jan Herzmann said that large number of voters had changed their mind in the last moments, which could not be detected by opinion polls. He argued that in the last week running up to the election it had become clear that Petr Fiala was an equal opponent to Prime Minister Andrej Babiš, and competition between the two men led voters of smaller parties to switch to Spolu or ANO 2011, leading to disappointing results for Pirates and Mayors and SPD. Ranocha said that undecided voters were still deciding between Spolu or Pirates and Mayors, and Spolu were ahead in the polls. He also said that a large number of voters decided to support Spolu due to the television debates.[5] Journalist Jan Horák of Aktuálně.cz said that Spolu were competing with Pirates and Mayors to be the main opposition option, but opinion polls showed Spolu as the stronger of the two, which won them votes. He also noted that Fiala was more acceptable than Pirate leader Ivan Bartoš. Political scientist Lubomír Kopeček said that inflation and the Pandora Papers affair may have contributed to ANO's defeat.[265]
New Chamber of Deputies has highest representation of women with 50 elected female MPs. PirStan has highest representation of women with 35% of MPs being female. Average age of elected MPs is 50 years with Bohuslav Svoboda at 77 years being oldest MP. Ondřej Babek is the youngest MP as he is 27 years old.[266]
On 12 November 2021, STEM published a poll conducted from 15 October to 25 October 2021. According to the poll, 61% of PirStan supporters were Pirate Party supporters, while 39% supported STAN. However, 58% of STAN supporters used preferential voting, compared to only 29% of Pirate Party supporters, resulting in a large difference in seat distribution between the two parties.[267] According to the poll, 49% of Spolu voters were supporters of ODS, 26% of TOP 09, and 25% of KDU-ČSL. 47% of KDU-ČSL supporters, 44% of ODS supporters and 35% of TOP 09 supporters used preferential voting.[268]
Complaints
[edit]
The Supreme Administrative Court received 210 complaints about election irregularities, three times more than in 2017.[269] Many complaints were directed at Czech Television, stating that its election coverage benefitted some parties. Others attacked the electoral coalitions and the rule of wearing masks at polling stations.[270]
It was reported on 22 October 2021 that the Pirates and Mayors had lodged a complaint stating that the Czech Statistical Bureau misinterpreted the electoral law, resulting in an incorrect allocation of seats. If the complaint is successful, then ANO 2011 will lose one seat to Pirates and Mayors. The deadline to respond to complaints is 11 November 2021.[271] Another complaint that received media attention was made by Zdeněk Černý, who was due to run as a candidate for SPOLU in South Moravia before his candidacy was withdrawn in the last moments before the election. Černý argued his withdrawal was illegal and wanted to invalidate the election of all SPOLU candidates in South Moravia to recount the preferential votes.[272]
On 5 November 2021, the Supreme Administrative Court rejected all complaints, including those made by Pirates and Mayors and by Zdeněk Černý. It stated that Pirates and Mayors had misunderstood the electoral law.[273][272] On 8 December 2021, Pirates and Mayors sent a complaint to Constitutional Court seeking to repeal the decision by the Supreme Administrative Court.[274] On 26 January 2022, the Constitutional Court rejected the complaint for procedural reasons.[275]
Government formation
[edit]
Incumbent prime minister Andrej Babiš conceded defeat and accepted the results of the vote on the night of 9 October, saying: "That's life. We understand and accept that." Babiš also accused the opposition of a "smear campaign" during the lead-up to the election.[276] Incumbent president Miloš Zeman had indicated that he would give the prime ministerial mandate to the candidate of the largest party, not the largest coalition. Babiš described ANO's performance as a great result, but said he was not expecting a loss. He congratulated the chairman of SPOLU for becoming the largest coalition, and said that he was open to talks with all parties who were going to enter the new parliament, except for PirStan, which he ruled out. PirStan said they would not join or support an ANO-led government, or a government that included SPD, calling them "parties with a corrupt past" (ANO) or parties "threatening liberal democracy" (SPD).[277]
SPD ruled out joining a coalition government with ANO but indicated that they were open to exploratory talks with ANO about providing direct or indirect support to an ANO-led minority government. SPD leader Tomio Okamura said in a press conference that passing a new law to allow national referendums, including on Czexit and possibly NATO membership, was his condition for supporting Babiš' campaign for a second term in office. Babiš left the door open to possible cooperation with SPD but indicated that this was not his first choice as he rejected a referendum on EU membership. After results showed that a potential ANO–SPD majority was mathematically impossible, Babiš indicated his willingness to form a grand coalition with SPOLU, if he were to be asked first by Zeman. Petr Just, a political scientist at the Metropolitan University Prague, said many in ODS were open to forming a government with ANO, as long as Babiš was not part of the government, while many in ANO preferred an alliance with ODS instead of SPD. Spolu ruled this scenario out, especially if Babiš continued as prime minister.[278][279][280]
After the results, Spolu and PirStan signed a memorandum to form a coalition government with Petr Fiala as prime minister.[281] Both groups said they would not work with Babiš.[282] Petr Fiala said: "The two democratic coalitions (SPOLU and Pirates and Mayors) have gained a majority and have a chance to form a majority government. We are the change. You are the change."[283] PirStan leader Ivan Bartoš said talks with SPOLU "on the possibilities of forming a new government" would likely begin on 9 October. He hailed the end of the "dominance of Andrej Babiš", and said that "the democratic parties have shown that the era of chaos will probably be behind us."[284]
On 10 October, Zeman was hospitalized, creating uncertainty over how and when the government formation talks would be held.[285][286] On 11 October, a spokesman for the hospital said that Zeman's condition had stabilized, stating: "The reason for [Zeman's] hospitalization is complications from the illnesses for which he has been receiving treatment."[287] On 15 October, Babis announced that he was prepared to go into opposition and would not accept an offer to try to create a new government, commenting: "We will hand it over to the new coalition and we will be in opposition."[288] On 18 October, Miloš Vystrčil, the President of the Senate of the Czech Republic, announced he had received a letter from the Central Military Hospital declaring Zeman unfit to fulfil his duties as the president, and indicated that he planned to trigger Article 66 of the constitution to remove Zeman from office.[289] In response, the Senate announced their intention to transfer Zeman's constitutional powers to the current prime minister, Andrej Babiš, and the speaker of the Chamber of Deputies. The Speaker is expected to ask Fiala to form a government if Article 66 is triggered.[290]
On 2 November, Spolu and PirStan agreed on the composition of the new government. SPOLU would have the Prime Minister and 10 ministers, while PirStan would have six ministers.[291] Ministries held by Spolu include Finance, Labour and Social affairs, Defence, Transportation, Health, Agriculture, Justice, Environment, Culture and Science. PirStan would get the minister for the Interior, Industry, Education, Local development, Foreign affairs, Legislature and European Union. The signature of the coalition agreement was set for 8 November.[292]

Fiala also said that he had been contacted by Zeman's staff on the same day, to say that the President was looking forward to meeting him, and intended to do so once he got transferred from the intensive care unit room to a normal room.[293] On 4 November, Zeman was transferred to a normal room.[294] On 5 November, Zeman confirmed during an interview for Frekvence 1 that he would appoint Fiala the new prime minister, and would do everything he could for the new government to be formed as quickly as possible.[295]

ODS and STAN approved the coalition agreement on 4 November.[296][297] KDU-ČSL and TOP 09 approved the agreement on 5 November.[298] The Czech Pirate Party announced that its members would vote on approving the agreement on 13 and 14 November.[299] The leadership of the Pirate Party approved the agreement on 7 November. As a result, Bartoš signed the agreement along with the leaders of the other parties on 8 November, even though party members were still to vote.[300] The leaders of all five parties signed the coalition agreement on 8 November.[301][302] The new Chamber of Deputies had its constituent meeting the same day. Babiš promised that his cabinet would resign soon afterward to allow a new government to be formed quickly.[303] On 9 November, Zeman asked Fiala to form a government.[304][305] The constituent meeting concluded on 10 November and the government resigned the day after. Zeman accepted the resignation the same day. Zeman's Chancellor Vratislav Mynář stated that Fiala would be appointed in a matter of weeks, after the President had met Fiala and the Ministerial candidates.[306][307]
On 12 November, a referendum began among Pirate Party members over whether to approve the coalition agreement. MP Jakub Michálek, who was expected to become Minister for Legislation, announced that he would not be part of the incoming government to avoid the cumulation of jobs, adding that he believed it could convince more members to vote for the government.[308] The referendum concluded on 15 November. 82% of party members agreed that the party should join the incoming government. Fiala was set to meet President Zeman on 17 November to present his cabinet and proposed government ministers.[309][310]
Presidential approval
[edit]Fiala met Zeman on 17 November and presented him with the names of his proposed cabinet. Zeman stated that he would appoint Fiala as the new prime minister on 26 November, but expressed his disagreement with one potential minister, reported in Czech media to be Jan Lipavský, the candidate for Minister of Foreign Affairs.[311][312][313] Fiala stated afterwards that he did not intend to make any changes to his cabinet.[314] On 25 November 2021, Zeman tested positive for COVID-19,[315][316] delaying the appointment until 28 November 2021.[317] Zeman said he would meet Fiala's nominations for cabinet positions over the next two weeks.[318] Outgoing Prime Minister Andrej Babiš said he expected the rest of the cabinet to be appointed after 13 December 2021.[319] Following his appointment, Fiala said he believed his government would bring change and improve the lives of people in the Czech Republic, but that the next year would be difficult for many citizens and the Czech Republic itself.[320]

Zeman started meeting the ministerial nominees on 29 November 2021, when he met Martin Baxa and Mikuláš Bek.[321] On 7 December 2021, he met Jan Lipavský, reported as the potential minister Zeman did not want to appoint.[322] According to sources cited by Frekvence 1, Zeman told Lipavský to withdraw his nomination.[323] Fiala subsequently declared that if Zeman did not appoint all of his ministers, he would submit a jurisdiction action to the Constitutional Court against Zeman.[324][325] The meetings concluded when Zeman met Vlastimil Válek on 10 December 2021.[326][327] Zeman then stated that he did not intend to appoint Lipavský.[328] Fiala responded that Constitutional Court would decide whether the president could reject a minister nominated by the prime minister, and said he would meet Zeman on 13 December 2021 to discuss the next steps for the appointment of the cabinet.[329]
Fiala met Zeman on 13 December 2021 at Lány Castle. After the meeting, Zeman agreed to appoint all cabinet members, including Lipavský, on 17 December 2021.[330][331] A vote of confidence in the Chamber of Deputies was scheduled for 12 January 2022.[332][333]
Fiala's cabinet was appointed by Zeman on 17 December 2021. Fiala said that his cabinet had taken over responsibility, noting that "we are not starting in a good situation as there are many overlooked problems. We will start working immediately as there is so much work and we want to do it differently than our predecessors."[333] Zdeněk Nekula was the only minister that was not appointed, as he had tested positive for COVID-19. His appointment as Minister of Agriculture was postponed until January 2022, and Marian Jurečka was temporarily designated to manage the Ministry of Agriculture.[334] Fiala confirmed on 2 January 2022 that Nekula would be appointed on 3 January, and the new cabinet would ask the Chamber of Deputies for confidence on 12 January 2022.[335] Nekula was appointed on 3 January 2022, completing the cabinet.[336]
Fiala's cabinet was presented to the Chamber of Deputies on 12 January 2022 for a confidence vote. The vote did not occur on that day as the pre-vote debate continued for 22 hours.[337] The vote was also delayed by Freedom and Direct Democracy leader Tomio Okamura, who called for a special meeting over the financing of Mayors and Independents, following media reports that the party had accepted gifts from Cyprus.[338][339] The confidence debate session continued in the evening of 13 January 2022.[337] After 23 hours of debate, the cabinet won the confidence vote by 106–87, with 193 MPs present.[340][341]
International response
[edit]Slovak President Zuzana Čaputová congratulated the Czech Republic and wished it a successful and conflict-free government formation. Prime Minister Eduard Heger congratulated the country for the high voter turnout and congratulated Spolu for victory, noting that he hoped Fiala would form a government that would govern well. He described Czechs as Slovakia's "closest friends and brothers."[342] Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán congratulated Fiala on his appointment as prime minister, calling the Czech Republic a friend and strategic partner.[343]
The international press identified the result as a sign of the decline of populism in Central Europe. The New York Times noted the surprise defeat for Babiš. The Wall Street Journal suggested that the result might echo in Hungary before the 2022 Hungarian parliamentary election.[344]
See also
[edit]- 2021 in politics and government
- 2021 in the Czech Republic
- 2021 Speaker of the Chamber of Deputies of the Parliament of the Czech Republic election
- Elections in the Czech Republic
- List of elections in 2021
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Spolu posiluje, ale ANO neporazí, Piráti už vůbec, říkají autoři posledních průzkumů". Aktuálně.cz (in Czech). 4 October 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Vyhrálo by hnutí ANO, favorité voleb mírně oslabili, říká poslední průzkum". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 4 October 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Volby 2021: Favoritem je Babiš před koalicí Spolu a Piráty se Starosty". newsbox.cz (in Slovak). Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ Kudrnáč, Aleš; Petrúšek, Ivan (2022). "Czech Republic: Political Developments and Data in 2021: Historic Electoral Loss of the Left". European Journal of Political Research Political Data Yearbook. 61 (1): 111–126. doi:10.1111/2047-8852.12358. ISSN 2047-8844.
- ^ a b "Proč nikdo neřekl, že vyhraje Fiala? Průzkumy nestihly volební finiš". Seznam Zprávy (in Czech). Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Czech PM's party loses election to liberal-conservative coalition". The Guardian. 9 October 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ Mastrini, John; McKenzie, Sheena (9 October 2021). "Czech Prime Minister Andrej Babiš's populist party loses grip on power in nail-bitingly close election". CNN. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ "Online: Nečekaný triumf koalice Spolu. V posledním momentu přeskočila ANO a vyhrála sněmovní volby". Czech Radio (in Czech). 9 October 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ "Koalice se dohodly, chtějí pro Fialu pověření od prezidenta". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ "Populist Czech PM Babis's party narrowly loses election in surprise result". France 24. 9 October 2021. Archived from the original on 9 October 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
Both the Social Democrats and the Communists, the country's traditional parliamentary parties, failed to win seats in parliament for the first time since the split of Czechoslovakia in 1993.
- ^ "Starostové kroužkováním zmasakrovali Piráty". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ "Czech Republic's Constitution of 1993 with Amendments through 2013" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 April 2021.
Article 19. 1. Any citizen of the Czech Republic who has the right to vote and has attained the age of twenty-one is eligible for election to the Assembly of Deputies.
- ^ Zlámalová, Lenka (4 April 2019). "Souboj o přízeň tažných koní. ODS a Piráti se spolu přetahují o voliče všech generací". Echo24 (in Czech). Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Fiasko vládních stran. Světová média si všímají vítězství ODS i porážky KSČM". Lidovky.cz (in Czech). 13 October 2018. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Hnutí ANO vyhrálo v drtivé většině měst. Výjimkami jsou Praha a Liberec". echo24.cz (in Czech). 6 October 2018. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Czech Senate and regional elections 2020: Bitter victory for the Prime Minister, dominance of the opposition in the Senate". Heinrich Böll Stiftung.
- ^ Kouba, Karel; Lysek, Jakub (2021). "The 2020 Czech regional elections: A story of a winner that lost". Regional & Federal Studies. 32 (4): 1–13. doi:10.1080/13597566.2021.1948839. S2CID 237827332.
- ^ "Results by national party: 2019–2024". European Parliament. 2 May 2019. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "2019 European Parliament election in the Czech Republic". European Sources Online. May 2019. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Málek, Jiří (26 May 2019). "Czechia: Results of EU Elections 2019". Transform! Europe. Party of the European Left. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Gričová, Andrea (3 October 2020). "Krajské volby ovládlo ANO, vyhráno ale nemá. ČSSD a komunisté propadli". Deník (in Czech). Vltave Labe Media. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Piráti jsou skokanem voleb. Za každou cenu vládnout nechceme, říká Bartoš". Seznam Zprávy. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Komentář: ANO drží pozice i náskok, ale ztrácí spojence". Mladá fronta Dnes. 3 October 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Volby do Senátu jsou sečteny. Debakl pro ANO a ČSSD, úspěch pro STAN". TV Nova Czech Republic (in Czech). 10 October 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Námluvy pokročily. Jak se pečou koalice proti Babišovi do velkých voleb?". CNN Prima News (in Czech). Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Pravicové strany směřují k očekávané volební koalici. V úterý mají podepsat memorandum". Lidové noviny (in Czech). 25 October 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "ODS, TOP 09 a KDU-ČSL půjdou do voleb společně. Chtějí je vyhrát". ČT24 (in Czech). Czech Television. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ "Trojkoalice si rozdělila lídry. ODS 9, lidovci 3, topka 2". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ "ODS, KDU-ČSL a TOP 09 jdou do voleb jako koalice SPOLU. Daly 17 slibů". Seznam Zprávy (in Czech). Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^ "Kandidát ODS, TOP 09 a KDU-ČSL na premiéra je Fiala, strany zachovají kluby". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 16 December 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ "STAN schválil zahájení vyjednávání s Piráty o koalici pro parlamentní volby". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 8 October 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Piráti zatím odmítají spolupráci se STAN. Bojí se zneužití". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ "Piráti o koalici se STAN: Nechceme si konkurovat. Jasno bude koncem listopadu". Deník (in Czech). 7 November 2020. Retrieved 19 November 2020.
- ^ "Piráti začnou jednat o koalici se STAN. Členové dali zelenou v referendu". Seznam Zprávy (in Czech). Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- ^ "Bartoš míří na lídra koalice se STAN". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 25 November 2020.
- ^ "Piráty povede do voleb Bartoš, potvrdili členové v referendu". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ "Koalici Pirátů a STAN povede Bartoš. Chtějí spolu do vlády či opozice". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 14 December 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ "Piráti potvrdili koalici se STAN. Vyvedeme spolu zemi z krize, slíbil Bartoš". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 12 January 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ "Formuje se třetí blok proti Babišovi. ČSSD chystá vlastní koalici". Seznam Zprávy (in Czech). Retrieved 8 January 2021.
- ^ "Zelení si dali podmínku pro spolupráci s ČSSD. Nesmí vést k vládě s Babišem". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 30 January 2021. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ Leinert, Ondřej (5 February 2021). "Trikolóra se Svobodnými a Soukromníky? Do voleb teď můžeme jít i s deseti stranami, plánuje Klaus mladší". Hospodářské noviny (in Czech). Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ "Trikolóra, Soukromníci a Svobodní půjdou do voleb spolu. Jsme otevřeni i pro další subjekty, řekl Klaus mladší". ČT24 (in Czech). Czech Television. Retrieved 4 March 2021.
- ^ "Už se to valí. Pravice nebude štěpit síly. Ke Klausovi, Vondráčkovi a Bajerovi se přidávají další". Parlamentní listy (in Czech). Retrieved 6 March 2021.
- ^ "Václav Klaus ml. končí v politice". Novinky.cz (in Czech). 23 March 2021.
- ^ "Trikolóru povede Majerová Zahradníková, Klaus ml. rezignoval". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 23 March 2021.
- ^ "Další koalice. Do voleb jde Aliance pro budoucnost". Týden (in Czech). 23 March 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
- ^ "K Alianci pro budoucnost se připojili Rozumní Petra Hanniga". České Noviny (in Czech). 14 July 2021. Retrieved 27 July 2021.
- ^ Neff, Ondřej (1 October 2021). "Kdopak by se pirátů bál". Neviditelný pes (in Czech). Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- ^ Novotný, František (4 October 2021). "Volby: Skryté referendum o EU". Neviditelný pes (in Czech). Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- ^ "Volební lídři v Praze se přeli o to, co Česku přináší členství v Evropské unii". ČT24 (in Czech). Czech Television. 1 October 2021. Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- ^ "IPU parline database: Czech Republic (Poslanecka Snemovna), Electoral system". archive.ipu.org. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ "Ústavní soud rozhodl o systému sněmovních voleb. Výsledek oznámí ve středu". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 2 February 2021. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ "Ústavní soud zrušil část volebního zákona, ulevil koalicím a zrušil bonus pro vítěze". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ "Chamber passes required changes to election law (7.04.2021)". PSP.cz. Retrieved 12 August 2024.
- ^ "Lhůta k přihlášení do sněmovních voleb se krátí. Zájem má zatím kolem 30 uskupení". Czech Radio (in Czech). 2 August 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "Úřady potvrdily kandidátky do voleb všem 22 přihlášeným uskupením". České Noviny (in Czech). Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "Česko opět pozve mezinárodní pozorovatele, aby přijeli na sněmovní volby". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 11 July 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "Férovost českých voleb budou hlídat čtyři mezinárodní experti. Nevládní organizace plošný dohled nechystají". ČT24 (in Czech). Czech Television. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "94/2021 Sb. Zákon o mimořádných opatřeních při epidemii onemocnění COVID-19 a o změně některých souvisejících zá..." Zákony pro lidi (in Czech). Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ "Zeman vyhlásil termíny voleb pro lidi v karanténě. Uskuteční se 6. října". Pražský Deník (in Czech). 16 September 2021. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ "Volby ve 20 obcích doplní místní referenda. Lidé rozhodnou o stavbách nebo osudu nemocnice". Czech Radio (in Czech). 8 October 2021. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- ^ Rogner, Šimon. "Spolu s volbami proběhne šestnáct místních referend. Rozhodnou o Zelené bráně i o chovu jelena". ČT24 (in Czech). Czech Television. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- ^ "VIDEO: Rozhlasová debata se zástupci hnutí ANO, koalice Spolu, Moravanů, Levice a hnutí Prameny". iROZHLAS (in Czech). 20 September 2021. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "Volby 2021: Hnutí Prameny". ČT24 (in Czech). Česká televize. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x "Zjišťovali jsme budoucnost poslanců. Kdo má šanci se vrátit. A kdo naopak končí". Aktuálně.cz (in Czech). 18 June 2021. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ^ "Dotazy, zda znovu kandiduji do... - Monika Červíčková". Facebook.com. Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ a b c "Místa ve Sněmovně nebude obhajovat asi pětina poslanců". eurozpravy.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ^ Prokeš, Jan (17 March 2021). "Odcházení průmyslníka Juříčka. ANO ustupovalo neomarxistickému pojetí světa, říká a připravuje syna na roli šéfa firmy". Hospodářské noviny (HN.cz) (in Czech). Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ "Hnutí ANO obhajuje v kraji tři mandáty, nový volební systém ale kraj pravděpodobně opět znevýhodní". Náš region (in Czech). Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ "Klaus mladší v politice skončí, pokud se Trikolóra nedostane do Sněmovny". iDNES.cz (in Czech). 14 October 2020. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ^ "Po volbách chci opustit SPD, se mnou chce odejít 90 procent členů v Pardubickém kraji, tvrdí poslanec Kohoutek". Deník N (in Czech). 16 September 2021. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ^ "Personální otřes u komunistů: Filip skončí v čele strany, stáhnou se i Grebeníček nebo Kováčik". E15.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ^ "Jana Levová". Facebook.com. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Holakovský, Milan (11 October 2021). "Část poslanců zamíří na trh práce. Podívejte se, kdo dá sbohem sněmovní lavici". Mělnický deník (in Czech). Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ^ a b c "Exposlanci z Královéhradeckého kraje se vracejí do ordinací i na radnici". iDNES.cz (in Czech). 1 November 2021. Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ Osvaldová, Marie. "Kdo by měl usednout do poslanecké sněmovny? Některé strany v kraji ještě nemají jasno". Plzen.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ "Předvolební kampaň končí a s ní intriky, lži a nekonečné hádky. Třeba se začne i vládnout". E15.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ Tvrdoň, Jan (27 August 2021). "Prokop: Opozice nedokázala využít covid. Koalice Spolu riskuje, že bude muset vládnout v rozporu se svým programem". Deník N (in Czech). Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ "Komentář: Inflace v kampani. Babišova drahota, nebo opoziční levota?". Seznam Zprávy (in Czech). Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ "Hlavní téma voleb: Daně, kvalita potravin, koronavirus i migrace". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 9 August 2021. Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ "Další koalice. Do voleb jde Aliance pro budoucnost". Týden (in Czech). 23 March 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Aliance pro budoucnost se rozrostla o další nové subjekty a známé osobnosti". Parlamentní listy. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Menší neparlamentní strany budou kandidovat do Sněmovny v alianci". České noviny (in Czech). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Formace dalšího miliardáře jde do voleb. Sehnal nabízí pravicovou politiku". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 16 June 2021. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Proč Babiš útočí jen na Piráty". Czech Radio (in Czech). 16 June 2021. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ^ "Piráti jako veřejný nepřítel číslo 1. Komu fandí dezinformátoři?". E15.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ^ "Zeman ve volbách hodí hlas hnutí ANO, volební koalice považuje za podvod. Jen útočí na konkurenci Babiše, míní politologové". Hospodářské noviny (in Czech). 27 June 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "Babiš se v knize chlubí úspěchy firem. Nikdo nám o tom neřekl, říkají rozpačitě podniky". E15.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ ""Je třeba vypláchnout špínu." Po Babišovi v Teplicích šel muž s hadicí, zasáhla ochranka". Blesk (in Czech). Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Nejdřív křížky, pak hozené vejce. Na autogramiádu Babiše v Průhonicích dorazili i odpůrci opatření". Czech Radio (in Czech). Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ Tauberová, Daniela (21 August 2021). "Video: Babišovo setkání v Přerově narušil protest odpůrců". Olomoucký deník (in Czech). Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Ideová nebo tradiční? Před volbami zuří zmrzlinová válka. Anketa". TV Nova (in Czech). Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Babiš v Ústí zahájil kampaň ANO. Slíbil zvýšit důchody a zaútočil na obě koalice". Aktuálně.cz (in Czech). 2 September 2021. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ^ Tvrdoň, Jan (22 September 2021). "Volební spoty: Babiš vsadil na negaci, Spolu spojuje a Piráti se STAN vyhánějí pijavice". Deník N (in Czech). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Babišův spot útočící na Piráty zafungoval, mobilizuje voliče ANO, zjistil výzkum". Aktuálně.cz (in Czech). 4 November 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Žádní ilegální migranti, průměrný důchod 20 tisíc. Babiš zahájil kampaň". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "Babiš mladší se pustil do svého otce. Oblbuješ národ, vyčetl mu". E15.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Volební kampaně už nectí žádná pravidla". E15.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ Jaroš, Milan. "Orbán podpořil Babiše". Týdeník Respekt. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "Orbán podpoří Babiše v jeho volebním kraji, potká se i se Zemanem". echo24.cz (in Czech). 28 September 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "Maďaři by z premiéra, jako je Babiš, měli radost, řekl Orbán před příznivci hnutí ANO". Aktuálně.cz (in Czech). 29 September 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ McEnchroe, Tom (4 October 2021). "Pandora Papers: Czech PM Babiš used offshore companies to buy USD 22 million French estate". Radio Prague International. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Revealed: Czech PM used offshore companies to buy £13m French mansion". The Guardian. 3 October 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "KSČM zahájila volební kampaň. Chce odchod z NATO a lepší vztahy s Ruskem a Čínou". Aktuálně.cz (in Czech). 4 June 2021. Retrieved 7 June 2021.
- ^ "Koruna Česká zahájila kampaň, prosazuje návrat krále i zemské zřízení". České noviny (in Czech). 9 August 2021. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Šustr, Ladislav (27 December 2020). "Piráti a STAN mají smlouvu: EET se celé nezruší, ochrana klimatu, přijetí eura". echo24.cz (in Czech).
- ^ "Pirát Bartoš slíbil zotavení Česka po krizi kvůli covidu a Babišově vládě". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 9 January 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ "Vraťme zemi budoucnost, zahájili Piráti a STAN kampaň s Úřadem vlády za zády". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 18 May 2021. Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- ^ Ryšavá, Michaela (18 May 2021). "Piráti se starosty zahájili kampaň: slibují obří digitalizaci, plánují zrušení státní maturity". Hospodářské noviny (in Czech). Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- ^ "Tornádo a silné bouřky smetly i kampaň. Koalice Pirátů se STAN i Spolu boj voliče pozdrží". Blesk (in Czech). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Piráti a STAN představili 10 největších korupčních kauz. Šijí hlavně do ODS". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ "Pirát Michálek s lasem jako lovec lidí. Strana po kritice plakát stáhla". echo24.cz (in Czech). 6 July 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ "Michálek chytal s lasem korupčníka. Zavádějící, kají se Piráti a reklamu stáhli". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ "Piráti po utahaném startu otáčejí kormidlo. Místo límečku přijde harmonika". Seznam Zprávy (in Czech). Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ "Piráti a STAN zjednoduší kampaň. Klíčová témata budou zadlužování či vzdělání". iDNES.cz (in Czech). 5 August 2021. Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ "Piráti recyklují kampaňovou atrakci. Za voliči vyrazil Švindlbus". Seznam Zprávy (in Czech). Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ "Jsme tradiční strana, která umí řešit krize, rozjela ČSSD kampaň". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ "Nejsme mrtvá strana, bojujeme, burcoval Hamáček. Pokud neuspěje, odejde z vedení ČSSD". Aktualne.cz (in Czech). 22 August 2021. Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ "ČSSD zahájila ostrou fázi kampaně, strana chce "spravedlivé Česko"". TV Nova (in Czech). Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ "Šlo to za Husáka, půjde to i teď. Hustá dvojka představila recept na bydlení". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 24 September 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- ^ "Zloději přitvrzují, pustila se ČSSD do ODS kvůli plánu prodat poštu i dráhy". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 10 September 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- ^ "S letáky u metra zastavuje Maláčová propad ČSSD. Voliče loví se Špidlou i Petříčkem". Aktuálně.cz (in Czech). 20 September 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- ^ "Dříve volili ANO, teď ČSSD. Pražané jihnou pod pohledem Jany Maláčové". Mladá fronta Dnes (in Czech). 16 September 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2021


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch