1856 United States presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
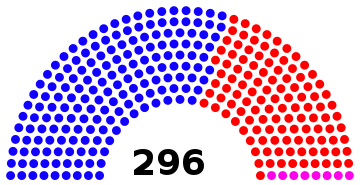
296 members of the Electoral College 149 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 79.4%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
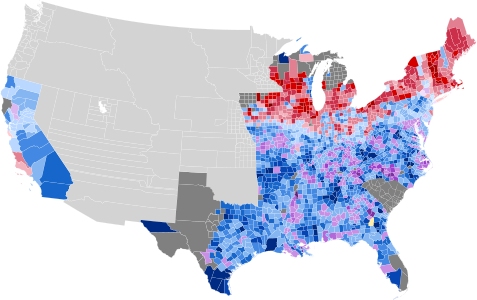
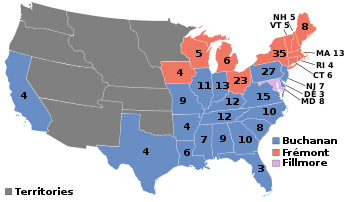 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Buchanan/Breckinridge, Red by Frémont/Dayton, and Lavender by Fillmore/Donelson. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1856 United States presidential election was the 18th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1856. In a threeway election, Democrat James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and Know Nothing/Whig nominee Millard Fillmore. The main issue was the expansion of slavery as facilitated by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854. Buchanan defeated President Franklin Pierce at the 1856 Democratic National Convention for the nomination. Pierce had become widely unpopular in the North because of his support for the pro-slavery faction in the ongoing civil war in territorial Kansas, and Buchanan, a former Secretary of State, had avoided the divisive debates over the Kansas–Nebraska Act by being in Europe as the Ambassador to the United Kingdom.
Slavery was the main issue, and with it the question of the survival of the United States as it then existed. The Democrats were seen as the pro-slavery party; the new Republican party, though hostile to slavery, limited its efforts to the politically more manageable question of the extension of slavery into federal territories (and its removal from the District of Columbia). The nativist Know Nothings (known formally as the American Party) competed with the Republicans to replace the moribund Whig Party as the primary opposition to the Democrats. They emphasized opposition to Catholic immigrants.
The 1856 Republican National Convention nominated a ticket led by Frémont, an explorer and military officer who had served in the Mexican–American War. The Know Nothings, who ignored slavery and instead emphasized anti-immigration and anti-Catholic policies, nominated a ticket led by former Whig President Millard Fillmore. Domestic political turmoil was a major factor in the nominations of both Buchanan and Fillmore, who appealed in part because of their recent time abroad, when they did not have to take a position on the divisive questions related to slavery.
The Democrats supported expansionist slave-holding policies generally of varying intensities. Southern Democrats were all in favor of the expansion of slavery. Some wanted to obtain Cuba as slave territory, as espoused by the Ostend Manifesto. Northern Democrats called for "popular sovereignty", which in theory would allow the residents in a territory to decide for themselves the legal status of slavery. In practice, in Kansas Territory, it produced a state-level civil war. Frémont opposed the expansion of slavery. Buchanan called that position "extremist", warning that a Republican victory would lead to disunion, a then constant issue of political debate which had already been long discussed and advocated. The Know Nothings attempted to present themselves as the one party capable of bridging the sectional divides. All three major parties found support in the North, but the Republicans had virtually no backing in the South.
Buchanan won a plurality of the popular vote and a majority of the electoral vote, taking all but one slave state and five free states. Frémont won a majority of electoral votes from free states and finished second in the nationwide popular vote, while Fillmore took 21.5% of the popular vote but only carried Maryland. The Know Nothings soon collapsed as a national party, as most of its anti-slavery members joined the Republican Party after the 1857 Dred Scott v. Sandford Supreme Court ruling. This election marked the end of the Second Party System, 1856 also proved to be the last Democratic presidential victory until 1884, as Republicans emerged as the dominant party during and after the Civil War. As of 2023, this is the only time that the Democrats won the presidency without any electoral votes from New England and the only time that a Republican swept this region without winning the presidency (losing New Hampshire to Woodrow Wilson in 1916 with a margin of 56 votes).
Nominations
[edit]The 1856 presidential election was primarily waged among three political parties. Though other parties had been active in the spring of the year. The conventions of these parties are considered below in order of the party's popular vote.
Democratic Party nomination
[edit]| 1856 Democratic Party ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| James Buchanan | John C. Breckinridge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Minister to Great Britain (1853–1856) | U.S. Representative for Kentucky's 8th (1851–1855) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Democratic candidates:
- James Buchanan, Minister to Great Britain and former Secretary of State
- Franklin Pierce, President of the United States
- Stephen Douglas, U.S. Senator from Illinois
- Lewis Cass, Former U.S. Senator and 1848 presidential nominee from Michigan
- President Franklin Pierce
(Name Withdrawn on the 15th Ballot in favor of Stephen Douglas) - Senator Stephen A. Douglas from Illinois
(Name Withdrawn on the 17th Ballot in favor of James Buchanan) -

The Democratic Party was wounded from its devastating losses in the 1854–1855 midterm elections. Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois, who had sponsored the Kansas-Nebraska Act, entered the race in opposition to President Franklin Pierce. The Pennsylvania delegation continued to sponsor its favorite son Buchanan.
The Seventh Democratic National Convention was held in Smith and Nixon's Hall in Cincinnati, Ohio, on June 2 to 6, 1856. The delegates were deeply divided over slavery. On the first ballot, Buchanan placed first with 135.5 votes to 122.5 for Pierce, 33 for Douglas, and 5 for Senator Lewis Cass, who had been the presidential nominee in 1848. With each succeeding ballot, Douglas gained at Pierce's expense. On the 15th ballot, most of Pierce's delegates shifted to Douglas in an attempt to stop Buchanan, but Douglas withdrew when it became clear Buchanan had the support of the majority of those at the convention, also fearing that his continued participation might lead to divisions within the party that could endanger its chances in the general election. For the first time in American history someone who had been elected president was denied re-nomination after seeking it.
A host of candidates were nominated for the vice presidency, but a number of them attempted to withdraw themselves from consideration, among them the eventual nominee, John C. Breckinridge of Kentucky. Breckinridge, besides having been selected as an elector, was also supporting former Speaker of the House Linn Boyd for the vice presidential nomination. However, following a draft effort led by the delegation from Vermont, Breckinridge was nominated on the second ballot.
Republican Party nomination
[edit]| 1856 Republican Party ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| John C. Frémont | William L. Dayton | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Senator from California (1850–1851) | U.S. Senator from New Jersey (1842–1851) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Republican candidates:
- John C. Frémont, former United States Senator from California
- John McLean, Associate Justice of the United States Supreme Court

The Republican Party was formed in early 1854 to oppose the Kansas-Nebraska Act. During the midterm elections of 1854–1855, the Republican Party was one of the patchwork of anti-administration parties contesting the election, but they were able to win thirteen seats in the House of Representatives for the 34th Congress. However, the party collaborated with other disaffected groups and gradually absorbed them. In the elections of 1855, the Republican Party won three governorships.
The first Republican National Convention was held in the Musical Fund Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on June 17 to 19, 1856. The convention approved an anti-slavery platform that called for congressional sovereignty in the territories, an end to polygamy in Mormon settlements, and federal assistance for a transcontinental railroad—a political outcome of the Pacific Railroad Surveys. John C. Frémont, John McLean, William Seward, Salmon Chase, and Charles Sumner all were considered by those at the convention, but the latter three requested that their names be withdrawn. Seward and Chase did not feel that the party was yet sufficiently organized to have a realistic chance of taking the White House and were content to wait until the next election. Sumner was in no fit condition to run after being violently assaulted on the Senate floor a month before the convention. McLean's name was initially withdrawn by his manager Rufus Spalding, but the withdrawal was rescinded at the strong behest of the Pennsylvania delegation led by Thaddeus Stevens.[2] Kentucky was the only southern state to have a delegation at the convention.[3] Frémont was nominated for president overwhelmingly on the formal ballot, and William L. Dayton was nominated for vice president over Abraham Lincoln.
American (Know-Nothing) Party nomination
[edit]| 1856 American Party ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Millard Fillmore | Andrew J. Donelson | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13th President of the United States (1850–1853) | 2nd U.S. Envoy to Prussia (1846–1849) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
American Party candidates:
- Millard Fillmore, former President of the United States from New York
- George Law, steamboat entrepreneur from New York
- Former President Millard Fillmore
from New York - Steamboat entrepreneur George Law from New York

The American Party, formerly the Native American Party, was the vehicle of the Know Nothing movement. The American Party absorbed most of the former Whig Party that had not gone to either the Republicans or Democrats in 1854, and by 1855 it had established itself as the chief opposition party to the Democrats. In the 82 races for the House of Representatives in 1854, the American Party ran 76 candidates, 35 of whom won. None of the six independents or Whigs who ran in these races were elected.
The party gained control over the state governments of California, Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island in the 1854 and 1855 elections. The party also controlled the Tennessee legislature and received at least 45% of the vote in multiple southern states, far better than the Whig Party following 1848.[4] The party then succeeded in electing Nathaniel P. Banks as Speaker of the House in the 34th Congress.[5]
However, the party started to break apart at sectional lines over slavery. Henry Wilson led northern delegates out of the party's 1855 national council in Philadelphia in protest of it adopting a plank endorsing the Kansas-Nebraska Act.[6] 70 northern delegates left the 1856 convention to create the North American Party after a resolution calling for the Kansas-Nebraska Act to be repealed was defeated.[7]
The American National Convention was held in National Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on February 22 to 25, 1856. Following the decision by party leaders in 1855 not to press the slavery issue, the convention had to decide how to deal with the Ohio chapter of the party, which was vocally anti-slavery. The convention closed the Ohio chapter and re-opened it under more moderate leadership. Delegates from Ohio, Pennsylvania, Illinois, Iowa, New England, and other northern states bolted when a resolution that would have required all prospective nominees to be in favor of prohibiting slavery north of the 36'30' parallel was voted down.[8] This removed a greater part of the American Party's support in the North outside of New York, where the conservative faction of the Whig Party remained faithful.[9]
While Banks was the early favorite for the party's presidential nomination, he publicly declined the nomination and effectively broke from the Know-Nothings, though he would not formally defect to the Republican Party until after the election. After Banks removed himself from consideration, the only name with much support was former President Millard Fillmore. Historian Allan Nevins says Fillmore was not a Know-Nothing or a nativist. He was out of the country when the presidential nomination came and had not been consulted about running. Furthermore, Fillmore was neither a member of the party nor had he ever attended an American [Know-Nothing] gathering nor had he by "spoken or written word [...] indicated a subscription to American tenets".[10] Fillmore was nominated with 179 votes out of the 234 votes cast. The convention chose Andrew Jackson Donelson of Tennessee for vice president with 181 votes to 30 scattered votes and 24 abstentions. Although the nativist argument of the American party had considerable success in local and state elections in 1854–55, Fillmore in 1856 concentrated almost entirely on national unity. Historian Tyler Anbinder says, "The American party had dropped nativism from its agenda." Fillmore won 22% of the national popular vote.
North American Party nomination
[edit]North American Party candidates:
- John C. Frémont, former Senator from California
- Nathaniel P. Banks. Speaker of the House from Massachusetts
- John McLean, Associate Justice
- Robert F. Stockton, former Senator from New Jersey
- William F. Johnston, Governor of Pennsylvania
- Former Senator John C. Frémont from California
-
- Former Senator Robert F. Stockton

The anti-slavery "Americans" from the North formed their own party after the nomination of Fillmore in Philadelphia. This party called for its national convention to be held in New York City, just before the Republican National Convention. Party leaders hoped to nominate a joint ticket with the Republicans to defeat Buchanan. The national convention was held on June 12 to 20, 1856 in New York. As John C. Frémont was the favorite to attain the Republican presidential nomination there was a considerable desire for the North American party to nominate him, but it was feared that in doing so they may possibly injure his chances to actually become the Republican presidential nominee. The delegates voted repeatedly on a nominee for president without a result. Nathaniel P. Banks was nominated for president on the 10th ballot over John C. Frémont and John McLean, with the understanding that he would withdraw from the race and endorse John C. Frémont once he had won the Republican presidential nomination. The delegates, preparing to return home, unanimously nominated Frémont on the 11th ballot shortly after his nomination by the Republican Party in Philadelphia. The chairman of the convention, William F. Johnston, had been nominated to run for vice president, but later withdrew when the North Americans and the Republicans failed to find an acceptable accommodation between him and the Republican vice presidential nominee, William Dayton.[11]
| Presidential ballots | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Vice presidential ballot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nathaniel P. Banks | 43 | 48 | 46 | 47 | 46 | 45 | 51 | 50 | 50 | 53 | 0 | William F. Johnston | 59 |
| John C. Frémont | 34 | 36 | 37 | 37 | 31 | 29 | 29 | 27 | 28 | 18 | 92 | Thomas Ford | 16 |
| John McLean | 19 | 10 | 2 | 29 | 33 | 40 | 41 | 40 | 30 | 24 | 0 | John C. Frémont | 12 |
| Robert F. Stockton | 14 | 20 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Scattering | 21 |
| William F. Johnston | 6 | 1 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Scattering | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
North American Seceders Party nomination
[edit]North American Seceders Party candidates:
- John C. Frémont, former senator from California
- Nathaniel P. Banks. Speaker of the House from Massachusetts
- John McLean, Associate Justice from Ohio
- Robert F. Stockton, former Senator from New Jersey
- William F. Johnston, Governor of Pennsylvania
A group of North American delegates called the North American Seceders withdrew from the North American Party's convention and met separately. They objected to the attempt to work with the Republican Party. The Seceders held their own national convention on June 16 and 17, 1856. 19 delegates unanimously nominated Robert F. Stockton for president and Kenneth Rayner for vice president. The Seceders' ticket later withdrew from the contest, with Stockton endorsing Millard Fillmore for the presidency.[12]
Whig Party nomination
[edit]The Whig Party was reeling from electoral losses since 1852. Half of its leaders in the South bolted to the Southern Democratic Party. In the North the Whig Party was moribund with most of its anti-slavery members joining the Republican Party. This party remained somewhat alive in states like New York and Pennsylvania by joining the anti-slavery movement.
The fifth (and last) Whig National Convention was held in the Hall of the Maryland Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, on September 17 and 18, 1856. There were one hundred and fifty delegates sent from twenty-six states. Though the leaders of this party wanted to keep the Whig Party alive, it became irretrievably doomed once these one hundred and fifty Whig delegates decided unanimously to endorse the American Party's national ticket of Fillmore and Donelson.
Liberty Party nomination
[edit]By 1856, very little of the Liberty Party remained. Most of its members joined the Free Soil Party in 1848 and nearly of all what remained of the party joined the Republicans in 1854. What remained of the party ran 1848 candidate Gerrit Smith under the name of the "National Liberty Party."
General election
[edit]Campaign
[edit]


None of the three candidates did any public campaigning. The Republican Party opposed the extension of slavery into the territories: in fact, its slogan was "Free speech, free press, free soil, free men, Frémont and victory!" The Republicans thus crusaded against the Slave Power, warning it was destroying republican values. Democrats warned that a Republican victory would bring a civil war.
The Republican platform opposed the repeal of the Missouri Compromise through the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which enacted the policy of popular sovereignty, allowing settlers to decide whether a new state would enter the Union as free or slave. The Republicans also accused the Pierce administration of allowing a fraudulent territorial government to be imposed upon the citizens of the Kansas Territory, thus engendering the violence that had raged in Bleeding Kansas. They advocated the immediate admittance of Kansas as a free state.
Along with opposing the spread of slavery into the continental territories of the United States, the party also opposed the Ostend Manifesto, which advocated the annexation of Cuba from Spain. In sum, the campaign's true focus was against the system of slavery, which they felt was destroying the republican values that the Union had been founded upon.
The Democratic platform supported the Kansas-Nebraska Act and popular sovereignty. The party supported the pro-slavery territorial legislature elected in Kansas, opposed the free-state elements within Kansas, and castigated the Topeka Constitution as an illegal document written during an illegal convention. The Democrats also supported the plan to annex Cuba, advocated in the Ostend Manifesto, which Buchanan helped devise while serving as minister to Britain. The most influential aspect of the Democratic campaign was a warning that a Republican victory would lead to the secession of numerous southern states. The main Democratic campaign was a counter-crusade against the Republicans. They ridiculed Frémont's military record and warned that his victory would bring civil war. Much of the private rhetoric of the campaign focused on unfounded rumors regarding Frémont—talk of him as president taking charge of a large army that would support slave insurrections, the likelihood of widespread lynchings of slaves, and whispered hope among slaves for freedom and political equality.[13][14]
Because Fillmore was considered by many incapable of securing the presidency on the American ticket, Whigs were urged to support Buchanan. Democrats also called on nativists to make common cause with them against the specter of sectionalism even if they had once attacked their political views.
Fillmore and the Americans, meanwhile, insisted that they were the only "national party" since the Democrats leaning in favor of the South and the Republicans were fanatically in favor of Northern fanaticism.[15]
A minor scandal erupted when the Americans, seeking to turn the national dialogue back in the direction of nativism, put out a false rumor that Frémont was in fact a Roman Catholic. Because of the Republican candidate's French-Canadian ancestry and surname, many voters accepted the allegation at face value. The Democrats ran with it, and the Republicans found themselves unable to counteract the rumor effectively given that while the statements were false, any stern message against those assertions might have crippled their efforts to attain the votes of German Catholics. Attempts were made to refute it through friends and colleagues, but the issue persisted throughout the campaign and might have cost Frémont the support of a number of American Party members.[15]
The campaign had a different nature in the free states and the slave states. In the free states, there was a three-way campaign, which Frémont won with 45.2% of the vote to 41.5% for Buchanan and 13.3% for Fillmore; Frémont received 114 electoral votes to 62 for Buchanan. In the slave states, however, the contest was for all intents and purposes between Buchanan and Fillmore; Buchanan won 56.1% of the vote to 43.8% for Fillmore and 0.1% for Frémont, receiving 112 electoral votes to 8 for Fillmore.
Nationwide, Buchanan won 174 electoral votes, a majority, and was thus elected. Frémont received no votes in ten of the fourteen slave states with a popular vote; he obtained 306 in Delaware, 285 in Maryland, 283 in Virginia, and 314 in Kentucky.
Of the 1,713 counties making returns, Buchanan won 1,083 (63.22%), Frémont won 366 (21.37%), and Fillmore won 263 (15.35%). One county (0.06%) in Georgia split evenly between Buchanan and Fillmore.
This would be the only presidential election where the Know Nothing Party put up a campaign, as the party began to splinter. After the Supreme Court's controversial Dred Scott v. Sandford ruling in 1857, most of the anti-slavery members of the party joined the Republicans. The pro-slavery wing of the American Party remained strong on the local and state levels in a few southern states, but by the 1860 election, they were no longer a serious national political movement. Most of their remaining members either joined or supported the Constitutional Union Party in 1860.
This was the last election in which the Democrats won Pennsylvania until 1936, the last in which the Democrats won Illinois until 1892, the last in which the Democrats won California until 1880, the last in which the Democrats won Indiana and Virginia until 1876 and the last in which the Democrats won Tennessee until 1872. This also started the long Republican trend in Vermont, which would not be broken until 1964, over a century later. The presidential election of 1856 was also the last time to date that a Democrat was elected to succeed a fellow Democrat as president,[16] and the last one in which a former president ran for election to the presidency on a third party ticket until 1912, when Theodore Roosevelt ran on the Progressive Party ticket.
Results
[edit]| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote(a) | Electoral vote | Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Electoral vote | ||||
| James Buchanan | Democratic | Pennsylvania | 1,836,072 | 45.28% | 174 | John C. Breckinridge | Kentucky | 174 |
| John C. Frémont | Republican | California | 1,342,345 | 33.11% | 114 | William L. Dayton | New Jersey | 114 |
| Millard Fillmore | American | New York | 873,053 | 21.53% | 8 | Andrew Jackson Donelson | Tennessee | 8 |
| Other | 3,177 | 0.08% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 4,054,647 | 100% | 296 | 296 | ||||
| Needed to win | 149 | 149 | ||||||
Source (Popular Vote): Leip, David. "1856 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved July 27, 2005. Source (Electoral Vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 31, 2005.
(a) The popular vote figures exclude South Carolina where the Electors were chosen by the state legislature rather than by popular vote.
Geography of results
[edit]- Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Cartographic gallery
[edit]- Map of presidential election results by county
- Map of Northern Democratic presidential election results by county
- Map of Republican presidential election results by county
- Map of American "Know-Nothing" presidential election results by county
- Map of "Other" presidential election results by county
- Cartogram of presidential election results by county
- Cartogram of Democratic presidential election results by county
- Cartogram of Republican presidential election results by county
- Cartogram of American presidential election results by county
- Cartogram of "Other" presidential election results by county
Results by state
[edit]Source: Data from Walter Dean Burnham, Presidential ballots, 1836–1892 (Johns Hopkins University Press, 1955) pp 247–57.
| States/districts won by Buchanan/Breckinridge |
| States/districts won by Frémont/Dayton |
| States/districts won by Fillmore/Donelson |
| James Buchanan Democratic | John C. Fremont Republican | Millard Fillmore American | Margin | State Total | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | # | |||||
| Alabama | 9 | 46,739 | 62.08 | 9 | no ballots | 28,552 | 37.92 | – | 18,187 | 24.16 | 75,291 | AL | ||||||
| Arkansas | 4 | 21,910 | 67.12 | 4 | no ballots | 10,732 | 32.88 | – | 11,178 | 34.24 | 32,642 | AR | ||||||
| California | 4 | 53,342 | 48.38 | 4 | 20,704 | 18.78 | – | 36,195 | 32.83 | – | 17,147 | 15.55 | 110,255 | CA | ||||
| Connecticut | 6 | 34,997 | 43.57 | – | 42,717 | 53.18 | 6 | 2,615 | 3.26 | – | −7,720 | −9.61 | 80,329 | CT | ||||
| Delaware | 3 | 8,004 | 54.83 | 3 | 310 | 2.12 | – | 6,275 | 42.99 | – | 1,729 | 11.84 | 14,589 | DE | ||||
| Florida | 3 | 6,358 | 56.81 | 3 | no ballots | 4,833 | 43.19 | – | 1,525 | 13.62 | 11,191 | FL | ||||||
| Georgia | 10 | 56,581 | 57.14 | 10 | no ballots | 42,439 | 42.86 | – | 14,142 | 14.28 | 99,020 | GA | ||||||
| Illinois | 11 | 105,528 | 44.09 | 11 | 96,275 | 40.23 | – | 37,531 | 15.68 | – | 9,253 | 3.86 | 239,334 | IL | ||||
| Indiana | 13 | 118,670 | 50.41 | 13 | 94,375 | 40.09 | – | 22,386 | 9.51 | – | 24,295 | 10.32 | 235,431 | IN | ||||
| Iowa | 4 | 37,568 | 40.70 | – | 45,073 | 48.83 | 4 | 9,669 | 10.47 | – | −7,505 | −8.13 | 92,310 | IA | ||||
| Kentucky | 12 | 74,642 | 52.54 | 12 | no ballots | 67,416 | 47.46 | – | 7,226 | 5.08 | 142,058 | KY | ||||||
| Louisiana | 6 | 22,164 | 51.70 | 6 | no ballots | 20,709 | 48.30 | – | 1,455 | 3.40 | 42,873 | LA | ||||||
| Maine | 8 | 39,140 | 35.68 | – | 67,279 | 61.34 | 8 | 3,270 | 2.98 | – | −28,139 | −25.66 | 109,689 | ME | ||||
| Maryland | 8 | 39,123 | 45.04 | – | 285 | 0.33 | – | 47,452 | 54.63 | 8 | −8,329 | −9.59 | 86,860 | MD | ||||
| Massachusetts | 13 | 39,244 | 23.08 | – | 108,172 | 63.61 | 13 | 19,626 | 11.54 | – | −68,928 | −40.53 | 170,048 | MA | ||||
| Michigan | 6 | 52,139 | 41.52 | – | 71,762 | 57.15 | 6 | 1,660 | 1.32 | – | −19,623 | −15.63 | 125,561 | MI | ||||
| Mississippi | 7 | 35,456 | 59.44 | 7 | no ballots | 24,191 | 40.56 | – | 11,265 | 18.88 | 59,647 | MS | ||||||
| Missouri | 9 | 57,964 | 54.43 | 9 | no ballots | 48,522 | 45.57 | – | 9,442 | 8.86 | 106,486 | MO | ||||||
| New Hampshire | 5 | 31,891 | 45.71 | – | 37,473 | 53.71 | 5 | 410 | 0.59 | – | −5,582 | −8.00 | 69,774 | NH | ||||
| New Jersey | 7 | 46,943 | 47.23 | 7 | 28,338 | 28.51 | – | 24,115 | 24.26 | – | 22,828 | 18.72 | 99,396 | NJ | ||||
| New York | 35 | 195,878 | 32.84 | – | 276,004 | 46.27 | 35 | 124,604 | 20.89 | – | −80,126 | −13.43 | 596,486 | NY | ||||
| North Carolina | 10 | 48,243 | 56.78 | 10 | no ballots | 36,720 | 43.22 | – | 11,523 | 13.56 | 84,963 | NC | ||||||
| Ohio | 23 | 170,874 | 44.21 | – | 187,497 | 48.51 | 23 | 28,126 | 7.28 | – | −16,623 | −4.30 | 386,497 | OH | ||||
| Pennsylvania | 27 | 230,686 | 50.13 | 27 | 147,286 | 32.01 | – | 82,189 | 17.86 | – | 83,400 | 18.12 | 460,161 | PA | ||||
| Rhode Island | 4 | 6,680 | 33.70 | – | 11,467 | 57.85 | 4 | 1,675 | 8.45 | – | −4,787 | −24.15 | 19,822 | RI | ||||
| South Carolina | 8 | no popular vote | 8 | no popular vote | no popular vote | – | – | – | SC | |||||||||
| Tennessee | 12 | 69,704 | 52.18 | 12 | no ballots | 63,878 | 47.82 | – | 5,826 | 4.36 | 133,582 | TN | ||||||
| Texas | 4 | 31,169 | 66.59 | 4 | no ballots | 15,639 | 33.41 | – | 15,530 | 33.18 | 46,808 | TX | ||||||
| Vermont | 5 | 10,577 | 20.84 | – | 39,561 | 77.96 | 5 | 545 | 1.07 | – | −28,984 | −57.12 | 50,748 | VT | ||||
| Virginia | 15 | 90,083 | 59.96 | 15 | no ballots | 60,150 | 40.04 | – | 29,933 | 19.92 | 150,223 | VA | ||||||
| Wisconsin | 5 | 52,843 | 44.22 | – | 66,090 | 55.30 | 5 | 579 | 0.48 | – | −13,247 | −11.08 | 119,512 | WI | ||||
| TOTALS: | 296 | 1,835,140 | 45.29 | 174 | 1,340,668 | 33.09 | 114 | 872,703 | 21.54 | 8 | 494,472 | 12.2 | 4,051,605 | US | ||||
| TO WIN: | 149 | |||||||||||||||||
States that flipped from Whig to Democratic
[edit]States that flipped from Democratic to Know-Nothing
[edit]States that flipped from Whig to Republican
[edit]States that flipped from Democratic to Republican
[edit]Close states
[edit]States where the margin of victory was under 5%:
- Louisiana 3.40% (1,455 votes)
- Illinois 3.86% (9,253 votes)
- Ohio 4.30% (16,623 votes)
- Tennessee 4.36% (5,826 votes) (tipping point state for Buchanan victory)
States where the margin of victory was under 10%:
- Kentucky 5.08% (7,226 votes)
- New Hampshire 8.00% (5,582 votes)
- Iowa 8.13% (7,505 votes)
- Missouri 8.86% (9,442 votes)
- Maryland 9.59% (8,329 votes)
- Connecticut 9.61% (7,720 votes)
Other tipping point states:
- Pennsylvania 18.12% (83,400 votes) (tipping point state for Fremont victory)
Congressional certification
[edit]During the joint session of Congress to count the electoral votes, a dispute occurred over Wisconsin's slate. The electors of Wisconsin, delayed by a snowstorm, did not cast their votes for Frémont and Dayton until several days after the appointed time and sent a certificate mentioning this fact. When the votes for the state were opened by acting Vice President James Mason, he counted them over the objections of the leadership of both Houses of Congress.[17]
See also
[edit]- Inauguration of James Buchanan
- Origins of the American Civil War
- Third Party System
- 1856–57 United States House of Representatives elections
- 1856–57 United States Senate elections
- American election campaigns in the 19th century
- History of the United States (1849–1865)
- History of the United States Democratic Party
- History of the United States Republican Party
References
[edit]- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ Eugene H. Roseboom. A History of Presidential Elections. p. 162.
- ^ National Party Conventions, 1831–1976. Congressional Quarterly. 1979.
- ^ McPherson 1988, p. 138-140.
- ^ McPherson 1988, p. 143-144.
- ^ McPherson 1988, p. 140.
- ^ McPherson 1988, p. 153-154.
- ^ Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr. American Presidential Elections. p. 1020.
- ^ Eugene H. Roseboom. A History of Presidential Elections. p. 159.
- ^ Allan Nevins, Ordeal of the Union: A House Dividing 1852–1857 (1947) 2:467
- ^ Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr. American Presidential Elections. pp. 1022–1023.
- ^ Eugene H. Roseboom. A History of Presidential Elections. p. 160.
- ^ Douglas R. Egerton, "The Slaves' Election: Frémont, Freedom, and the Slave Conspiracies of 1856." Civil War History 61#1 (2015): 35–63.
- ^ Allan Nevins, Ordeal of the Union: A House Dividing, 1852–1857 (1947) pp. 496–502
- ^ a b Eugene H. Roseboom. A History of Presidential Elections. p. 166.
- ^ Murse, Tom. "Last Time Consecutive Democratic Presidents Were Elected". Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- ^ Kesavan, Vasan (2001–2002). ""Is the Electoral Count Act Unconstitutional?"". NC Law Review. 80 (2001–2002). Archived from the original on December 29, 2020. Retrieved December 30, 2020.
Works cited
[edit]Further reading
[edit]- Anbinder, Tyler (1992). Nativism and Slavery: The Northern Know Nothings and the Politics of the 1850s. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-508922-7.
- Bicknell, John. Lincoln's Pathfinder (2017) popular history of election from Fremont's perspective. 355 pages
- Foner, Eric (1970). Free Soil, Free Labor, Free Men: The Ideology of the Republican Party before the Civil War. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Gienapp, William E. (1987). The Origins of the Republican Party, 1852–1856. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-504100-3.
- Gienapp, William E. "Nativism and the Creation of a Republican Majority in the North before the Civil War." Journal of American History 72.3 (1985): 529-559 online
- Holt, Michael F. (1978). The Political Crisis of the 1850s. New York: Norton. pp. 139–181. ISBN 0-393-95370-X.
- Nevins, Allan (1947). Ordeal of the Union: vol 2: A House Dividing, 1852–1857. New York.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) The most detailed narrative. - Pierson, Michael D. (2002). "'Prairies on Fire': The Organization of the 1856 Mass Republican Rally in Beloit, Wisconsin". Civil War History. 48. ISSN 0009-8078.
- Potter, David (1976). The Impending Crisis, 1848–1861. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 0-06-090524-7.
- Rawley, James A. (1969). Race and Politics: "Bleeding Kansas" and the Coming of the Civil War. Philadelphia: Lippincott.
- Sewell, Richard H. (1976). Ballots for Freedom: Antislavery Politics in the United States, 1837–1860. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 254–291. ISBN 0-19-501997-0.
Primary sources
[edit]- Buchanan and Breckinridge. The Democratic hand-book, compiled by Mich. W. Cluskey ... Recommended by the Democratic national committee (1856) ...
- Address of Working Men of Pittsburgh to Their Fellow Working Men in Pennsylvania. Pittsburgh, PA: W.S. Haven, 1856.
- Chester, Edward W A guide to political platforms (1977) online
- Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. National party platforms, 1840–1964 (1965) online 1840–1956
External links
[edit]- Presidential Election of 1856: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- 1856 state-by-state popular voting results Archived December 9, 2004, at the Wayback Machine
- Election of 1856 in Counting the Votes Archived November 12, 2017, at the Wayback Machine


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch