2019–2020 Hong Kong protests
| 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Part of democratic development in Hong Kong, Hong Kong–Mainland China conflict and the Chinese democracy movement | |||
Counterclockwise from top left:
| |||
| Date | Entire movement: Since 15 March 2019[1] Large-scale break-out: 9 June 2019 – mid-2020
| ||
| Location | Hong Kong (solidarity protests worldwide) | ||
| Caused by |
| ||
| Goals | Five Demands
| ||
| Methods | Diverse (see tactics and methods) | ||
| Resulted in | Government crackdown on protesters and their supporters
External consequences
| ||
| Concessions | Bill suspended on 15 June 2019 and officially withdrawn on 23 October 2019 | ||
| Parties | |||
| |||
| Lead figures | |||
No centralised leadership | |||
| Deaths, injuries and arrests | |||
| Death(s) | 15 (2 directly, 13 indirectly) (as of 20 April 2020[update])[a] | ||
| Injuries | |||
| Arrested | 10,279[18][c] | ||
| Charged | almost 3,000[21] | ||
| 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests |
|---|
 |
The 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests (also known by other names) were a series of demonstrations against the Hong Kong government's introduction of a bill to amend the Fugitive Offenders Ordinance in regard to extradition. It was the largest series of demonstrations in the history of Hong Kong.[22][23]
The protests began with a sit-in at the government headquarters on 15 March 2019 and a demonstration attended by hundreds of thousands on 9 June 2019, followed by a gathering outside the Legislative Council Complex on 12 June which stalled the bill's second reading. On 16 June, just one day after the Hong Kong government suspended the bill, a larger protest took place to push for its complete withdrawal. The protest was also in response to the perceived excessive use of force by the Hong Kong Police Force on 12 June. As the protests progressed, activists laid out five key demands. Police inaction during the 2019 Yuen Long attack and brutality in 2019 Prince Edward station attack further escalated the protests.
Chief Executive Carrie Lam withdrew the bill on 4 September, but refused to concede to the other four demands. A month later, she invoked emergency powers to implement an anti-mask law, escalating the confrontations. The storming of the Legislative Council in July 2019, deaths of Chow Tsz-lok and Luo Changqing, one of whom was unarmed, and sieges of the Chinese University and the Polytechnic University in November 2019 were landmark events. The unprecedented landslide victory of the pro-democracy camp in the November local election was widely regarded as a de facto referendum on the city's governance.
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in Hong Kong in early 2020 largely silenced the protests. Tensions mounted again in May 2020 after Beijing's decision to promulgate a national security bill for Hong Kong. By mid-2020, the Hong Kong government had declared the restoration of peace and stability with the imposition of the national security law. More than a hundred people, including several prominent activists, have been arrested since the imposition of the law. The resulting political atmosphere, along with the crackdown on civil society, sparked a wave of mass emigration from the city.[5][24]
The approval ratings of the government and the police plunged to their lowest points since the 1997 handover. The Central People's Government alleged that foreign powers were instigating the conflict, although the protests have been largely described as "leaderless". The United States passed the Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act on 27 November 2019 in response to the movement. The tactics and methods used in Hong Kong inspired other protests that followed worldwide.[25]
Names
[edit]In Hong Kong, the name Anti-Extradition Law Amendment Bill Movement or Anti-Extradition Bill Movement (Chinese: 反對逃犯條例修訂草案運動/反修例運動) is often used to refer to the protests as a whole, including demonstrations after the suspension of the bill.[22][26][27] The name 2019 Hong Kong protests is sometimes used as there is no generally agreed upon end date to the protests.[28]
On 27 October 2019, Politico editor-in-chief Jamil Anderlini published an article in the Financial Times titled "Hong Kong's 'water revolution' spins out of control".[29] A reference to martial artist Bruce Lee's fighting advice to "be [like] water", the name Water Revolution subsequently gained popularity among protesters.[30][31]
Background
[edit]Direct cause
[edit]The Fugitive Offenders and Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters Legislation (Amendment) Bill 2019 was first proposed by the government of Hong Kong in February 2019 in response to the 2018 murder of Poon Hiu-wing by her boyfriend Chan Tong-kai in Taiwan, which the two Hongkongers were visiting as tourists. As there is no extradition treaty with Taiwan (because the government of China does not recognise Taiwan's sovereignty), the Hong Kong government proposed an amendment to the Fugitive Offenders Ordinance (Cap. 503) and Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters Ordinance (Cap. 525) to establish a mechanism for case-by-case transfers of fugitives, on the order of the chief executive, to any jurisdiction with which the territory lacks a formal extradition treaty.[32]
The inclusion of mainland China in the amendment was of concern to Hong Kong society; citizens, academics and the legal profession fear the removal of the separation of the region's jurisdiction from the legal system administered by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) would erode the "one country, two systems" principle in practice since the 1997 handover; furthermore, Hong Kong citizens lack confidence in China's judiciary system and human rights protection due to its history of suppressing political dissent.[33] Opponents of the bill urged the Hong Kong government to explore other mechanisms, such as an extradition arrangement solely with Taiwan, and to sunset the arrangement immediately after the surrender of the suspect.[32][34]
Underlying causes
[edit]After the failure of the Umbrella Revolution in 2014[35] and the 2017 imprisonment of Hong Kong democracy activists,[36] citizens began to fear the loss of the "high degree of autonomy" as provided for in the Hong Kong Basic Law, as the government of the People's Republic of China appeared to be increasingly and overtly interfering with Hong Kong's affairs. Notably, the NPCSC saw fit to rule on the disqualification of six lawmakers; fears over state-sanctioned rendition and extrajudicial detention were sparked by the Causeway Bay Books disappearances.[36][37] Xi Jinping's accession to General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party, the top position of paramount leader in 2012 marked a more hardline authoritarian approach, most notably with the construction of Xinjiang internment camps. The spectre that Hong Kong may similarly be brought to heel became an important element in the protests.[38]
Anti-mainland sentiment had begun to swell in the 2010s. The daily quota of 150 immigrants from China since 1997, and the massive flows of mainland visitors strained Hong Kong's public services and eroded local culture; mainlanders' perceived arrogance drew the scorn of Hongkongers.[38] The rise of localism and the pro-independence movement after the Umbrella Revolution was marked by the high-profile campaign for the 2016 New Territories East by-election by activist Edward Leung.[39] Fewer and fewer young people in Hong Kong identified themselves as Chinese nationals, as found by pollsters at the University of Hong Kong. The younger respondents were, the more distrustful they were of the Chinese government.[37] Scandals and corruption in China shook people's confidence of the country's political systems; the Moral and National Education controversy in 2012, the Express Rail Link project connecting Hong Kong with mainland cities and the subsequent co-location agreement proved highly controversial. Citizens saw these policies as Beijing's decision to strengthen its hold over Hong Kong. By 2019, almost no Hong Kong youth identified only as Chinese.[40]
The Umbrella Revolution provided inspiration and brought about a political awakening to some,[35][41] but its failure and the subsequent split within the pro-democratic bloc prompted a re-evaluation of strategy and tactics. In the years that followed, a general consensus emerged that peaceful protests were ineffective in advancing democratic development, and became an example of what not to do in further protests. Media noted that protests in 2019 were driven by a sense of desperation rather than the optimism of 2014.[42][43] The aims of the protests had evolved from withdrawing the bill, solidifying around achieving the level of freedom and liberties promised.[44]
Objectives
[edit]Initially, protesters demanded only the withdrawal of the extradition bill. Following an escalation in the severity of policing tactics on 12 June 2019, the protesters' objective was to achieve the following five demands (under the slogan "Five demands, not one less"):[45]
- Complete withdrawal of the extradition bill from the legislative process: Although the chief executive announced an indefinite suspension of the bill on 15 June, its status of "pending resumption of second reading" in the Legislative Council meant that its reading could have been resumed quickly. It was formally withdrawn on 23 October 2019.[46][47]
- Retraction of the "riot" characterisation for protests: The government originally characterised the 12 June protest as "riots", which the crime carries a maximum penalty of 10 years in prison, and later said there were "some" rioters except for five individuals in Admiralty on 12 June.[48]
- Release and exoneration of arrested protesters: Protesters considered their lawbreaking acts to be mostly motivated by a politically righteous cause; they also questioned the legitimacy of police arresting protesters at hospitals through access to their confidential medical data in breach of patient privacy.
- Establishment of an independent commission of inquiry into police conduct and use of force during the protests: Civic groups felt that the level of violence used by the police against protesters and bystanders, arbitrary stop-and-search,[49] and officers' failure to observe Police General Orders pointed to a breakdown of accountability.[50][51] The absence of independence of the existing watchdog, the Independent Police Complaints Council, was also an issue.[52]
- Resignation of Carrie Lam and the implementation of universal suffrage for Legislative Council elections and for the election of the chief executive:[53] The chief executive is selected in a small-circle election, and 30 of the 70 legislative council seats are filled by representatives of institutionalised interest groups, forming the majority of the so-called functional constituencies, most of which have few electors.
History
[edit]Early large-scale demonstrations
[edit]
After several protests in March and April 2019,[54][55] the anti-extradition issue attracted more attention when pro-democratic lawmakers in the Legislative Council launched a filibuster campaign against the bill. In response, the Secretary of Security John Lee announced that the government would resume second reading of the bill in full council on 12 June 2019, bypassing the Bills Committee.[56] With the possibility of a second reading of the bill, the Civil Human Rights Front (CHRF) launched their third protest march on 9 June. While police estimated attendance at the march on Hong Kong Island at 270,000, the organisers claimed that 1.03 million people had attended the rally, a number unprecedently high for the city.[57][58] Carrie Lam insisted second reading and debate over the bill be resumed on 12 June.[59] Protesters successfully stopped the LegCo from resuming second reading of the bill by surrounding the LegCo Complex.[60] Police Commissioner Stephen Lo declared the clashes a "riot" but on 17 June said that he had merely meant protesters who had displayed violent behaviour.[48] Police were criticised for using excessive force at the clashes, such as firing tear gas at protesters at an approved rally.[61][62] Following the clashes, protesters began calling for an independent inquiry into police brutality; they also urged the government to retract the "riot" characterisation.

On 15 June, Carrie Lam announced the bill's suspension but did not fully withdraw it.[63] The same day, Marco Leung Ling-kit, a 35-year-old man, fell to his death after slipping on scaffolding and plunging 17 metres to his death whilst protesting Lam's decision and claims of police brutality.[64] Ruled by an inquest jury in May 2021 as "death by misadventure",[65] this accident formed a rallying point for the movement and his anti-extradition slogans later became the foundations for the "five demands" of the protests, and his yellow raincoat became one of the symbols of the protests.[66] A protest on the following day had almost 2 million people participating according to an CHRF estimate, while the police estimated that there were 338,000 demonstrators at its peak.[67] While Lam offered a personal apology on 18 June,[68] she dismissed calls for her resignation.[69]
Storming of the Legislative Council and escalation
[edit]
The CHRF claimed a record turnout of 550,000 for their annual march on 1 July 2019, while police estimated around 190,000 at the peak;[70][71] an independent polling organisation estimated attendance at 260,000.[72] The protest was largely peaceful. At night, partly angered by several more suicides since 15 June 2019, some radical protesters stormed into the Legislative Council; police took little action to stop them.[73][74][75]
After 1 July 2019, protests spread to different neighbourhoods in Hong Kong.[76][77][78] CHRF held another anti-extradition protest on 21 July on Hong Kong Island. Instead of dispersing, protesters headed for the Liaison Office in Sai Ying Pun, where they defaced the Chinese national emblem.[79] While a standoff between the protesters and the police occurred on Hong Kong Island,[80] groups of white-clad individuals, suspected to be triad members,[81][82][83] appeared and indiscriminately attacked people inside Yuen Long station.[84] Police were absent during the attacks, and the local police stations were shuttered, leading to suspicion that the attack was coordinated with police. The attack was often seen as the turning point for the movement, as it crippled people's confidence in the police and turned a lot of citizens who were politically neutral or apathetic against the police.[85]

A call for a general strike on 5 August was answered by about 350,000 people according to the Confederation of Trade Unions;[88] over 200 flights had to be cancelled.[89][90][91] Various incidents involving alleged police brutality on 11 August prompted protesters to stage a three-day sit-in at Hong Kong International Airport from 12 to 14 August, forcing the Airport Authority to cancel numerous flights.[92][93][94] On 23 August, an estimated 210,000 people participated in the "Hong Kong Way" campaign to draw attention to the movement's five demands. The chain extended across the top of Lion Rock.[95] On 25 August, six police officers raised their guns and one fired a warning shot into the air in a confrontation with protesters, the first use of live ammunition during the protests.[96][97]
Ignoring a police ban, thousands of protesters took to the streets of Hong Kong Island on 31 August following the arrests of high-profile pro-democracy activists and lawmakers the previous day.[98][99][100] At night, the Special Tactical Squad (officially known as the Special Tactical Contingent) stormed Prince Edward station, where they beat and pepper-sprayed the commuters inside.[101] On 4 September, Carrie Lam announced the formal withdrawal of the extradition bill once Legco reconvened in October and the introduction of additional measures to calm the situation. However, protests continued to push for the realisation of all five demands.[102]
Intensification and sieges of the universities
[edit]
On 1 October 2019, mass protests and violent conflict occurred between the protesters and police in various districts of Hong Kong during the 70th anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China. An 18-year-old protester named Tsang Chi-kin was shot in the chest by police in Tsuen Wan after charging towards a riot policeman.[103][104][105] He was later charged with rioting and assaulting officers,[106] arrested in July 2022 trying to flee to Taiwan after two years of hiding, and appeared in court in April 2023.[107] He was sentenced on 18 October 2023 to 3.5 years in prison for the two charges of rioting and assaulting a police officer, and to 11 months and two weeks for perverting the course of justice.[108][109]
Carrie Lam invoked the Emergency Regulations Ordinance to impose a law to ban wearing face masks in public gatherings, attempting to curb the ongoing protests on 4 October.[110] The law's enactment was followed by continued demonstrations in various districts of Hong Kong, blocking major thoroughfares, vandalising shops considered to be pro-Beijing and paralysing the MTR system.[111][112][113] Protests and citywide flash rallies persisted throughout the month.[114][115]

Protesters clashed with the police late at night on 3 November 2019. Alex Chow Tsz-lok, a 22-year-old student at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), was later found unconscious on the second floor of the estate's car park. He died on 8 November following two unsuccessful brain surgeries.[116][117] After his death, protesters engaged in flash rallies against the police and attended vigils in various districts of Hong Kong. They blamed the police for his death, though the police denied any involvement.[118] In response to Chow's death, protesters planned a city-wide strike starting on 11 November by disrupting transport in the morning in various districts of Hong Kong.[119] That morning, a policeman fired live rounds in Sai Wan Ho, in response to an unarmed 21 year-old attempting to swat his gun aside.[120][failed verification] On 14 November, an elderly man named Luo Changqing died from a head injury which he had sustained the previous day during a confrontation between two groups of anti-government protesters and residents in Sheung Shui.[121][122]

For the first time, during a standoff on 11 November, police shot numerous rounds of tear gas, sponge grenades and rubber bullets into the campuses of universities, while protesters threw bricks and petrol bombs in response.[123] Student protesters from the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) confronted the police for two consecutive days.[124] After the conflict, protesters briefly occupied several universities.[125][126] A major conflict between protesters and police took place in Hung Hom on 17 November after protesters took control of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) and blockaded the Cross-Harbour Tunnel. Thus began the siege of PolyU by police which ended with them storming onto the campus and arresting several protesters and volunteer medics in the early morning of 18 November.[127][128] On March 11, 2023, 20 people were jailed for up to 64 months over riot near besieged PolyU campus in 2019.[129]
Electoral landslide and COVID-19
[edit]
The 24 November 2019 District Council election, considered a referendum on the government and the protests, attracted a record high voter turnout.[130] The results saw the pro-democracy camp win by a landslide, with the pro-Beijing camp suffering their greatest electoral defeat in Hong Kong's history.[131][132] The unprecedented electoral success of the pro-democracy voters, the mass arrests during the PolyU siege, and faster response by police contributed to a decrease in the intensity and frequency of the protests in December 2019 and January 2020.[133] Despite this, the CHRF organised two marches to maintain pressure on the government on 8 December 2019 and 1 January 2020.[134][135]
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in Mainland China and subsequent escalation of the COVID-19 crisis in February and March 2020 caused the number of large-scale rallies to dwindle further because of fears that they might facilitate the spread of the virus. Despite this, the pro-democratic movement's tactics were repurposed to pressure the government to take stronger actions to safeguard public health in the face of the pandemic's outbreak in Hong Kong.[136][3][137] Police used COVID-19 laws banning groups of more than four, for example, to disperse protesters.[138][139] On 18 April, police arrested 15 pro-democracy activists including Jimmy Lai, Martin Lee and Margaret Ng for their activities in 2019, drawing international condemnation.[140]
Implementation of the national security law
[edit]
On 21 May 2020, state media announced that the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (NPCSC) would begin drafting a new law that covers "secession, foreign interference, terrorism and subversion against the central government", to be added into the Annex III of the Hong Kong Basic Law. This meant that the law would come into effect through promulgation, bypassing local legislation.[142] Despite international pressure, the NPCSC passed the national security law unanimously on 30 June, without informing the public and the local officials of the content of the law.[143] The law created a chilling effect in the city.[144][145][146][147][148] Demosistō, which had been involved in lobbying for other nations' support, and several pro-independence groups announced that they had decided to disband and cease all operations, fearing that they would be the targets of the new law.[149] Thousands of protesters showed up on 1 July to protest against the newly implemented law. On that day, the police arrested at least ten people for "breaching national security" for displaying protest art.[150]
Following the implementation of the national security law, the international community reassessed their policies towards China. Major countries in the West (Canada, the US, the UK, Australia, Germany and New Zealand) suspended their extradition treaties with Hong Kong over the introduction of the national security law.[151][152][153][154][155] The US Congress passed the Hong Kong Autonomy Act and president Donald Trump signed an Executive Order to revoke the city's special trade status after Mike Pompeo informed the Congress that Hong Kong was no longer autonomous from China and so should be considered the same country in trade and other such matters.[156] On 7 August, the US announced that they would impose sanctions on eleven Hong Kong and Chinese top officials, including Carrie Lam, for undermining Hong Kong's freedom and autonomy.[157] The British Home Office announced that starting from early 2021, current and former holders of the BN(O) passport in Hong Kong can resettle in the UK along with their dependents for five years before they become eligible to apply for permanent citizenship.[158]
Subsequent clampdown and exodus
[edit]

Invigorated by its success in the November 2019 District Council election, the pro-democratic bloc was eyeing to win over half of the 70 seats in the Legislative Council in the election set to be held on 6 September.[159] Unfazed by the national security law, more than 600,000 people cast their votes in the bloc's historic first primaries in mid July 2020. The Hong Kong government then disqualified twelve candidates on 30 July, nearly all of whom were winners from the pro-democratic primaries.[160][161] The decision drew international condemnation for obstructing the election and the democratic process.[162] On the following day, Carrie Lam, going against the public opinion,[163] invoked emergency powers to delay the election, citing the pandemic as the reason. While the NPCSC allowed the four disqualified incumbent lawmakers to transition to the extended term in July, they decided to remove them from office in November 2020, resulting in the mass resignation of all of opposition lawmakers.[164]

The police continued to use the law to target local activists and critics of Beijing, including business tycoon Jimmy Lai. In January 2021, the police arrested more than 50 individuals, all of whom were connected to the primaries for "subverting state power".[165] This meant that most of the active and prominent politicians in the opposite camp in Hong Kong have been arrested by the authorities using the national security law.[166] Arrest warrants were issued to exiled activists for breaching the national security law, including former lawmakers Nathan Law, Baggio Leung and Ted Hui.[167][168] Twelve Hong Kong activists who were released on bail were captured by China's Coast Guard Bureau while fleeing to Taiwan on a speedboat on 23 August. Detained in Yantian, Shenzhen, they were subsequently charged with crossing the Chinese border illegally and were prevented from choosing their lawyers and meeting their families.[169][170]
As protest activities dwindled, the government continued to tighten its control in Hong Kong, censoring school textbooks and removing any mention of the Tiananmen massacre,[171] arresting organisers of vigils for the victims of the massacre,[172] removing public examination questions which the authorities deemed politically inappropriate,[173] deregistering "yellow-ribbon" teachers,[174] and declaring that separation of powers never existed in Hong Kong despite previous comments by the city's top judges recognising its importance in Hong Kong.[175] It also attempted to reshape the narrative of the Yuen Long attack by claiming that the attack had not been indiscriminate, changing the officially reported police response time, and arresting Lam Cheuk-ting, a pro-democracy lawmaker who was hurt in the attack, for "rioting".[176]
Civil society faced a crackdown by authorities,[177] which triggered a massive exodus from Hong Kong. Pro-democracy activists and lawmakers were among the first to leave the territory; the first wave of emigres also included young professionals, as well as families whose parents wanted to have their children be schooled with emphasis on independent critical thinking.[178] More than 89,000 Hongkongers left the city in a year after the national security law was imposed, and the city witnessed a record 1.2% drop in population.[179] Schools were shrinking as parents feared "brainwashing" "patriotic" education be implemented,[180] and tens of thousands applied for British National (Overseas) visas after the UK government unveiled a new immigration path for passport holders.[181]
Clashes between protesters and counter-protesters
[edit]Clashes between protesters and counter-protesters had become more frequent since the movement began in June 2019. During a pro-police rally on 30 June, their supporters began directing profanities at their opposition counterparts and destroyed their Lennon Wall and the memorial for Marco Leung, leading to intense confrontations between the two camps.[183] Pro-Beijing citizens, wearing "I love HK police" T-shirts and waving the Chinese national flag, assaulted people perceived to be protesters on 14 September in Fortress Hill.[184] Lennon Walls became sites of conflict between the two camps, with pro-Beijing citizens attempting to tear down the messages or removing poster art.[185][186] Some protesters and pedestrians were beaten and attacked with knives near Lennon Walls by a single perpetrator[187][188] or by suspected gang members.[189] A reporter was stabbed and a teenager distributing pro-protest leaflets had his abdomen slashed.[190] Owners of small businesses seen to be supportive of the protests and their employees have been assaulted in suspected politically motivated attacks and their businesses vandalised.[191][192]
Some civilians rammed their cars into crowds of protesters or the barricades they set up.[193][194] In one instance, a female protester suffered severe thigh fractures.[195] Protest organisers, including Jimmy Sham from the CHRF, and pro-democratic lawmakers such as Roy Kwong were assaulted and attacked.[196][197][198] On 3 November, politician Andrew Chiu had his ear bitten off by a Chinese mainlander who had reportedly knifed three other people outside Cityplaza.[199][200] Meanwhile, pro-Beijing lawmaker Junius Ho was stabbed and his parents' grave was desecrated.[201][202]

The 2019 Yuen Long attack occurred following a mass protest organised by the CHRF on 21 July. Suspected gangsters vowed that they would "defend" their "homeland" and warned all anti-extradition bill protesters not to set foot in Yuen Long.[203] The perpetrators attacked people on Fung Yau Street North in Yuen Long before entering Yuen Long station, where they indiscriminately attacked commuters in the concourse and on the platform, as well as inside train compartments, resulting in a widespread backlash from the community. The Department of Justice has since been criticised by some lawyers for making "politically motivated" prosecutions. After the Yuen Long attack, no assailant was charged for weeks after the event, while young protesters were charged with rioting within several days.[204] Protesters were also attacked with fireworks in Tin Shui Wai on 31 July,[205] and then attacked by knife-wielding men in Tsuen Wan[206] and suspected "Fujianese" gang members wielding long poles in North Point on 5 August, though they fought back against the attackers.[207][208]
Amidst frustration that police had failed to prosecute pro-government violent counter-protesters and being increasingly distrustful of police because of this,[209] hard-core protesters began to carry out vigilante attacks—described by protesters as "settling matters privately"—targeting individuals perceived to be foes.[209][210] Pro-Beijing actress Celine Ma,[211] plainclothed officers,[212] and a taxi driver who drove into a crowd of protesters in Sham Shui Po on 8 October, were attacked.[213] A middle-aged man was doused with flammable liquid and set on fire by a protester after he had an altercation with protesters at Ma On Shan station on 11 November.[214][215] On 14 November, an elderly man died from head injuries sustained earlier during a violent confrontation between two groups of protesters and Sheung Shui residents.[216]
Tactics and methods
[edit]



The protests have been described as being largely "leaderless".[217] Protesters commonly used LIHKG, an online forum similar to Reddit, as well as Telegram, an optionally end-to-end encrypted messaging service to communicate and brainstorm ideas for protests and to make collective decisions.[217] Unlike previous protests, those of 2019 spread over 20 different neighbourhoods.[218] Protesters and their supporters remained anonymous to avoid prosecutions or future potential retaliation from the authorities, employers who had a different political orientation, and corporations which kowtowed to political pressure.[219]
For the most part there were two groups of protesters, namely the "peaceful, rational and non-violent" protesters and the "fighters" group.[220] Nonetheless, despite differences in methods, both groups refrained from denouncing or criticising the other and provided tacit support. The principle was the "Do Not Split" praxis, which was aimed to promote mutual respect for different views within the same protest movement.[221][38]
Moderate group
[edit]The moderate group participated in different capacities. The peaceful group held mass rallies, and engaged in other forms of protest such as hunger strikes,[222] forming human chains,[223] launching petitions,[224] labour strikes,[225] and class boycotts.[226][227] Lennon Walls were set up in various neighbourhoods to spread messages of support and display protest art.[228][229] Protesters had set up pop-up stores that sold cheap protest gadgets,[230] provided undercover clinics for young activists,[231] and crowdfunded to help people in need of medical or legal assistance.[232]
To raise awareness of their cause and to keep citizens informed, artists supporting the protest created protest art and derivative works.[233] Social media platforms were used to deliver information about the protests to raise awareness to users abroad[234][235] and circulate images of police brutality.[236] Protesters held "civil press conferences" to counter press conferences by police and the government.[237] AirDrop was used to broadcast anti-extradition bill information to the public and mainland tourists.[238] A protest anthem, "Glory to Hong Kong", was composed, its lyrics crowdsourced on the LIHKG online forum, and sung in flash protests in shopping centres.[239] The Lady Liberty Hong Kong statue was also crowdfunded by citizens to commemorate the protests.[240]
Protesters have attempted to gain international support. Activists organised and coordinated numerous rallies to this end.[241][242] Joshua Wong, Denise Ho and several other democrats provided testimonies during the US congressional hearing for the Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act.[243] To increase the political pressure on China, they also advocated for the suspension of the United States–Hong Kong Policy Act, which grants Hong Kong's special status.[244] Advertisements on the protesters' cause were financed by crowdfunding and placed in major international newspapers.[245][246] At events, protesters waved the national flags of other countries, such as the United States and the United Kingdom, calling for their support.[247]
Efforts were made to transform the protests into a long-lasting movement. Protesters have advocated a "Yellow Economic Circle".[248] Supporters of the protesters labelled different establishments based on their political stance and chose to patronise only in businesses which are sympathetic to the movement, while boycotting businesses supporting or owned by mainland Chinese interests.[249][250] Flash rallies were held in the central business districts as office workers used their lunch break to march on the street.[251] The protests prompted various professions to set up labour unions that compete with pro-Beijing lobbies to pressure the government further.[252] Newly elected District Council members put forward motions to condemn the police and used their power to assist the detained protesters.[253]
Radical group
[edit]

Radical protesters adopted the "be water" strategy, inspired by Bruce Lee's philosophy, often moving in a fluid and agile fashion to confound and confuse the police.[29] They often retreated when police arrived, only to re-emerge elsewhere.[256] In addition, protesters adopted black bloc tactics to protect their identities. Frontliners' "full gear" consisted of umbrellas, face masks, hard hats and respirators to shield themselves from projectiles and teargas.[257] Furthermore, protesters used laser pointers to distract police officers and interfere with the operation of their cameras.[257] At protest scenes, protesters used hand gestures for nonverbal communication, and supplies were delivered via human chains.[258] Different protesters adopted different roles. Some were "scouts" who shared real-time updates whenever they spotted the police,[259][260] A mobile app was developed to allow crowdsourcing the location of police.[261]
Starting in August 2019, radical protesters escalated the controversial use of violence and intimidation. They dug up paving bricks and threw them at police; others used petrol bombs, corrosive liquid and other projectiles against police.[113][262][263] As a result of clashes, there were multiple reports of police injuries and the assault of officers throughout the protests.[264][265] One officer was slashed in the neck with a box cutter,[114] and a media liaison officer was shot in the leg with an arrow during the PolyU siege.[266] Protesters also directed violence towards undercover officers suspected to be agents provocateurs.[267][268] Several individuals were arrested for illegal possession of firearms or making homemade explosives.[269]
Unlike other civil unrests, little random smashing and looting were observed, as protesters vandalised targets they believed embodied injustice.[270] Corporations that protesters accused of being pro-Beijing and mainland Chinese companies were also vandalised, subject to arson or spray-painted.[271][272][273][274] Protesters also directed violence at symbols of the government by vandalising government and pro-Beijing lawmakers' offices,[275][276] and defacing symbols representing China.[210][277] The MTR Corporation became a target of vandalism after protesters had accused the railway operator of kowtowing to pressure by Chinese media by closing several stations[278] and not releasing the CCTV footage from the 2019 Prince Edward station incident amid fears that police may have beaten someone to death.[279] Protesters also disrupted traffic by setting up roadblocks,[280][281] damaging traffic lights,[282] deflating the tires of buses,[283] and throwing objects onto railway tracks.[284] Protesters occasionally intimidated and assaulted mainlanders.[285]
Some radical protesters promoted the idea of "mutual destruction" or "phoenixism", these terms being translations of the Cantonese lam chau. They theorised that sanctions against the ruling CCP and the loss of Hong Kong's international finance centre and special trade status (caused by China's interference of the one-country, two systems principle) would destabilise mainland China's economy, and therefore, undermine the rule of the CCP and give Hong Kong a chance to be "reborn" in the future.[286][287] They believed that further government crackdown would ultimately speed up the process of lam chau, ultimately hurting the regime.[288]
Online confrontations
[edit]Doxing and cyberbullying were tactics used by both supporters and opponents of the protests. Some protesters used these tactics on police officers and their families and uploaded their personal information online.[289] More than 1,000 officers' personal details had been reportedly leaked online, and nine individuals had been arrested. Protest leaders have been attacked after being doxed and intimidated.[290] HK Leaks, an anonymous website based in Russia, and promoted by groups linked to the CCP, doxed about 200 people seen as being supportive of the protests. On 25 October 2019, Hong Kong Police obtained a court injunction prohibiting anyone from sharing any personal information about police officers or their families.[291]
Both sides of the protests spread unverified rumours, misinformation and disinformation. This included tactics such as using selective cuts of news footage and creating false narratives.[292][293][294][295] Several deaths, most notably, that of Chan Yin-lam, a 15-year-old girl whom the police suspected had committed suicide, were the subject of a conspiracy theory given the unusual circumstances surrounding her death.[296] Pro-Beijing camp spread rumour was that the CIA was involved in instigating the protests after photographs of Caucasian men taking part in the protests were shared online.[297] The police blamed fake news for causing public distrust towards law enforcement,[298] though the police itself were also accused by several media outlets and prosecutors of lying to the public.[299][300] Both Twitter and Facebook announced that they had discovered what they described as large-scale disinformation campaigns operating on their social networks to vilify and discredit the protesters.[301][302] According to investigations by Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube, some attacks were coordinated, state-backed operations that were believed to have been carried out by agents of the Chinese government.[303]
On 13 June 2019, allegations of organised cyberattacks were made against the Chinese government. Pavel Durov, the founder of Telegram, suggested that the Chinese government may be behind the DDoS attacks on Telegram. Additionally, Durov further tweeted that some of the DDoS attacks coincided with the protest on 12 June 2019.[304] Another DDoS attack occurred on 31 August; two Chinese websites including Baidu Tieba were involved in the attack.[305]
Police misconduct
[edit]
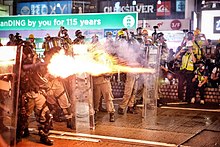


| External videos | |
|---|---|
According to polls conducted by the Hong Kong Public Opinion Research Institute, net approval of the Hong Kong Police Force fell to 22 percent in mid-2019, due to its handling of the protests.[306] At the end of July, 60 percent of respondents in public surveys were dissatisfied with police handling of incidents since June 2019.[307] Nearly 70 percent of Hong Kong citizens believe the police have acted unprofessionally by making indiscriminate arrests and losing self-control.[308] Their role and actions have raised questions about their accountability, the manner in which they wielded their physical force, and their crowd control methods. There have also been allegations of lack of consistency of law enforcement whether through deliberate inaction or poor organisation.
Alleged inappropriate use of force
[edit]Hong Kong police were accused of using excessive and disproportionate force and not following both international safety guidelines and internal protocols while using their weapons.[309][310] Amnesty International claimed that, "police aimed horizontally while firing, targeting protesters' heads and torsos".[124][310] Police use of bean bag rounds and rubber bullets allegedly ruptured the eyes of several protesters and the eye of an Indonesian journalist.[311][312][313] Police were found to have been using tear gas as an offensive weapon,[314] firing it indoors inside a railway station,[314] using expired tear gas, which could release toxic gases upon combustion,[315] and firing canisters from high-rise buildings.[316] Between June and November 2019, approximately 10,000 volleys of gas had been fired.[317] Chemical residues were found on different public facilities in various neighbourhoods.[318][319][d] The use of tear gas sparked public health concerns after a reporter was diagnosed with chloracne in November 2019,[321] though both the environment department and the health department disputed these claims.[322]
Several police operations, in particular in Prince Edward station where the Special Tactical Squad (STS) assaulted commuters on a train, were thought by protesters and pro-democrats to have disregarded public safety.[323][324] Police were accused of using disproportionate force[325] after an officer shot two young protesters with live ammunition in Tsuen Wan and Sai Wan Ho on 1 October 2019 and 11 November 2019, respectively.[e][331][332] An off-duty officer shot and injured a 14-year-old boy in Yuen Long on 4 October 2019 when he was assaulted by protesters who accused him of bumping into people with his car.[333] The siege of PolyU, which was described as a "humanitarian crisis" by democrats and medics,[334][335] prompted the Red Cross and Medecins Sans Frontieres to intervene as the wounded protesters trapped inside ran out of supplies and lacked first-aid care.[335]
Police were accused of obstructing first-aid service and emergency services[118][336][323] and interfering with the work of medical personnel inside hospitals.[337][338] The arrest of volunteer medics during the siege of PolyU was condemned by medical professionals.[339] Police were accused of using excessive force on already subdued, compliant arrestees. Videos showed the police kicking an arrestee,[340] pressing one's face against the ground,[341] using one as a human shield,[342] stomping on a demonstrator's head,[343] and pinning a protester's neck to the ground with a knee.[344] Video footage also shows the police beating passers-by, pushing and kicking people who were attempting to mediate the conflict,[345][346] and tackling minors and pregnant women.[347]
Protesters reported suffering brain haemorrhage and bone fractures after being violently arrested by the police.[348][349] Amnesty International stated that police had used "retaliatory violence" against protesters and mistreated and tortured some detainees. Detainees reported being forced to inhale tear gas, and being beaten and threatened by officers. Police officers shined laser lights directly into one detainee's eyes.[350][351][352][353] The police were accused of using sexual violence on female protesters.[354] A female alleged that she was gang raped inside Tsuen Wan police station, while the police reported that their investigation did not align with her accusation,[355] and later announced plans to arrest her on suspicion of providing false information.[356] Some detainees reported police had denied them access to lawyers and delayed their access to medical services.[352][357] Many of these allegations were believed to have taken place in San Uk Ling Holding Centre.[358]
Questionable tactics and unprofessional behaviour
[edit]The kettling of protesters,[324][359] the firing of pepper ball rounds at protesters at near point-blank range,[360] driving dangerously were also sources of controversy. A police officer was suspended after he hit one protester with a motorcycle and dragged him on 11 November 2019.[361][362] He was later reinstated while the investigation continued.[363] A police van suddenly accelerated into a crowd of protesters, causing a stampede as STS officers exiting from the van chased protesters in Yau Ma Tei on 18 November 2019. Police defended the latter action as an appropriate response by well-trained officers to attacks by protesters, and that "[driving] fast doesn't mean it is unsafe".[364]
Some police officers did not wear uniforms with identification numbers or failed to display their warrant cards,[365][366] making it difficult for citizens to file complaints. The government explained in June 2019 that there was not enough space on the uniforms to accommodate identification numbers. In June 2020, the appearance of various decorations on uniforms caused this explanation to be doubted.[367] The court ruled in November 2020 that the police had breached the Hong Kong Bill of Rights Ordinance by hiding or not displaying their identification number.[368] In late 2019 the government introduced "call signs" to replace warrant cards, but it was found that officers shared call signs.[369]
The police have also repeatedly interfered with the justice process. They have been suspected of tampering with evidence,[370][371][372] giving false testimony before court,[373] and coercing false confessions from arrestees.[374] The deployment of undercover officers who were suspected of committing arson and vandalism also generated controversy, and the ability of police officers to identify the differences between ordinary protesters and undercover officers was questioned.[375][376] A police officer was arrested in April 2020 for perverting the course of justice after he allegedly instructed a teen to throw petrol bombs at a police station he works at.[f][377]
Some uniformed officers used foul language to harass and humiliate protesters and journalists[378] and provoked protesters.[379] The slur "cockroach"—whose dehumanising qualities have been recognised in the social sciences and psychology—was used frequently by frontline officers to insult protesters; some officers sought to counter this development,[380] and suggested that in several instances, verbal abuse by protesters may have led officers to use the term.[381] An officer was reprimanded by his superiors for shouting derisive comments to protesters about the death of Chow Tsz-lok.[382] Police described a man wearing a yellow vest who was taken to an alley, surrounded by police officers, and apparently physically abused by one of them, as a "yellow object".[383]
Police were also accused of spreading a climate of fear[384] by conducting hospital arrests,[385][386] attacking protesters while undercover,[348][387] arresting people arbitrarily,[388] targeting youngsters,[389][350] banning requests for demonstrations,[390] and arresting high-profile activists and lawmakers.[391] During the pandemic period, it has also used the law banning groups of 4 to further ban peaceful protests.[392] However, the police were accused of applying double standards by showing leniency towards violent counter-protesters.[393] It has also failed to fulfill its duty to protect the protesters. Their slow response and inaction during the Yuen Long attack sparked accusations they had colluded with the attackers.[81][394]
Lack of accountability
[edit]Police modified the Police General Orders by removing the sentence "officers will be accountable for their own actions" ahead of the 1 October 2019 confrontation. Police sources of the Washington Post have said that a culture of impunity pervades the police force, such that riot police often disregarded their training or became dishonest in official reports to justify excessive force.[309] Police officers who felt that their actions were not justified were marginalised.[395] Police commanders reportedly ignored the wrongdoings and the unlawful behaviours of frontline riot police and refused to use any disciplinary measures to avoid upsetting them.[309] Lam's administration also denied police wrongdoings and backed the police multiple times.[396] As of December 2019, no officer had been suspended for their actions or charged or prosecuted over protest-related actions.[309] When the District Councils were passing motions to condemn police violence, police commissioner Chris Tang and other civil servants walked out in protest.[397]
The Independent Police Complaints Council (IPCC) launched investigations into alleged incidents of police misconduct during the protests. Protesters demanded an independent commission of inquiry instead, as the members of the IPCC are mainly pro-establishment and it lacks the power to investigate, make definitive judgements, and hand out penalties.[398][399][102] Despite calls from both local[400] and international opinion leaders, Carrie Lam and both police commissioners Stephen Lo and his successor from 19 November 2019,[363] Chris Tang rejected the formation of an independent committee.[401] Lam insisted that the IPCC was able to fulfill the task,[402] while Tang called the formation of such a committee an "injustice" and a "tool for inciting hatred" against the force.[309]
On 8 November 2019, a five-member expert panel headed by Sir Denis O'Connor and appointed by Lam in September 2019 to advise the IPCC, concluded that the police watchdog lacked the "powers, capacity and independent investigative capability necessary" to fulfill its role as a police watchdog group and suggested the formation of an independent commission of inquiry given the current protest situation.[403] After negotiations to increase the IPCC's powers fell through, the five panel members quit on 11 December 2019.[404] The IPCC report on police behaviour during the protests released in May 2020 concluded that police has mostly followed the guidelines though there was room for improvement.[405] While government officials called the report "comprehensive", democrats and human rights organisations were unanimous in declaring it a whitewash of police misdeeds.[406] One of the expert panel members, Clifford Stott, said in June 2020 that the police had misjudged the dynamics of the protests and had used disproportionate force at almost all protests, thus creating more disorder than it prevented.[407] A report co-authored by Stott, published in November 2020, saw the "absence of any credible system of accountability for the police" as one major reason for why the protests became more radical.[50]
Local media coverage
[edit]

The protests received significant press attention. Nathan Ruser from ASPI identified the protests as the most live-streamed social unrest in history. He suggested that unlike other protests, the widespread use of livestreaming technology in the Hong Kong protests meant that there was "almost parity when it comes to what [one] can learn remotely researching it to actually being there".[409]
Many of Hong Kong's media outlets are owned by local tycoons who have significant business ties in the mainland, so many of them adopt self-censorship at some level and have mostly maintained a conservative editorial line in their coverage of the protests. The management of some firms have forced journalists to change their headline to sound less sympathetic to the protest movement.[410] A report by BBC suggested that the management of local terrestrial broadcaster Television Broadcasts Limited (TVB) had forced employees to include more voices supporting the government and highlight the aggressive actions of the protesters, without including segments focusing on the responses from the protesters or the democrats.[411] Journalists from South China Morning Post, which was acquired by the Chinese Alibaba Group in 2016, had their news pieces significantly altered by senior editors to include a pro-government viewpoint before they were published.[412] TVB and local news outlet HK01 were accused of pro-government bias, and protesters have physically assaulted their news crews and damaged their equipment and vehicles.[413][414] Protesters also placed political pressure on various corporations, urging them to stop placing advertisements on TVB.[415]
On the other hand, Radio Television Hong Kong (RTHK), a public broadcasting service, faced criticisms of bias in favour of the protest movement. Its critics have surrounded the headquarters of RTHK and assaulted its reporters.[416] RTHK also faced political pressure from the police directly: police commissioner Chris Tang filed complaints to RTHK against the satirical TV show Headliner and opinion program Pentaprism for "insulting the police" and "spreading hate speech" respectively.[g] The police were criticised by journalists and democrats for interfering with press freedom.[419] In response to around 200 complaints received by the Communications Authority, RTHK apologised "to any police officers or others who have been offended" and cancelled Headliner in May 2020, ending its 21-year run.[420] RTHK journalist Nabela Qoser, known for her blunt questioning of government officials at press conferences, was subjected to racist abuse online by pro-Beijing groups, prompting a statement of "grave concern" from the Equal Opportunities Commission.[421][422] She also had her probation period at RTHK extended.[423]
Journalists encountered interference and obstruction from the police in their reporting activities.[424] Police frequently used flashlights against reporters, shining light at cameras to avoid them being filmed or photographed; journalists also reported frequently being harassed, searched,[408][425][426] and insulted. In some cases, despite identifying themselves, they were jostled, subdued, pepper-sprayed, or violently detained by the police.[427][428][429][430] Several female reporters complained about being sexually harassed by police officers.[425] Journalists were also caught in the crossfire of protests:[431][432] Indonesian journalist Veby Mega Indah of Suara was blinded by a rubber bullet;[433] a reporter from RTHK suffered burns after he was hit by a petrol bomb.[434] Student journalists were also targeted and attacked by police.[435]
Police raided the headquarters of pro-democratic newspaper Apple Daily and searched its editorial and reporters' areas on 10 August 2020. During the operation, reporters from several major news outlets were rejected from entering cordoned-off areas where a scheduled press briefing was held. Police stated that media who were "unprofessional", or had been reporting in the past in a manner considered by police as biased against the force, would be denied access to such briefings in the future.[436][437] In September 2020, the police further limited press freedom by narrowing the definition of "media representatives", meaning that student reporters and freelancers would have to face more risks when they are reporting.[438]
Hong Kong's fall by seven places to 80th in the World Press Freedom Index was attributed by Reporters without Borders to the policy of violence against journalists. When the Press Freedom Index was established in 2002, Hong Kong had ranked 18th.[439] Following the passing of the national security law, The New York Times announced that it would relocate its digital team's office to Seoul, as the law has "unsettled news organisations and created uncertainty about the city's prospects as a hub for journalism in Asia".[440] The Immigration Department also started declining work visas for foreign journalists, including those working for New York Times and local outlet Hong Kong Free Press.[441]
Impact
[edit]Economy
[edit]
Official statistics showed that Hong Kong had slipped into recession as its economy had shrunk in the second and third quarters of 2019.[442] Retail sales declined and consumer spending decreased.[443] Some restaurants saw their customers cancel bookings, and certain banks and shops were forced to close their doors. Some supply chains were disrupted because of the protests. Lower consumer spending caused several luxury brands to delay shop openings, while other brands quit.[444] While some hawkers protested about declining sales,[445] some shops prospered as nearby protesters bought food and other commodities.[446] Stock of protest supplies ran low in both Hong Kong and Taiwan.[447]
The protests also affected property owners: fearing the instability, some investors abandoned purchases of land. Demand for property also declined, as overall property transactions dropped by 24 per cent when compared with the Umbrella Revolution; property developers were forced to slash prices.[448] Trade shows reported decreased attendance and revenue, and many firms cancelled their events in Hong Kong.[449] The Hang Seng Index declined by at least 4.8 per cent from 9 June 2019 to late August 2019. As investment sentiment waned, companies awaiting listing on the stock market put their initial public offerings (IPO) on hold, there being only one in August 2019 – the lowest since 2012. Fitch Ratings downgraded Hong Kong's sovereignty rating from AA+ to AA due to doubts over the government's ability to maintain the "one country, two systems" principle; the outlook on the territory was similarly downgraded from "stable" to "negative".[450]
Tourism was also affected: the number of visitors travelling to Hong Kong in August 2019 declined by 40 per cent compared to a year earlier,[451] while the National Day holiday saw a decline of 31.9 per cent.[452][better source needed] Unemployment increased from 0.1 per cent to 3.2 per cent from September to November 2019, with the tourist and the catering sectors, seeing rises to 5.2 per cent and 6.2 per cent respectively during the same period, being the hardest hit.[453] Flight bookings also declined, with airlines cutting or reducing services.[454] During the airport protests on 12 and 13 August 2019, the Airport Authority cancelled numerous flights, which resulted in an estimated US$76 million loss according to aviation experts.[455] Various countries issued travel warnings to their citizens concerning Hong Kong, and many mainland Chinese tourists avoided travelling to Hong Kong due to safety concerns.[456]

The economy in Hong Kong became increasingly politicised. Some corporations bowed to pressure and fired employees who expressed their support for the protests.[458][459] Several international corporations and businesses including the National Basketball Association and Activision Blizzard decided to appease China during the protests and faced intense criticisms.[460] The Diplomat called the Yellow Economic Circle "one of the most radical, progressive, and innovative forms of long-term struggle" during the protests.[461] Corporations perceived to be pro-Beijing faced boycotts, and some were vandalised.[462] Meanwhile, "yellow" shops allied with protesters enjoyed a flurry of patrons even during the coronavirus crisis.[463]
Governance
[edit]Lam's administration was criticised for its performance during the protests – her perceived arrogance and obstinacy,[464][465] and her reluctance to engage in dialogue with protesters. Her extended absences, stonewalling performance at press conferences,[466] were all believed to have enabled the protesters to escalate events.[467][h] According to public opinion polls, approval ratings of Lam and her government were the lowest among all chief executives,[469] with Lam's rating plunged to 19.5 out of 100 in November 2019.[470] Her performance and those of Secretary for Security John Lee and Secretary for Justice Teresa Cheng were called "disastrous".[471] On 2 September, Reuters received a leaked audio recording in which Carrie Lam admitted that she had "very limited" room to manoeuvre between the Central People's Government and Hong Kong, and that she would quit, if she had a choice.[472] However, the next day she told the media that she had never contemplated discussing her resignation with the Beijing authorities.[473] Lam's behaviour on this and later occasions strengthened the perception among a broad part of the protesters and their supporters that she was not able to make any crucial decision without instructions from the Beijing government, effectively serving as its puppet.[474] Distrust toward the government and the lack of police accountability also led to the temporary prevalence of conspiracy theories.[375]
Both sides claimed that rule of law in Hong Kong was undermined during the protests. While the government, the police and government supporters criticised the protesters for breaking the law and using violence to "extort" the government to accept the demands, the protesters and their sympathisers felt that lack of police oversight, selective law enforcement, selective prosecution, police brutality, and the government's blanket denial of all police wrongdoings all harmed rule of law and expressed their disappointment that the law cannot help them achieve justice.[475] The judiciary was also scrutinised after judge Kwok Wai-kin dedicated much of his sentencing statement to comment on the negative impacts of the protests and to expressing sympathy toward a stabber who attacked three people in September 2019 near a Lennon Wall. He was later removed from handling all protest-related cases.[476]
The government's extended absence and its lack of a political solution in the early stage of the protests catapulted the police into the front line, and heavy-handed policing became a substitute for solving a political crisis.[477] The police force was initially "lost and confused" and was discontent with the government for not offering enough support.[478] Subsequently, Lam's blanket denial of allegations of police brutality led to accusations that Lam and her administration endorsed police violence.[396] Throughout the protests, the establishment waited for demonstrators' aggression to increase so they could justify greater militarisation of the police and dismiss the protesters as "insurgents" and thereby also dismiss their demands.[479]
The protests and backlashes against them resulted in Hong Kong governance increasingly orienting to the mainland.[480]: 182
One common view in the rest of China was that leadership on Hong Kong issues needed to be revamped both at the SAR and in the central government.[480]: 182
Police's image and accountability
[edit]The reputation of the police took a serious drubbing following the heavy-handed treatment of protesters.[481][482][483] In October 2019, a survey conducted by CUHK revealed that more than 50 percent of respondents were deeply dissatisfied with the police's performance.[484] The satisfaction rate of police force dropped to a record low after the handover.[485] According to some reports, their aggressive behaviours and tactics have caused them to become a symbol that represents hostility and suppression. Their actions against protesters resulted in a breakdown of citizens' trust of the police.[486][487] Citizens were also concerned over the ability of the police to regulate and control their members and feared their abuse of power.[488] The suspected acts of police brutality led some politically neutral or political apathetic citizens to become more sympathetic towards the young protesters.[489] Fearing Hong Kong was changing into a police state, some citizens actively considered emigration.[490] The lack of any prosecutions against officers, and the absence of independent police oversight, sparked fears that the police could not be held accountable for their actions and that they were immune to any legal consequences.[309]
Affected by the controversies surrounding the police force's handling of the protests, between June 2019 to February 2020, 446 police officers quit (which was 40 per cent higher than the figure in 2018), and the force only managed to recruit 760 officers (40 per cent lower than the previous year), falling well short of the police force's expectations.[491] The police cancelled foot patrols because of fears officers may be attacked,[492] and issued extendable batons to off-duty officers.[488] Police officers also reported being "physically and mentally" tired, as they faced the risks of being doxed, cyberbullied, and distanced by their family members.[493] Police relations with journalists,[494] social workers,[495][496] medical professionals[497] and members from other disciplined forces[498] became strained.
Society
[edit]The protests deepened the rift between the "yellow" (pro-democracy) and "blue" (pro-government) camps created since the Umbrella Revolution. People who opposed the protests argued that protesters were spreading chaos and fear across the city, causing damage to the economy and thus harming people not involved in the protests. On the other hand, protesters justified their actions by what they saw as the greater good of protecting the territory's freedoms against the encroachment of mainland China.[499] Anti-mainland sentiments swelled during this period.[500] Family relationships were strained, as children argued with their parents over their attending protests, disagreeing with their parents' political stance, avoidance of politics or views on the manner of the protests.[501]

As the protests continued to escalate, citizens showed an increasing tolerance towards confrontational and violent actions.[502] Pollsters found that among 8,000 respondents at protest sites, 90% of them believed that the use of these tactics was understandable because of the government's refusal to respond to the demands.[503] The protest movement provided a basis for challenging the government over its controversial handling of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020,[136] and some observers ascribed the success in halting the first wave of the pandemic to protesters' related efforts.[504] Unity among the protesters was seen across a wide spectrum of age groups and professions.[i] While some moderate protesters reported that the increase in violence alienated them from the protests,[499] public opinion polls conducted by CUHK suggested that the movement was able to maintain public support.[484] The unity among protesters fostered a new sense of identity and community in Hong Kong, which had always been a very materialistic society. This was evidenced by the adoption of "Glory to Hong Kong" as a protest anthem.[38]
A study conducted by the University of Hong Kong found that the protests were having negative impacts on the mental health of Hong Kong residents with one third of adults, around 2 million adults of a total population of 7.4 million, reporting symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) during the protests, up from 5 per cent in March 2015.[514] This was a six times increase from four years earlier with levels of depression and PTSD comparable to a war zone.[515][516] A survey, on social media, of more than 1,000 people by the Chinese University of Hong Kong found that 38 per cent were troubled by depression-related problems.[517] Symptoms of PTSD were found not only to afflict protesters, but also those watching events unfold on the news, living in affected areas, or working in jobs that are related to the movement (nurses, doctors, reporters, police, and street cleaners).[518] Suspected PTSD in 2019 was found to have a prevalence of 12.8 per cent in the population. Heavy social media use of 2 or more hours per day was associated with likelihood of both depression or PTSD.[519] A Guardian article dated 22 October 2019 reported that "protesters have tracked at least nine cases of suicides that appear to be linked directly to the demonstrations" since June.[520] In five of these cases, the victims left a suicide note referring to the protests, and three were attributed to events following the extradition bill.[521][522][523][524] With the passage of the national security law and the establishment of a national security hotline, societal mistrust and stress was expected to increase as of 2020.[525]
Reactions
[edit]Hong Kong government
[edit]
Carrie Lam continued to push for the second reading of the bill despite a mass anti-extradition bill protest, saying that the government was "duty-bound" to amend the law.[526][527] She had previously rejected meeting the protesters, believing that such meeting would have "no purpose".[528] Following the 12 June conflict, both Police Commissioner Stephen Lo and Lam characterised the conflict as a "riot". The police later backed down on the claim, saying that among the protesters, only five of them rioted. Protesters demanded that the government fully retract the riot characterisation.[529] Lam's analogy as Hong Kong people's mother attracted criticisms after the violent crackdown on 12 June.[530][528]
Lam announced the suspension of the bill on 15 June 2019,[69] and officially apologised to the public on 18 June two days after another massive march.[531] In early July, Lam reiterated that the bill "had passed away" and reaffirmed that all efforts to amend the law had ceased, though her use of language was thought to be ambiguous.[532] During July and August 2019, the government insisted that it would not make any concessions and that the IPCC would suffice to investigate police misconduct. She also refused to declare the withdrawal of the bill, and ignored calls for her to resign.[533][534] On 4 September 2019, Lam announced that she would formally withdraw the extradition bill, as well as introduce measures such as adding new members to the IPCC, engage in dialogue at the community level, and invite academics to join an "independent review committee" – with no investigative powers – to evaluate Hong Kong's deep-rooted problems. However, protesters and democrats saw the withdrawal as coming too late,[102] and insisted that all of their five core demands be answered.[535] One day prior to the first dialogue session of Lam on 26 September 2019, a Chinese envoy termed the demands "political blackmail", leading to doubts on the leeway Lam had in the sessions.[536] The independent review committee was then shelved by Lam in May 2020.[537]
After condemning the protesters who had stormed the legislature on 1 July for their "use of extreme violence",[538] and those who had defaced the national emblem during the 21 July protest,[539] Lam suggested in early August 2019 that the protests had deviated from their original purpose and that their goal now was to challenge China's sovereignty and damage "one country, two systems".[468] She suggested that radical protesters were dragging Hong Kong to a "path of no return"[468] and that they had "no stake in society", and therefore, government meetings need not to include them.[540][528] On 5 October 2019, after what Lam referred to as "extreme violence" had taken place, an emergency law from the colonial era was enacted to ban face masks in Hong Kong—without declaring a state of emergency—which sparked criticism from various human rights organisations.[541][j] Starting from October, Lam regularly referred to the protesters as "rioters" and dismissed the protesters, despite them amassing mass support, throughout late 2019.[528] She also allied with the police, and claimed that ending violence and restoring order, rather than responding to political demands, was what people wanted in Hong Kong.[528]
To cope with the ongoing protests, on 15 November 2019, the police had appointed no more than 100 Correctional Services Department (CSD) officers as special constables to assist them.[545] In May 2020, the authorities announced they would recruit more personnel from the other five disciplinary services and bring the total number of special constables to 700.[546] Several protesters who were detained at a correctional facility in Pik Uk reported that they had been tortured and physically abused by guards. They reported that the guards beat their hands and feet, slapped their face, then forced them to slap themselves after they were taken to a room without security camera during their time in detention.[547]
According to Reuters, the government contacted eight public relations firms to improve the image of the government in late September 2019, but six of them declined to participate for fear that partnering with the HKSAR government may tarnish their reputation.[548] On 30 July 2020, the Hong Kong government made ineligible a dozen pro-democracy candidates from running in Legislative Council elections which had been scheduled for 6 September; the elections were later postponed by a year, for which the government cited a new surge in COVID-19 cases as reason. Observers noted that the delay could have been politically motivated as the pro-Beijing camp may lose their majority in the LegCo following the election.[549] The government claimed that the disqualified candidates had colluded with foreign forces and opposed the new national security law.[550]
Macau government
[edit]The Macau government supported the Hong Kong government during the protests. Macau's Chief Executive Ho Iat-seng applauded the imposition of the national security law in Hong Kong a day after it came in to effect.[551] The Macau government announced on 19 March 2021 that any lawmaker in the Legislative Assembly who expresses support for the Hong Kong protests would be disqualified from their positions under the Macau Basic Law.[552]
Domestic reactions
[edit]
The pro-Beijing camp supported the government in promoting the bill, though U-turned when the government withdrew the bill.[553] They condemned the use of violence by protesters, including breaking into the LegCo Complex and using petrol bombs and unidentified liquids against the police.[554][555] They maintained their support for the Hong Kong Police Force and held various counter-demonstrations to support them,[556][557] and criticised the government for not taking enough actions to "halt the violence".[558] Members of the Executive Council, Ip Kwok-him and Regina Ip alleged that there was a "mastermind" behind the protests but could not provide substantial evidence to support their claim.[559]
Many lawmakers from the pan-democratic camp, such as Ted Hui and Roy Kwong, assisted the protesters in various scenarios.[560] Responding to the escalation of the mid-August protests at the airport, the convenor of the pro-democratic caucus, Claudia Mo, while disagreeing with some protesters' actions, asserted that her group of lawmakers would not split with the protesters.[561][562][563] Pro-democrats also condemned the arrests of and the violence directed at the protests' organisers, lawmakers and election candidates.[564] Former government officials, including Anson Chan, the former Chief Secretary for Administration, issued several open letters to Carrie Lam, urging her to respond to the five core demands raised by protesters.[565]
In August, 17 members from the Real Estate Developers Association of Hong Kong and the Chinese General Chamber of Commerce released statements condemning the escalating protests because of the instability they had brought to the city's economy and business community, as well as the negative effects on society as a whole.[566] Annie Wu, the daughter of Maxim's Catering founder and also a member of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, condemned the protesters at the United Nations Human Rights Council and suggested that Hong Kong should give up the "lost" protesters.[567][568] On 30 October, Abraham Shek, a lawmaker representing the Real Estate and Construction constituency, supported the formation of an independent commission and said that the problem could not be resolved by only addressing the severe housing shortage.[569] Tycoon Li Ka-shing took out a two-page advertisement in newspapers, urging people to "stop anger and violence in the name of love", and quoting a Chinese poem: "The melon of Huangtai cannot bear the picking again".[570]
Despite the government, the pro-Beijing camp and state media invoking the notion of a "silent majority" who opposed the protests, and urging citizens to cut ties with the "violent protesters", citizens generally favoured the pro-democratic camp and supported the protest movement.[571] The 2019 Hong Kong District Council election, the first poll since the beginning of the protests, had been billed as a "referendum" on the government.[572] More than 2.94 million votes were cast for a turnout rate of 71.2%, up from 1.45 million and 47% from the previous election.[573] This was the highest turnout in Hong Kong's history, both in absolute numbers and in turnout rates.[574] The results were a resounding landslide victory for the pro-democracy bloc, as they saw their seat share increased from 30% to almost 88%, with a jump in vote share from 40% to 57%.[574] Among those who were also legislators, the overwhelming majority of the losing candidates were from the pro-Beijing bloc.[575]
Reuters conducted polls in December 2019,[576] March 2020,[577] June 2020[578] and August 2020. The last poll showed that an increasing number of Hongkongers support the pro-democracy goals since the national security law was implemented. More than half of the respondents opposed the national security law. 70% wanted an independent commission of inquiry that looked into how the police handled the protests. 63% wanted universal suffrage. The support for amnesty of all arrested protesters rose to 50%. More than half of people still wanted Carrie Lam to resign. The number of people who opposed the pro-democracy demands went down to 19%. The majority (60%) still opposed Hong Kong independence, 20% supported the idea.[579]
Mainland China reactions
[edit]The Chinese government expressed its opposition to the protests, while taking measures against the protests and their supporters. The protests were depicted by the government and media as separatist riots.[580] Beijing accused the movement of displaying characteristics of colour revolutions" and signs of terrorism.[581][582] The Beijing government and state-run media accused foreign forces of interfering with domestic affairs and supporting the protesters.[583] These allegations were rejected by Hong Kong pro-democrats,[584] and CNN noted that China had a record of blaming foreign forces for causing domestic unrest.[585] On 22 October 2019, following protests and violence in Catalonia and Chile, the Chinese government accused Western media of hypocrisy for not providing similar coverage and support to those protests.[586][587] Chinese diplomats and ambassadors in more than 70 countries broadcast Beijing's position on the protests to shape international opinion.[588] CCP General Secretary Xi Jinping, Chinese Premier Li Keqiang, and Chinese Vice Premier Han Zheng repeatedly backed Lam's administration and the police.[589][590][591]
Chinese state media outlets largely ignored the protests until 17 April 2019.[592] The protests were mostly censored from Mainland Chinese social media, such as Sina Weibo, though state-owned media and Chinese social media users later condemned the protesters.[593] State-run media pressured various companies, including railway operator MTR Corporation and airline Cathay Pacific to take a hardline approach against employees who took part in the protests. Cathay Pacific saw its top managers "reshuffled" and began firing pro-democratic employees after the Civil Aviation Administration of China threatened to block Cathay's access to Chinese airspace.[594] Chinese media also attempted to appeal to the "silent majority"[595] and blame the protests on Hong Kong's education system.[596] It also hailed police officers as "heroes",[597] and demanded the government take more "forceful" actions and the court to hand out heavy punishments.[598][599] On 8 March 2021, UK broadcasting authority Ofcom imposed a fine of £125,000 on Chinese state broadcaster CGTN for having "failed to maintain due impartiality" in five programmes on the protests aired in 2019.[600]
Foreign envoys reported the deployment in late August of a sizeable number of People's Liberation Army (PLA) troops to Hong Kong, well beyond the usual rotation and possibly doubling the number of PLA troops compared to before the start of the protests. Drills by the People's Armed Police were observed across the border in Shenzhen in August.[601] On 6 October 2019, the PLA issued its first warning to the protesters, who were shining laser lights on the exterior of the PLA garrison in Kowloon Tong.[602] On 16 November, soldiers appeared publicly in the streets for the first time during the protests, in plain clothes and unarmed, to clear roadblocks and other debris left during protests alongside local residents, firefighters, and police officers before marching back to the Kowloon Tong barracks. The government insisted the soldiers were volunteers, and that it had made no request for assistance.[603] The act was criticised by pro-democrats who deemed it a violation of the Basic Law.[604] The Chinese government required goods mailed from mainland China to Hong Kong to be investigated while goods which were believed to relate to the protests were blocked.[605][606] Chinese authorities also detained several individuals in mainland China after they voiced their support for the protesters.[607]
China further tightened its control in Hong Kong by changing the officials in charge of Hong Kong affairs in early 2020.[480]: 182 Luo Huining was appointed director of the Liaison Office of the Central People's Government in Hong Kong.[480]: 182 The decision was widely linked to the poor performance of pro-government candidates at the District Council elections in November, and predecessor Wang Zhimin's perceived poor judgment of how the protests evolved.[608] Hong Kong and Macau Affairs Office director Zhang Xiaoming was demoted and replaced by Xia Baolong in February 2020.[609] The new directors triggered the Basic Law Article 22 controversy in April when they claimed that the two offices were not covered by Article 22.[610] In May, China announced that the NPCSC, China's rubber-stamp legislative body, would directly draft a national security law for Hong Kong and skip the local legislation procedures.[611] Political analysts believed that Beijing's action would mark the end of the "one country, two systems" principle and Hong Kong's autonomy as promised in the Sino-British Joint Declaration.[612][613] On 28 May 2020, the NPC approved the controversial national security laws for Hong Kong. The legislation allows the government's national security agencies to operate in Hong Kong.[614] On 30 June 2020, China implemented "Hong Kong national security law". Its 66 articles target crimes of secession, subversion, terrorism and collusion with foreign forces, and includes serious penalties between 10 years of prison to life imprisonment.[615]
International reactions
[edit]As a result of the protests, many nations issued travel warnings for Hong Kong.[616] Demonstrations in reaction to the extradition protests also took place in various locations around the world, including: Australia,[617] Brazil, Canada,[618] Chile, France, Germany,[619] India, Italy, Japan, Lithuania,[620] South Africa, South Korea,[621] Taiwan, the United Kingdom, the United States and Vietnam.[622][623] Solidarity rallies held by Hong Kong international students studying abroad were often met by mainland Chinese counter-protesters.[624][617][625][626] Following the death of Chow Tsz-lok, Secretary for Justice Teresa Cheng was heckled and jostled by protest supporters in Bloomsbury Square in London; she fell to the ground and injured her arm.[627] Some protesters in the concurrent 2019 Catalan protests claimed inspiration from, and solidarity with the Hong Kong protests.[628][629] Protesters also formed the Milk Tea Alliance with Taiwanese and Thai netizens to counter online supporters of China, but it slowly evolved into an online democratic solidarity movement that advocates for democracy in Southeast Asia.[630]
Some protesters fled to Taiwan to avoid prosecution.[631] The Hong Kong protests were considered a contributing factor in the landslide victory of Tsai Ing-wen during the 2020 Taiwanese presidential election. Tsai, who had repeatedly shown a supportive attitude toward the Hong Kong protesters, used the slogan "today Hong Kong, tomorrow Taiwan" during her presidential campaign, referring to the city's unrest as evidence of the threats posed by the "one country, two systems" principle to Taiwan's autonomy and democracy.[632] Christina Lai from Academia Sinica concurred that the situation in Hong Kong created a sense of "urgency" for Taiwanese voters, as China's hardline reaction implied that they would use the same strategy to undermine Taiwan's autonomy in the future. Tsai's rejection of the principle enabled her to gain support from young voters.[633]
In the United States, the House of Representatives, with one dissenting vote, and the Senate unanimously passed the Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act in light of the extradition bill and protests.[634][635][636][637] President Donald Trump signed the bill on 27 November, alongside a companion bill restricting US exports of crowd control devices to the Hong Kong police forces.[638] Various US politicians have expressed disapproval of corporate decisions related to the protests.[639][640][641][642] On 29 May 2020, Trump ordered the removal of the special status enjoyed by Hong Kong due to Beijing's new national security law for the territory, after Pompeo declared that the city was no longer autonomous from China and should therefore, be treated as any one of Chinese cities.[643]
Dominic Raab, the Foreign Secretary of the United Kingdom, urged China to uphold the promises it made in the Sino-British Joint Declaration, which was a legally binding international treaty.[644] The UK had already stopped selling crowd control equipment to the HKPF.[645] Former UK consulate employee Simon Cheng was granted asylum in the UK in June 2020. He was previously detained by Chinese authorities who reportedly tortured him to force a confession that the UK was involved in instigating the protests, though Chinese authorities stated that he was detained for "soliciting prostitutes".[646] On 3 June 2020, Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced that if China were to continue pursuing the national security law, he would open a path to British citizenship for Hong Kong residents who were eligible for a British National (Overseas) passport (BNO).[647] After the passing of the law on 30 June 2020, the UK confirmed these Hong Kong residents are able to come to the United Kingdom with a five-year limited leave to remain.[648] Following those five years they will be able to apply for indefinite leave to remain in the United Kingdom and, after a further 12 months with settled status, they will be able to apply for British citizenship.[649] More than 200,000 Hong Kong residents have immigrated to the United Kingdom since 2021.[650]
United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights Michelle Bachelet demanded the Hong Kong government conduct an investigation into police use of force against the protesters;[651] she previously said that she was "troubled and alarmed" by the escalating violence used by the protesters.[652] Amnesty International praised the protesters for their dedication despite facing "abusive policing tactics" which include the "wanton use of tear gas, arbitrary arrests, physical assaults and abuses in detention".[653] Kenneth Roth, the head of Human Rights Watch (HRW), was denied entry to Hong Kong at Hong Kong International Airport on 12 January 2020. Hong Kong officials insisted that the decision to bar Roth from entry had been made in Hong Kong, not in mainland China.[654]
Several African countries expressed support for the Chinese government during the protests.[655]: 41 In October 2019, Uganda's Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement that Uganda "firmly supports the one country, two systems policy of the People's Republic of China on the matter of Hong Kong and other areas" and that "Hong Kong's affairs are China's domestic affairs."[655]: 41 Also in October 2019, Tanzania's chief government spokesperson stated that the country supports China's one country, two systems policy, that the Hong Kong government was taking the best approach to the situation, and that other countries should support China.[655]: 41 In January 2020, Namibia's land reform minister stated that Namibia fully supports Chinese territorial integrity and sovereignty, including with respect to Hong Kong.[655]: 41 In June 2020, 53 countries, mostly in Africa, declared their support for the Hong Kong national security law at the UNHCR.[656]
At the 2020 China-Arab States Cooperation Forum ministers meeting, the Arab countries stated that they supported China's position regarding Hong Kong.[655]: 57
See also
[edit]- 25 August 2019 Hong Kong protest
- 1967 Hong Kong riots by pro-Beijing protesters
- 2010 Hong Kong democracy protests
- 2016 Mong Kok civil unrest
- 2020s in political history
- 2022 COVID-19 protests in China
- 30th anniversary of the 1989 Tiananmen Square protests and massacre
- Hong Kong 1 July marches
- Human rights in China
- Human rights in Hong Kong
- List of protests in the 21st century
- Sunflower Student Movement
- Umbrella Movement
- 2020 Thai protests
Notes
[edit]- ^ Two died during protests and clashes,[11][12] 13 committed suicide.[13][14][15]
- ^ The number of civilians injured is understated as many protesters sought medical help from underground clinics due to mistrust in government services.[17]
- ^ This figure, up-to-date as of 31 August 2022[update], includes an unknown number of repeat arrests occurring in the course of the protests. According to an article in the South China Morning Post, as of 10 October 2019 there were close to 2,400 arrests, with about 60 being repeat arrests.[19] The number of arrestees currently in custody is uncertain as of 18 April 2020.[20]
- ^ The government refused to disclose the chemical composition of the gas, citing "operational concerns".[320]
- ^ Police defended the officer's actions at the Tsuen Wan incident saying that he and his colleague's lives were at risk as a group of protesters was assaulting another officer at the time.[326][327] Protesters argued that the officer shooting the man's chest was unnecessary and that he had other less lethal alternatives available at his disposal.[328][329] Explaining the Sai Wan Ho incident, police alleged the unarmed young man was trying to grab the officer's service weapon.[330]
- ^ The teen was arrested before any petrol bomb was thrown.
- ^ Headliner had a segment that poked fun at the police. This forced the broadcaster to suspend the airing of the segment and the production of future seasons.[417] An episode from Pentaprism features a lecturer from The Education University of Hong Kong (EdU) who described the Siege of PolyU as a "humanitarian crisis" and compared it to the Tiananmen Square crackdown. The broadcaster was issued with a "serious warning" in April 2020.[418]
- ^ At a press conference on 5 August 2019, Lam explained her absence from the public eye in the preceding two weeks. She was concerned about the risk to organisers over the possible disruption by protesters of public events and press conferences.[468]
- ^ On many occasions, middle-aged and elderly volunteers attempted to separate the police and the young protesters where the two groups confronted each other, and provided various forms of assistance.[505] Various professions organised rallies to stand in solidarity with protesters. These professions included: teachers, civil servants, the aviation industry, accountants, medical professionals, social workers, the advertising sector, and the finance sector.[506][459][507][508][509][510] To express their support, sympathisers of the protest movement chanted rallying cries from their apartments every night,[511] wrote Christmas cards to injured protesters and those in detention,[512] and rallied outside Lai Chi Kok Reception Centre where the detainees were held.[513]
- ^ The democrats filed a judicial review to challenge Lam's decision,[542] and the High Court ruled that the mask ban was unconstitutional.[543] In April 2020, after the government had filed an appeal, the court ruled that the ban is only unconstitutional during legal demonstrations, and ruled that the police cannot physically remove the face masks worn by violators.[544]
References
[edit]- ^ 眾志衝入政總靜坐促撤回逃犯條例修訂 [Demosistō got to HK Govt. HQ against the extradition bill amendment] (video). Now.com (in Chinese). 2019-03-15. Archived from the original on 2019-11-04.
- ^ Griffiths, James (2020-04-20). "As coronavirus crisis passes, Hong Kong might be set for more mass protests". CNN News. Archived from the original on 2024-05-20. Retrieved 2024-05-06.
- ^ a b Davidson, Helen (2020-03-15). "Hong Kong: with coronavirus curbed, protests may return". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2020-04-18. Retrieved 2024-05-14.
- ^ Ramzy, Austin; Yu, Elaine (2020-05-21). "Under Cover of Coronavirus, Hong Kong Cracks Down on Protest Movement". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2020-09-20. Retrieved 2020-09-20.
- ^ a b "HKSAR Government condemns European Parliament's resolution". HKSAR Press Release. 2021-07-09. Archived from the original on 2024-04-22. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
Since its [National Security Law's] implementation in June 2020, the positive effect of the National Security Law in restoring peace and stability ... in the HKSAR has been obvious and indisputable.
- ^ Cheng, Kris; Grundy, Tom (2019-06-15). "Hong Kong democrats urge leader Carrie Lam to drop extradition law plans entirely and resign; Sunday protest to proceed". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-06-15. Retrieved 2019-06-15.
- ^ Wong, Tessa (2019-08-17). "How Hong Kong got trapped in a cycle of violence". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2019-08-17. Retrieved 2019-08-30.
- ^ Sala, Ilaria Maria (2019-08-21). "Why There's No End in Sight to the Hong Kong Protests". The Nation. Archived from the original on 2019-08-21. Retrieved 2019-08-27.
- ^ 林鄭月娥電視講話 宣布撤回修例 拒設獨立委員會 (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). Stand News. 2019-09-05. Archived from the original on 2021-12-29. Retrieved 2019-09-05.
- ^ 傘運感和理非無用 勇武者:掟磚非為泄憤. Ming Pao (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). 2019-08-18. Archived from the original on 2019-09-13. Retrieved 2019-09-01.
- ^ "【抗暴之戰】科大生周梓樂留院第5日 今晨8時不治". Apple Daily. Archived from the original on 2020-03-05. Retrieved 2019-11-08.
- ^ "頭中磚 上水清潔工不治治". Apple Daily. Archived from the original on 2020-03-05. Retrieved 2019-11-15.
- ^ "快訊/黃之鋒「90天內8人以死明志」:撤回條例只是分化手段". ETtoday. 2019-09-04. Archived from the original on 2019-09-05. Retrieved 2019-09-21.
- ^ "女子墮亡 遺言「港人加油」". Apple Daily. Archived from the original on 2019-09-05. Retrieved 2019-09-23.
- ^ "英籍夫婦留「反送中」遺書 K11 ARTUS寓館墮樓雙亡". Apple Daily. Archived from the original on 2020-01-15. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ "Anti-government protests enter their seventh month". RTHK. Archived from the original on 2020-02-12. Retrieved 2019-12-09.
- ^ "In Pictures: Hong Kong's volunteer frontline medics rush to treat protest casualties". Hong Kong Free Press. 2019-12-21. Archived from the original on 2019-12-25. Retrieved 2019-12-24.
- ^ Ho, Kelly (2022-10-27). "Almost 3,000 people, including 517 minors, prosecuted so far over 2019 Hong Kong protests". Hong Kong Free Press. Retrieved 2022-10-29.
- ^ "Hong Kong protests: growing number of repeat arrests prompts calls for special court to fast-track cases related to violent unrest". South China Morning Post. 2019-10-21. Archived from the original on 2020-01-13. Retrieved 2020-01-04.
- ^ Pang, Jessie (2020-04-18). "Hong Kong police detain veteran democracy activists in raids". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2020-04-24. Retrieved 2020-04-23.
- ^ Lee, James (2024-04-12). "90% of Hong Kong protest, national security cases have been through court, as judiciary's manpower woes persist". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2024-06-10. Retrieved 2024-04-14.
- ^ a b Wang, T. Y. (February 2023). "Hong Kong and the 2019 Anti-Extradition Bill Movement". Journal of Asian and African Studies. 58 (1): 3–7. doi:10.1177/00219096221124983. ISSN 0021-9096. S2CID 255930560. Archived from the original on 2023-03-09. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
The 2019 Anti-extradition Law Amendment Bill Movement is the largest series of protests in Hong Kong's history.
- ^ "Hong Kong Rocked by Worst Unrest in Decades". Time. Archived from the original on 2024-05-30. Retrieved 2022-02-11.
- ^ "林郑月娥:香港国安法实施后社会秩序逐步恢复正常". 紫荆网新闻 (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). 2020-08-18. Archived from the original on 2021-10-19. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ "How Hong Kong protests are inspiring movements worldwide – DW – 10/22/2019". dw.com. Archived from the original on 2023-01-14. Retrieved 2023-01-14.
- ^ Cheng, Edmund W.; Yuen, Samson (2022-06-10). "Hong Kong Anti-Extradition Movement (2019)". The Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Social and Political Movements: 1–6. doi:10.1002/9780470674871.wbespm692. ISBN 9781405197731.
The Anti-extradition Law Amendment Bill movement, in short the Anti-extradition movement, was a mass mobilization that erupted in Hong Kong between February 2019 and January 2020.
- ^ "【反修例風暴透視】暫緩不撤回 示威衝衝衝 威信不復回 警民打打打". Ming Pao (in Traditional Chinese). 2019-11-05. Archived from the original on 2020-08-11. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ "10,250 arrests and 2,500 prosecutions linked to 2019 Hong Kong protests, as security chief hails dip in crime rate". HKFP. 2021-05-17. Archived from the original on 2021-07-04. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ a b Anderlini, Jamil (2019-09-02). "Hong Kong's 'water revolution' spins out of control". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 2019-10-12. Retrieved 2019-10-27.
- ^ Wong, Wilson (2019-09-27). "The Water Movement represents the best of times for Hong Kong". Asia Dialogue. Archived from the original on 2023-11-28. Retrieved 2023-03-09.
The name 'Water Revolution' for the Anti-Extradition Bill protest[s] in Hong Kong was first coined by the Financial Times.
- ^ Lee, Heidi (2020-10-19). "2019–20 Hong Kong protests: Storytelling through the best and worst times". the Eyeopener. Archived from the original on 2023-05-28. Retrieved 2024-04-29.
- ^ a b Leung, Christy (2019-04-01). "Extradition bill not made to measure for mainland China and won't be abandoned, Hong Kong leader Carrie Lam says". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2020-11-08. Retrieved 2019-06-20.
- ^ Chernin, Kelly (2019-06-18). "Mass protests protect Hong Kong's legal autonomy from China – for now". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 2020-11-07. Retrieved 2020-01-14.
- ^ Lam, Jeffie; Cheung, Tony (2019-04-16). "Hong Kong's pro-democracy lawmakers seek last-minute adjustment to extradition bill to ensure Taiwan murder suspect faces justice". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2021-01-06. Retrieved 2019-06-20.
- ^ a b Cheung, Helier (2019-06-17). "Hong Kong extradition: How radical youth forced the government's hand". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2019-06-17. Retrieved 2019-09-08.
- ^ a b Leung, Hillary (2019-08-27). "Then and Now: 79 Days of Protest in Hong Kong". Time. Archived from the original on 2020-11-27. Retrieved 2019-09-08.
- ^ a b Cheung, Helier (2019-09-04). "Why are there protests in Hong Kong? All the context you need". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2019-09-08. Retrieved 2019-09-08.
- ^ a b c d Branigan, Tania; Kuo, Lily (2020-06-09). "How Hong Kong caught fire: the story of a radical uprising". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2021-01-28. Retrieved 2020-07-02.
- ^ Lam, Jeffie (2019-08-06). "'Liberate Hong Kong; revolution of our times': Who came up with this protest chant and why is the government worried?". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-09-09. Retrieved 2019-09-08.
- ^ "Almost nobody in Hong Kong under 30 identifies as "Chinese"". The Economist. 2019-08-26. Archived from the original on 2019-11-22. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ Dissanayake, Samanthi (2014-09-30). "Things that could only happen in a Hong Kong protest". BBC. Archived from the original on 2024-05-05. Retrieved 2020-07-02.
- ^ "The Guardian view on Hong Kong's protests: the mood hardens". The Guardian. 2019-07-02. Archived from the original on 2019-07-23. Retrieved 2019-07-23.
- ^ Griffiths, James (2019-07-22). "Hong Kong's democracy movement was about hope. These protests are driven by desperation". CNN. Archived from the original on 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2019-07-23.
- ^ Ferguson, Adam (2019-08-15). "Arrests, Tear Gas and Uncertainty: Scenes From Hong Kong's Summer of Unrest". Time. Archived from the original on 2019-08-22. Retrieved 2019-09-08.
- ^ Hsu, Stacy (2019-06-27). "World leaders urged to address Hong Kong issue ahead of G20". Focus Taiwan. Archived from the original on 2021-03-23. Retrieved 2019-07-24.
- ^ Pang, Jessie; Siu, Twinnie (2019-10-23). "Hong Kong extradition bill officially killed, but more unrest likely". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2019-10-23. Retrieved 2019-10-24.
- ^ Lum, Alvin; Chung, Kimmy; Lam, Jeffie (2019-10-23). "Hong Kong's 'dead' extradition bill finally buried as government formally withdraws it". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-10-23. Retrieved 2019-10-23.
- ^ a b Ng, Kang-chung; Sum, Lok-kei (2019-06-17). "Police roll back on categorisation of Hong Kong protests as a riot". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-06-17. Retrieved 2019-06-17.
- ^ "Police in Central Hong Kong Stop, Search Subway Passengers Ahead of Vote". Radio Free Asia. Archived from the original on 2021-03-23. Retrieved 2019-06-30.
- ^ a b Kwan, Rhoda (2020-11-19). "Hong Kong police played pivotal role in radicalising protests in build-up to Poly-U siege, policing expert report says". Hong Kong Free Press. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- ^ 便衣警拍攝示威者 拒展示委任證 警員反問記者:憑乜嘢. Stand News (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). Hong Kong. 2019-06-27. Archived from the original on 2021-12-29. Retrieved 2019-06-30.
- ^ Ng, Kang-chung (2019-09-25). "Disband Hong Kong's police force? Online poll shows most in favour of move". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-10-14. Retrieved 2019-11-02.
- ^ Qin, Amy (2019-07-08). "Hong Kong Protesters Are Fueled by a Broader Demand: More Democracy". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2019-07-08. Retrieved 2019-07-25.
- ^ "Timeline: Key dates for Hong Kong extradition bill and protests". Reuters. 2019-07-01. Retrieved 2024-04-25.
- ^ Chan, Holmes (2019-03-31). "In Pictures: 12,000 Hongkongers march in protest against 'evil' China extradition law, organisers say". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-03-31. Retrieved 2019-06-10.
- ^ Sum, Lok-kei (2019-05-21). "Hong Kong leader Carrie Lam defends Beijing's involvement in extradition bill row, pointing out foreign powers 'escalated' controversy". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-05-21. Retrieved 2020-06-13.
- ^ Gunia, Amy; Leung, Hillary (2019-06-10). "Hong Kong's Leader Says Extradition Bill to Go Ahead Prompting Calls for Fresh Protests". Time. Archived from the original on 2019-06-20. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ Lague, David; Pomfret, James; Torode, Greg (2019-12-20). "How murder, kidnappings and miscalculation set off Hong Kong's revolt – A REUTERS SPECIAL REPORT". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2020-01-19. Retrieved 2019-12-21.
- ^ "Government response to procession". The Hong Kong Government. 2019-06-09. Archived from the original on 2019-06-10. Retrieved 2019-06-10.
- ^ "As it happened: Hong Kong police and extradition protesters renew clashes as tear gas flies". South China Morning Post. 2019-06-12. Archived from the original on 2019-10-12. Retrieved 2019-08-18.
- ^ Lomas, Claire (2019-06-13), "Hong Kong protests: Police accused of shooting at journalists amid demonstration over China extradition bill", The Independent, archived from the original on 2019-06-14, retrieved 2019-07-16
- ^ "How not to police a protest: Unlawful use of force by Hong Kong Police". Amnesty International. 2019-06-21. Archived from the original on 2019-06-21. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ Leung, Kanis; Su, Xinqi; Sum, Lok-kei (2019-06-15). "Hong Kong protest organisers vow to press ahead with Sunday march and strike action despite government backing down on extradition bill". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-06-15. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ Grundy, Tom (2019-06-15). "Man protesting Hong Kong's extradition law dies after falling from mall in Admiralty". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2021-07-04. Retrieved 2021-06-02.
- ^ Wang, Wallis (2021-05-26). "Misadventure verdict on Pacific Place protester who plunged to his death". The Standard. Archived from the original on 2021-06-02. Retrieved 2021-06-02.
- ^ a b Creery, Jennifer (2020-06-25). "Explainer: From 'five demands' to 'independence' – the evolution of Hong Kong's protest slogans". Hong Kong Free Press. Retrieved 2020-10-07.
- ^ "As it happened: A historic day in Hong Kong concludes peacefully as organisers claim almost 2 million people came out in protest against the fugitive bill". South China Morning Post. 2019-06-16. Archived from the original on 2019-08-12. Retrieved 2021-06-05.
- ^ Graham-Harrison, Emma; Yu, Verna (2019-06-18). "Hong Kong protesters unimpressed by Lam's 'sincere' apology". The Guardian. Retrieved 2021-06-05.
- ^ a b Cheung, Tony (2019-06-15). "Hong Kong leader Carrie Lam suspends extradition bill, but won't apologise for rift it caused or withdraw it altogether". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-08-07. Retrieved 2019-09-07.
- ^ 【7.1遊行】歷來最多!55萬人上街促查6.12警暴 起步6小時龍尾先到金鐘. Apple Daily (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). Archived from the original on 2019-07-01. Retrieved 2019-07-01.
- ^ "Organisers say 550,000 attend annual July 1 democracy march as protesters occupy legislature". Hong Kong Free Press. 2019-07-01. Archived from the original on 2019-07-01. Retrieved 2019-07-02.
- ^ "CORRECTED-Mass movement: counting marchers in Hong Kong". Reuters. 2019-07-05. Archived from the original on 2023-04-06. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ Ruwitch, John; Pang, Jessie (2019-07-01). "Hong Kong protesters smash up legislature in direct challenge to China". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2019-07-01. Retrieved 2019-07-01.
- ^ Cheung, Eric (2019-07-01). "New manifesto of Hong Kong protesters released". CNN. Archived from the original on 2019-07-04. Retrieved 2019-07-04.
- ^ Su, Alice (2019-07-02). "Crackdown, arrests loom over Hong Kong as martyrdom becomes part of protest narratives". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 2019-07-03. Retrieved 2019-07-04.
- ^ 【逃犯條例】全港各區接力示威 遍地開花. Sing Tao Daily (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). 2019-07-07. Archived from the original on 2019-10-12. Retrieved 2019-09-07.
- ^ Cheng, Kris (2019-07-05). "Hong Kong extradition bill battle continues with more protests planned for the weekend". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-07-05. Retrieved 2019-07-07.
- ^ Creery, Jennifer (2019-07-13). "'Reclaim Sheung Shui': Thousands of Hongkongers protest influx of parallel traders from China". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-07-13. Retrieved 2019-08-18.
- ^ Chan, Holmes (2019-07-22). "Hong Kong chief Carrie Lam condemns protesters defacing national emblem; says Yuen Long attacks 'shocking'". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2019-08-18.
- ^ "Tear gas fails to clear Sheung Wan protesters". RTHK. 2019-07-21. Archived from the original on 2019-07-21. Retrieved 2019-08-18.
- ^ a b Chan, Holmes (2019-07-22). "'Servants of triads': Hong Kong democrats claim police condoned mob attacks in Yuen Long". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ Kuo, Lily (2019-07-22). "Hong Kong: why thugs may be doing the government's work". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2019-07-30. Retrieved 2019-07-31.
- ^ Barron, Laignee (2019-07-23). "Suspected 'Triad' gangs mark dangerous new phase in Hong Kong's crisis". Time. Archived from the original on 2021-01-24. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ "Junius Ho accused of supporting Yuen Long mob". The Standard. 2019-07-22. Archived from the original on 2019-10-12. Retrieved 2019-08-18.
- ^ Purbrick, Martin (2019-10-14). "A Report of the 2019 Hong Kong Protests". Asian Affairs. 50 (4): 465–487. doi:10.1080/03068374.2019.1672397.
- ^ Sum, Lok-kei; Lo, Clifford; Leung, Kanis. "Protesters shine light on arrest of Hong Kong student with new kind of laser rally". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-08-07. Retrieved 2019-08-08.
- ^ Cheng, Kris (2019-08-07). "Angry protests and tear gas in Sham Shui Po after arrest of Hong Kong student leader for possessing laser pens". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-08-08. Retrieved 2019-08-07.
- ^ "Another general strike possible, says organiser". RTHK. 2019-08-06. Archived from the original on 2019-08-06. Retrieved 2019-08-06.
- ^ Lee, Danny. "Hundreds of flights cancelled leaving travellers facing chaos as citywide strike action hits Hong Kong International Airport". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2019-08-05. Retrieved 2019-08-05.
- ^ Hui, Mary (2019-08-05). "Photos: Hong Kong protesters paralyzed the city's transport". Quartz. Archived from the original on 2019-08-05. Retrieved 2019-08-05.
- ^ Cheng, Kris. "Calls for general strike and 7 rallies across Hong Kong on Monday, as protests escalate". Hong Kong Free Press. Archived from the original on 2019-08-02. Retrieved 2019-08-05.
- ^ "HK airport shuts down as protesters take over". RTHK. 2019-08-12. Archived from the original on 2019-08-1


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch









